glFramebufferTexture2D に渡す GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0 は何か
以前フレームバッファをやってみたときに、glFramebufferTexture2D関数を使ったが、第二引数に与えたGL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0について言及しなかった(気がする)。当時は調べて納得はしていたが改めて読み返して混乱したのでここで明確にしておきたい。
glGenFramebuffers(1, &framebuffer); glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, framebuffer); /* ... */ glGenTextures(1, texture0); glGenTextures(1, texture1); /* ... */ glFramebufferTexture2D(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture0, 0); glFramebufferTexture2D(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT1, GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1, 0);
このように指定し、フラグメントシェーダ側で以下のように出力する。
#version 460 core layout (location = 0) out vec4 DefaultOut;// 0、つまりGL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0 layout (location = 1) out vec4 RedOnly; // 1、つまりGL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT1 in vec4 vertexColor; void main() { DefaultOut = vertexColor; RedOnly = vec4(vertexColor[0],0,0,1); }
つまり、GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0はフラグメントシェーダのlocationを指定している。
サンプル全体
#include <memory> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <array> #include<windows.h> #include <gl/glew.h> #include "CglfwBase.hpp" #pragma warning(disable:4996) #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"glew32.lib")
//! @brief PPM(RGB各1byte,カラー,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] vmax 全てのRGBの中の最大値 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details RGBRGBRGB....のメモリを渡すと、RGBテキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pnmP3_Write(const TCHAR* const fname, const int vmax, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p) { // PPM ASCII FILE* fp = _wfopen(fname, L"wb"); fprintf(fp, "P3\n%d %d\n%d\n", width, height, vmax); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d ", p[k * 3 + 0], p[k * 3 + 1], p[k * 3 + 2]); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
//! @brief フレームバッファに関する変数と機能をまとめる class FramebufferTest { public: GLuint ID_texture_0; // テクスチャ1 GLuint ID_texture_1; // テクスチャ2 GLuint ID_fbo;// フレームバッファ int width, height;//テクスチャのサイズ private: GLuint ID_depth;
//! @brief テクスチャを一枚作成し、フレームバッファに関連付ける void generate_texture(GLuint *texname, GLenum attachment) { glGenTextures(1, texname); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, *texname); //テクスチャを転送する。 //ただし最後がnullptrなので実質転送しない glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, width, height, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, nullptr); //テクスチャのフィルタリングの設定 glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); //描画先の設定 // attachmentへの書き込みで、texnameに書き込まれるようにする glFramebufferTexture2D(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, attachment, GL_TEXTURE_2D, *texname, 0); }
public:
// フレームバッファオブジェクトの作成と設定を行う // 途中で描画先のテクスチャも作成する void prepare(int WIDTH,int HEIGHT) { width = WIDTH; height = HEIGHT; ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //フレームバッファの作成 // 削除はglDeleteFrameBuffersを使用する glGenFramebuffers(1, &ID_fbo); glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, ID_fbo);
////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //テクスチャバッファの作成 // 削除はglDeleteTextures generate_texture(&ID_texture_0, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0); generate_texture(&ID_texture_1, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT1); // fragment shaderの // layout (location = 0) ・・・ GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0 // layout (location = 1) ・・・ GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT1 // が書き込み先であることを教える(?) GLenum DrawBuffers[2] = { GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0 , GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT1 }; glDrawBuffers(2, DrawBuffers); // "2"はDrawBuffersのサイズです。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // デプスバッファの作成 // レンダーバッファの一種なので、削除はglDeleteRenderbuffersを使用する glGenRenderbuffers(1, &ID_depth); glBindRenderbuffer(GL_RENDERBUFFER, ID_depth); glRenderbufferStorage(GL_RENDERBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, width, height); glFramebufferRenderbuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_ATTACHMENT, GL_RENDERBUFFER, ID_depth); /////////////////////////////////////////////////// // フレームバッファのエラーチェック。 if (glCheckFramebufferStatus(GL_FRAMEBUFFER) != GL_FRAMEBUFFER_COMPLETE) return;/*エラーデータ*/ }
}; class MyWindow :public MyWindowBase { int width; int height; FramebufferTest myfb; GLuint vertexbufferName; GLuint colorbufferName; public:
//! @brief glew,glfwの設定 フレームバッファの初期化、シェーダの作成、データの作成 virtual void setting()override { glewInit(); glfwGetFramebufferSize(_window, &width, &height); //フレームバッファの初期化 myfb.prepare(width, height); //シェーダに渡す描画データの作成 prepare_data(); //シェーダの作成 prepare_shaders(); }
//! @brief キーイベント。フレームバッファによって書き込んだテクスチャデータをファイルへ出力 virtual void key(int key, int scancode, int action, int mods)override { //テクスチャ(ID_texture_output)に書き込んだデータを取り出す領域を用意 std::vector<GLubyte> texdata; texdata.resize(myfb.width*myfb.height * 3); //////////////////////////////////////////////////// //テクスチャのデータを取り出す glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, myfb.ID_texture_0); glGetTexImage(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, &texdata[0]); // 取り出したテクスチャをファイルに書き出す pnmP3_Write(LR"(C:\test\texture0.ppm)", 255, width, height, texdata.data()); //////////////////////////////////////////////////// //テクスチャのデータを取り出す glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, myfb.ID_texture_1); glGetTexImage(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, &texdata[0]); // 取り出したテクスチャをファイルに書き出す pnmP3_Write(LR"(C:\test\texture1.ppm)", 255, width, height, texdata.data()); }
//! @brief 描画関数 virtual void draw()override { //以後の描画はフレームバッファに対して行われる glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, myfb.ID_fbo); draw_core(); //以後の描画は画面に対して行われる glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, 0); draw_core(); glfwSwapBuffers(_window); }
//! @brief 描画関数本体
void draw_core() { ///////////////////// // 描画 glViewport(0, 0, width, height); glClearColor(0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 1); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glEnable(GL_BLEND); glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA); glUseProgram(ProgramID); //gl_PointSizeを有効にする glEnable(GL_VERTEX_PROGRAM_POINT_SIZE); // 頂点バッファ glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbufferName); glVertexAttribPointer( 0, // 属性0 3, // 1要素の要素数 x y z GL_FLOAT, // タイプ GL_FALSE, // 正規化しない(データが整数型の時) 0, // ストライド (void*)0 // 配列バッファオフセット ); // カラーバッファ glEnableVertexAttribArray(1); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, colorbufferName); glVertexAttribPointer( 1, // 属性1 4, // 1要素の要素数 r g b a GL_FLOAT, // タイプ GL_FALSE, // 正規化しない(データが整数型の時) 0, // ストライド (void*)0 // 配列バッファオフセット ); // 5頂点を描く glDrawArrays(GL_POINTS, 0, 5); glDisableVertexAttribArray(0); glDisableVertexAttribArray(1); // ///////////////////// glFlush(); } GLuint VertexShaderID; GLuint FragmentShaderID; GLuint ProgramID;
//! @brief シェーダの作成
//! シェーダコードを直接埋め込んで、compileshaderを呼び出している
void prepare_shaders() { const char* vshader = R"(
#version 460 core layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos; layout (location = 1) in vec3 incolor; out vec4 vertexColor; uniform mat4 gl_ModelViewMatrix; uniform mat4 gl_ProjectionMatrix; void main() { gl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * gl_ModelViewMatrix * vec4(aPos, 1.0); vertexColor = vec4(incolor, 1.0); gl_PointSize=30.0; // 頂点のサイズ(ピクセル) }
)"; VertexShaderID = compileshader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER, vshader); const char* fshader = R"(
#version 460 core layout (location = 0) out vec4 DefaultOut;// 0、つまりGL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0 layout (location = 1) out vec4 RedOnly; // 1、つまりGL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT1 //out vec4 FragColor; in vec4 vertexColor; void main() { DefaultOut = vertexColor; RedOnly = vec4(vertexColor[0],0,0,1); }
)"; FragmentShaderID = compileshader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, fshader); GLint Result = GL_FALSE; int InfoLogLength; //////////////////////////////////////// // プログラムをリンクします。 fprintf(stdout, "Linking program\n"); ProgramID = glCreateProgram(); glAttachShader(ProgramID, VertexShaderID); glAttachShader(ProgramID, FragmentShaderID); glLinkProgram(ProgramID); //////////////////////////////////////// // プログラムをチェックします。 glGetProgramiv(ProgramID, GL_LINK_STATUS, &Result); glGetProgramiv(ProgramID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength); std::vector<char> ProgramErrorMessage((std::max)(InfoLogLength, int(1))); glGetProgramInfoLog(ProgramID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &ProgramErrorMessage[0]); fprintf(stdout, "%s\n", &ProgramErrorMessage[0]); }
//! @brief シェーダに渡す描画データの作成 void prepare_data() { using point_t = std::array<GLfloat, 3>; //モデルの座標用 x y z using color_t = std::array<GLfloat, 4>;//テクスチャ座標用 r g b a ///////////////////////////////// //バッファとデータ point_t vertex[5]; color_t color[5]; const int elemcount = 5; ////////////////////////////////////////// vertex[0] = { -0.7, 0.7, 0 }; vertex[1] = { -0.7,-0.7, 0 }; vertex[2] = { 0.7,-0.7, 0 }; vertex[3] = { 0.7, 0.7, 0 }; vertex[4] = { 0 , 0 , 0 }; color[0] = { 1.0,0.0,0.0,1.0 }; color[1] = { 0.0,1.0,0.0,1.0 }; color[2] = { 0.0,0.0,1.0,1.0 }; color[3] = { 1.0,0.0,1.0,1.0 }; color[4] = { 1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0 }; ////////////////////////////////////////// // バッファの転送 glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbufferName); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbufferName); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 3 * elemcount * sizeof(GLfloat), vertex, GL_STATIC_DRAW); glGenBuffers(1, &colorbufferName); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, colorbufferName); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 4 * elemcount * sizeof(GLfloat), color, GL_STATIC_DRAW); }
//! @brief シェーダをコンパイル・リンク GLuint compileshader(GLenum type,const char* VertexShaderCode) { GLuint shaderID; ////////////////////////////////////////////// // シェーダを作ります // (作るといっても宣言みたいなもの) shaderID = glCreateShader(type); //////////////////////////////////////////// // 頂点シェーダをコンパイルします。 printf("Compiling shader... \n"); glShaderSource(shaderID, 1, &VertexShaderCode, NULL); glCompileShader(shaderID); //////////////////////////////////////////// // エラーチェック GLint Result = GL_FALSE; int InfoLogLength; // 頂点シェーダをチェックします。 glGetShaderiv(shaderID, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &Result); glGetShaderiv(shaderID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength); if (Result == FALSE) { std::vector<char> VertexShaderErrorMessage(InfoLogLength); glGetShaderInfoLog(shaderID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &VertexShaderErrorMessage[0]); fprintf(stdout, "%s\n", &VertexShaderErrorMessage[0]); } return shaderID; }
virtual void framebuffer_size(int _width, int _height)override { width = _width; height = _height; } }; int main() { MyWindow win; win.init(600,600,"glfw window"); win.setting(); win.loop(); }
出力
画面出力ができたら、キーを何か押すとc:\test\texture0.ppmとtexture1.ppmを出力する。
画像が逆転しているのはOpenGLは左下原点なので仕方がない。

GLFWのコールバック関数でメンバ変数を呼び出す
glfwSetWindowUserPointerでthisポインタを指定し、非メンバ関数であるコールバック関数の第一引数からthisを取り出せるようにすれば、間接的にだが自作クラスのメンバ関数を呼び出す事ができる。
CglfwBase.hpp
#pragma once #pragma comment(lib,"glfw3.lib") #include <gl/glfw/glfw3.h> class MyWindowBase { protected: GLFWwindow* _window; protected:
// コールバック関数から呼ばれるメンバ関数群 //////////////////////////
virtual void key(int key, int scancode, int action, int mods) {} virtual void mouse_button(int button, int action, int mods) {} virtual void mouse_move(double xpos, double ypos) {} virtual void mouse_wheel(double xoffset, double yoffset) {} virtual void framebuffer_size(int width, int height) {} ////////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////////////// virtual void setting() {} virtual void draw() {}
protected:
// GLFWに指定するコールバック関数(staticメンバ関数) ////////////////////////// // GLFWのコールバック関数にはこれを指定する。glfwSetWindowUserPointerで指定したthisポインタを // glfwGetWindowUserPointerで取得し、メンバ関数を呼び出す
static void key_callback(GLFWwindow* pwin, int key, int scancode, int action, int mods) { MyWindowBase* myw = static_cast<MyWindowBase*>(glfwGetWindowUserPointer(pwin)); myw->key(key, scancode, action, mods); } static void mouse_button_callback(GLFWwindow* pwin, int button, int action, int mods) { MyWindowBase* myw = static_cast<MyWindowBase*>(glfwGetWindowUserPointer(pwin)); myw->mouse_button(button, action, mods); } static void mouse_move_callback(GLFWwindow* pwin, double xpos, double ypos) { MyWindowBase* myw = static_cast<MyWindowBase*>(glfwGetWindowUserPointer(pwin)); myw->mouse_move(xpos, ypos); } static void mouse_wheel_callback(GLFWwindow* pwin, double xoffset, double yoffset) { MyWindowBase* myw = static_cast<MyWindowBase*>(glfwGetWindowUserPointer(pwin)); myw->mouse_wheel(xoffset, yoffset); } static void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* pwin, int width, int height) { MyWindowBase* myw = static_cast<MyWindowBase*>(glfwGetWindowUserPointer(pwin)); myw->framebuffer_size(width, height); } static void draw_callback(GLFWwindow* pwin) { MyWindowBase* myw = static_cast<MyWindowBase*>(glfwGetWindowUserPointer(pwin)); myw->draw(); }
public:
// ここでGLFWの初期化を行う ///////////////////////////////// int init(int winwidth,int winheight,const char* wintitle) {
// GLFW の初期化 if (glfwInit() == GL_FALSE) { // 初期化に失敗したら終了 return 1; }
// ウィンドウを作成 _window = glfwCreateWindow( winwidth, //width winheight, //height wintitle,//title NULL, //monitor NULL //share ); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // ウィンドウを作成できなければ終了 if (_window == nullptr) { glfwTerminate(); return 1; }
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 自身のポインタをGLFWwindowオブジェクトにセット glfwSetWindowUserPointer(_window, this);
//////////////////////////////////////////// // コールバック関数の設定 glfwSetKeyCallback(_window, MyWindowBase::key_callback); glfwSetMouseButtonCallback(_window, MyWindowBase::mouse_button_callback); glfwSetScrollCallback(_window, MyWindowBase::mouse_wheel_callback); glfwSetCursorPosCallback(_window, MyWindowBase::mouse_move_callback); glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(_window, MyWindowBase::framebuffer_size_callback); glfwSetWindowRefreshCallback(_window, MyWindowBase::draw_callback); glfwMakeContextCurrent(_window); }
// イベントループ /////////////////////////////////
void loop() { while (glfwWindowShouldClose(_window) == GL_FALSE) { draw(); // イベント取得 glfwPollEvents(); } glfwTerminate(); }
};
main.cpp
#include <memory> #include <iostream> #include<windows.h> #include "CglfwBase.hpp" #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") class MyWindow :public MyWindowBase { int width; int height; public:
virtual void setting()override { glfwGetFramebufferSize(_window, &width, &height); } virtual void key(int key, int scancode, int action, int mods)override { // https://www.glfw.org/docs/latest/group__keys.html#ga99aacc875b6b27a072552631e13775c7 // action ... GLFW_PRESS , GLFW_REPEAT , GLFW_RELEASE //特殊キー if (key == GLFW_KEY_UP && action == GLFW_PRESS) { } if (key == GLFW_KEY_DOWN && action == GLFW_PRESS) { } if (key == GLFW_KEY_LEFT && action == GLFW_PRESS) { } if (key == GLFW_KEY_RIGHT && action == GLFW_PRESS) { } if (key >= GLFW_KEY_A && key <= GLFW_KEY_Z) { if (action == GLFW_PRESS) { const char* key_name = glfwGetKeyName(key, 0); printf("key - %s\n", key_name); } } } virtual void mouse_button(int button, int action, int mods)override { double xpos, ypos; glfwGetCursorPos(_window, &xpos, &ypos); if (button == GLFW_MOUSE_BUTTON_LEFT && action == GLFW_PRESS) { printf("mouse L pressed\n"); } if (button == GLFW_MOUSE_BUTTON_LEFT && action == GLFW_RELEASE) { printf("mouse L released\n"); } if (button == GLFW_MOUSE_BUTTON_RIGHT && action == GLFW_PRESS) { } if (button == GLFW_MOUSE_BUTTON_RIGHT && action == GLFW_RELEASE) { } if (button == GLFW_MOUSE_BUTTON_MIDDLE && action == GLFW_PRESS) { } draw(); } virtual void mouse_move(double xpos, double ypos)override { printf("mouse is moving\n"); draw(); } // マウスホイールを処理するコールバック関数 virtual void mouse_wheel(double xoffset, double yoffset)override { if (yoffset < 0) { } if (yoffset > 0) { } draw(); } virtual void framebuffer_size(int _width, int _height)override { width = _width; height = _height; } virtual void draw()override { ///////////////////// // 描画 glViewport(0, 0, width, height); glClearColor(0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 1); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glEnable(GL_BLEND); glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA); float v = 0.7; glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES); glColor3f(0, 0, 1); glVertex3f(-v, -v, 0.0); glColor3f(1, 0, 1); glVertex3f(v, -v, 0.0); glColor3f(1, 1, 1); glVertex3f(v, v, 0.0); glEnd(); // ///////////////////// glFlush(); glfwSwapBuffers(_window); }
}; int main() { MyWindow win; win.init(600,600,"glfw window"); win.setting(); win.loop(); }
オブジェクトの頂点に行列を適用するプログラムにUIを付けてアドオン風にする
import bpy import mathutils
# 行列をモデルに適用するボタン class execButton(bpy.types.Operator): bl_idname = "szl.multmatrixbutton" bl_label = "multi matrix" def execute(self, context): M11 = context.scene.myinputs.m11 M12 = context.scene.myinputs.m12 M13 = context.scene.myinputs.m13 M14 = context.scene.myinputs.m14 ####################################### M21 = context.scene.myinputs.m21 M22 = context.scene.myinputs.m22 M23 = context.scene.myinputs.m23 M24 = context.scene.myinputs.m24 ####################################### M31 = context.scene.myinputs.m31 M32 = context.scene.myinputs.m32 M33 = context.scene.myinputs.m33 M34 = context.scene.myinputs.m34 ####################################### M41 = context.scene.myinputs.m41 M42 = context.scene.myinputs.m42 M43 = context.scene.myinputs.m43 M44 = context.scene.myinputs.m44 ####################################### #apply matrix matrix = mathutils.Matrix(( (M11 ,M12 ,M13 ,M14), (M21 ,M22 ,M23 ,M24), (M31 ,M32 ,M33 ,M34), (M41 ,M42 ,M43 ,M44))) msh = bpy.context.active_object for vt in msh.data.vertices: src = mathutils.Vector((vt.co[0],vt.co[1],vt.co[2],1)) dst = matrix @ src vt.co[0] = dst[0] vt.co[1] = dst[1] vt.co[2] = dst[2] return{'FINISHED'}
# 行列を単位行列にする class execButtonLoadIdentity(bpy.types.Operator): bl_idname = "szl.loadidentitybutton" bl_label = "load identity" def execute(self, context): context.scene.myinputs.m11 =1.0 context.scene.myinputs.m12 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m13 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m14 =0.0 ####################################### context.scene.myinputs.m21 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m22 =1.0 context.scene.myinputs.m23 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m24 =0.0 ####################################### context.scene.myinputs.m31 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m32 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m33 =1.0 context.scene.myinputs.m34 =0.0 ####################################### context.scene.myinputs.m41 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m42 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m43 =0.0 context.scene.myinputs.m44 =1.0 return{'FINISHED'}
#テキストボックスを定義 class myCInputs(bpy.types.PropertyGroup): m11: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m11") m12: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m12") m13: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m13") m14: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m14") ####################################### m21: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m21") m22: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m22") m23: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m23") m24: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m24") ####################################### m31: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m31") m32: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m32") m33: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m33") m34: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m34") ####################################### m41: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m41") m42: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m42") m43: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m43") m44: bpy.props.FloatProperty(name="m44")
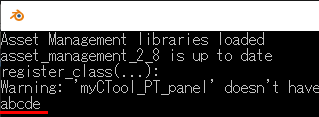
class myCTool_PT_panel(bpy.types.Panel): bl_label = "行列適用" bl_category = "行列適用" bl_space_type = "VIEW_3D" bl_region_type = "UI" def draw(self, context): layout = self.layout column = layout.column(align=True) # テキストボックスを並べる row = column.row(align=True) row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m11", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m12", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m13", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m14", text="") row = column.row(align=True) row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m21", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m22", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m23", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m24", text="") row = column.row(align=True) row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m31", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m32", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m33", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m34", text="") row = column.row(align=True) row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m41", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m42", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m43", text="") row.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "m44", text="") # ボタンを配置 layout.operator("szl.loadidentitybutton") layout.operator("szl.multmatrixbutton")
classes = ( myCInputs, execButton, execButtonLoadIdentity, myCTool_PT_panel ) def register(): for cls in classes: bpy.utils.register_class(cls) bpy.types.Scene.myinputs = bpy.props.PointerProperty(type=myCInputs) def unregister(): for cls in classes: bpy.utils.unregister_class(cls) del bpy.types.Scene.myinputs if __name__ == "__main__": register()
Blender Python Addonのチェックボックスの追加とプロパティへのアクセス
Blender PythonでUIにGUI部品を追加するときは、「チェックボックス」「エディットボックス」として追加するのではなく、
「String型のプロパティ」を登録するとエディットボックスとして表示され、
「Bool型のプロパティ」を登録するとチェックボックスとして表示される。
import bpy #テキストボックスを定義 class myCInputs(bpy.types.PropertyGroup):
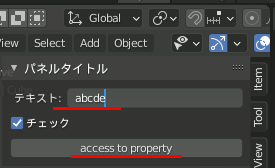
myTextField: bpy.props.StringProperty( name="テキスト", description="説明文", default="", maxlen=1024, # 最大文字数 subtype="NONE" )
myCheckField: bpy.props.BoolProperty( name="チェック", default=True )
class myCTool_PT_panel(bpy.types.Panel): bl_label = "パネルタイトル" bl_category = "タブタイトル" bl_space_type = "VIEW_3D" bl_region_type = "UI" def draw(self, context): layout = self.layout #横に並べるならrow.propを使う # row = layout.row() layout.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "myTextField") layout.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "myCheckField") classes = ( myCInputs, myCTool_PT_panel ) def register(): for cls in classes: bpy.utils.register_class(cls) bpy.types.Scene.myinputs = bpy.props.PointerProperty(type=myCInputs) def unregister(): for cls in classes: bpy.utils.unregister_class(cls) del bpy.types.Scene.myinputs if __name__ == "__main__": register()
値の取得方法
import bpy
# ボタンを定義 class execButton(bpy.types.Operator): bl_idname = "szl.button" bl_label = "access to property" def execute(self, context): print( context.scene.myinputs.myTextField)# 他のGUI部品の値を取得 return{'FINISHED'}
# ボタン以外のUIを定義 class myCInputs(bpy.types.PropertyGroup): myTextField: bpy.props.StringProperty( name="テキスト", description="説明文", default="", maxlen=1024, # 最大文字数 subtype="NONE" ) myCheckField: bpy.props.BoolProperty( name="チェック", default=True )
class myCTool_PT_panel(bpy.types.Panel): bl_label = "パネルタイトル" bl_category = "タブタイトル" bl_space_type = "VIEW_3D" bl_region_type = "UI" def draw(self, context): layout = self.layout #横に並べるならrow.propを使う # row = layout.row() layout.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "myTextField") layout.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "myCheckField") layout.operator("szl.button")
classes = ( myCInputs, execButton, myCTool_PT_panel, ) def register(): for cls in classes: bpy.utils.register_class(cls) bpy.types.Scene.myinputs = bpy.props.PointerProperty(type=myCInputs) def unregister(): for cls in classes: bpy.utils.unregister_class(cls) del bpy.types.Scene.myinputs if __name__ == "__main__": register()
Blender Python アドオンのパネルにエディットボックスを追加
テキストフィールドを追加するときはpropを使用する。
import bpy
class myCInputs(bpy.types.PropertyGroup): # テキストボックスを定義 myTextField: bpy.props.StringProperty( name="タイトル", description="説明文", default="", maxlen=1024, # 最大文字数 subtype="NONE" ) # subtype: # ['FILE_PATH', 'DIR_PATH', # 'FILE_NAME', 'BYTE_STRING', # 'PASSWORD', 'NONE']
class myCTool_PT_panel(bpy.types.Panel): bl_label = "パネルタイトル" bl_category = "タブタイトル" bl_space_type = "VIEW_3D" bl_region_type = "UI" def draw(self, context): layout = self.layout #横に並べるならrow.propを使う # row = layout.row() layout.prop(context.scene.myinputs, "myTextField")
classes = ( myCInputs, myCTool_PT_panel ) def register(): for cls in classes: bpy.utils.register_class(cls) # bpy.types.Scene.myinputs変数を作成し、テキストボックスを代入 bpy.types.Scene.myinputs = bpy.props.PointerProperty(type=myCInputs) def unregister(): for cls in classes: bpy.utils.unregister_class(cls) del bpy.types.Scene.myinputs if __name__ == "__main__": register()
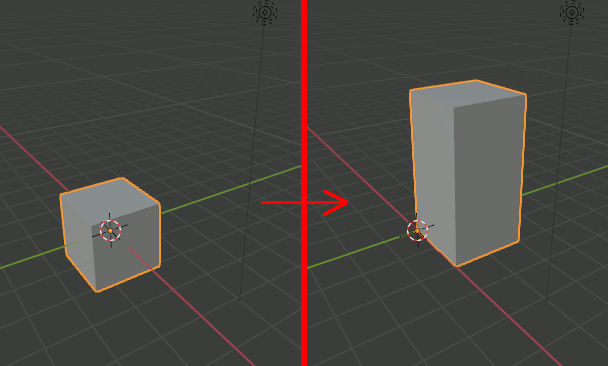
Blender Pythonでモデルの頂点に変換行列を適用する
import bpy import mathutils msh = bpy.context.active_object Sx = 1 Sy = 1 Sz = 2 Tx = 1 Ty = 1 Tz = 1 Tmatrix = mathutils.Matrix(( (Sx ,0 , 0 , 0), (0 ,Sy , 0 , 0), (0 ,0 , Sz , 0), (0 ,0 , 0 , 1))) Smatrix = mathutils.Matrix(( (1 ,0 ,0 ,Tx), (0 ,1 ,0 ,Ty), (0 ,0 ,1 ,Tz), (0 ,0 ,0 , 1))) Matrix = Tmatrix @ Smatrix for vt in msh.data.vertices: src = mathutils.Vector((vt.co[0],vt.co[1],vt.co[2],1)) dst = Matrix @ src vt.co[0] = dst[0] vt.co[1] = dst[1] vt.co[2] = dst[2]
Blender Python Meshオブジェクトの頂点のIndexをエッジの接続順にソートする(ループしている場合)
前回は端点がある連続したエッジだったが、エッジがループしている場合のコードも書く。ループしているときはどのエッジでもいいから一本取り出して、その二点から探索を開始する。
探索終了は、探索した結果一番最初の要素が見つかったら終了する。
import bpy ###################################################### # textオブジェクトの追加 def add_text_numbers(vertexes): # 新しいCollrectionを作成 newCol = bpy.data.collections.new('Vertex Numbers') # 現在のシーンにコレクションをリンク bpy.context.scene.collection.children.link(newCol) for v in range(len(vertexes)): fontCurve1 = bpy.data.curves.new(type="FONT",name="fontCurve1") obj = bpy.data.objects.new("vert[ "+str(v)+" ]",fontCurve1) obj.data.body = "" + str(v) # textオブジェクトの内容 obj.location.x=vertexes[v].co.x obj.location.y=vertexes[v].co.y obj.location.z=vertexes[v].co.z obj.scale=[0.5,0.5,0.5] newCol.objects.link(obj) ###################################################### # 現在選択中のオブジェクトを取得 def select_object(): ob = bpy.context.active_object if ob.type != 'MESH': raise TypeError("Active object is not a Mesh") mesh = ob.data #print( len(mesh.edges) ) #print( len(mesh.vertices) ) return mesh.vertices, mesh.edges ###################################################### ###################################################### # @bref 端点を取得 # @param [in] verts 頂点リスト # @param [in] edges エッジリスト # @param [in] target 端点は二つあるので0,1のどちらか # @return 頂点番号 def get_end_points(verts,edges,target): dic = {} for v in range(len(verts)): dic[v] = 0 for e in edges: dic[e.vertices[0]] += 1 dic[e.vertices[1]] += 1 ends = [] for i in range(len(dic)): if dic[ i ] == 1: ends.append( i )
######################### ## ループしている場合 ### if not ends: return None
return ends[target]
######################################################
######################################################
# @brief vtxを持つエッジのリストを取得
# @param [in] edges エッジリスト
# @param [in] vtx 頂点index
# @return エッジindexの配列
def get_edge_by_point(edges,vtx):
edgelist = []
for e in _edges:
if e.vertices[0] == vtx or e.vertices[1] ==vtx:
edgelist.append(e.index)
return edgelist
######################################################
######################################################
# @brief V1を持ち、V2を持たないエッジ
# @param [in] V1 頂点index(持つ頂点)
# @param [in] v2 頂点index(持たない頂点)
# @return 見つかったエッジindex
# @retval None そのようなエッジはなかった
def get_edge_V1_but_V2(edges,V1,V2):
for e in _edges:
if e.vertices[0] == V1 and e.vertices[1] != V2:
return e.index
if e.vertices[1] == V1 and e.vertices[0] != V2:
return e.index
return None
######################################################
######################################################
# @brief edgeを構成する2頂点のうち、vertexでないほうの頂点を返す
# @param [in] edge エッジリスト
# @param [in] vertex 基準となる頂点のIndex
# @return 頂点番号
def get_another_point_on_edge(edge,vertex):
if edge.vertices[0] == vertex:
return edge.vertices[1]
if edge.vertices[1] == vertex:
return edge.vertices[0]
######################################################
######################################################
# @brief 一直線に連続した順番の頂点一覧を取得
# @param [in] verts 頂点リスト
# @param [in] edges エッジリスト
# @param [in] order 端点のどちら側から探索するか(0 or 1)
# @return 頂点一覧
def get_connected_vertex_list(verts,edges,order):
# 結果の格納先
vlist = []
# 最初の頂点を取得。「端点」は二つだけ存在するので
# 結果は二つ求まる(0,1)。そのうちのorder番を取得
EP = get_end_points(verts,edges,order)
if EP is not None:
vlist.append(EP) #その要素が結果の一番目
edgeidxlist = get_edge_by_point(edges,EP)# EPを持つエッジの一覧。要素数1の配列になるはず
# エッジ最初の頂点を持つエッジ
endpointedge = edges[edgeidxlist[0]]
#EP(最初の端点)でない方の頂点を取得
another = get_another_point_on_edge( endpointedge , EP )
# 端点を持つエッジの、端点でないほうの頂点は、二番目の頂点
vlist.append(another)
else:
#############################
## ループしている場合 #######
if order == 0:
vlist.append( edges[0].vertices[0] )
vlist.append( edges[0].vertices[1] )
else:
vlist.append( edges[0].vertices[1] )
vlist.append( edges[0].vertices[0] )
# 無限ループを使うのでループ上限を設けておく
looplimit = 100
while True:
# 前回の前回見つけた頂点
before = vlist[len(vlist)-2]
# 前回見つけた頂点。この頂点の次の頂点を探したい
now = vlist[len(vlist)-1]
#nowを持ち、beforeを持たないエッジを検索
nextedge = get_edge_V1_but_V2(edges,now,before)
# 端点には「nowを持ち、beforeを持たないエッジ」がないので、Noneが入っている
if nextedge is None:
break
#nextedgeの、nowでない方の頂点を取得
next = get_another_point_on_edge( edges[nextedge] , now )
#####################################
## ループしている場合 ###############
if next == vlist[0]:
break
vlist.append(next)
looplimit -= 1
if looplimit == 0:
break
return vlist
# 頂点群を取得
ret = select_object()
_verts = ret[0]
_edges = ret[1]
# 頂点番号のテキストオブジェクトを追加
add_text_numbers(_verts)
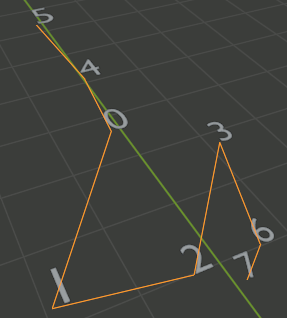
vtx_c_list = get_connected_vertex_list(_verts,_edges,0)
print(vtx_c_list)
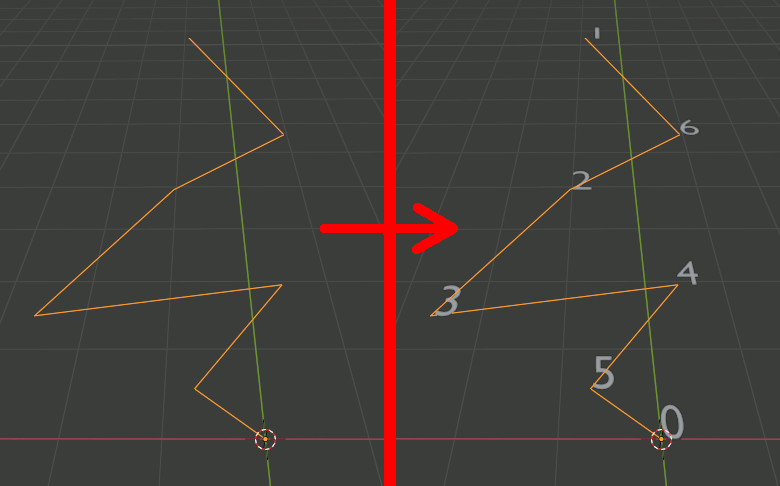
Blender Python Meshオブジェクトの頂点のIndexをエッジの接続順にソートする
import bpy
###################################################### # textオブジェクトの追加 def add_text_numbers(vertexes): # 新しいCollrectionを作成 newCol = bpy.data.collections.new('Vertex Numbers') # 現在のシーンにコレクションをリンク bpy.context.scene.collection.children.link(newCol) for v in range(len(vertexes)): fontCurve1 = bpy.data.curves.new(type="FONT",name="fontCurve1") obj = bpy.data.objects.new("vert[ "+str(v)+" ]",fontCurve1) obj.data.body = "" + str(v) # textオブジェクトの内容 obj.location.x=vertexes[v].co.x obj.location.y=vertexes[v].co.y obj.location.z=vertexes[v].co.z obj.scale=[0.5,0.5,0.5] newCol.objects.link(obj) ###################################################### # 現在選択中のオブジェクトを取得 def select_object(): ob = bpy.context.active_object if ob.type != 'MESH': raise TypeError("Active object is not a Mesh") mesh = ob.data #print( len(mesh.edges) ) #print( len(mesh.vertices) ) return mesh.vertices, mesh.edges
###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief 端点を取得 # @param [in] verts 頂点リスト # @param [in] edges エッジリスト # @param [in] target 端点は二つあるので0,1のどちらか # @return 頂点番号 def get_end_points(verts,edges,target): dic = {} for v in range(len(verts)): dic[v] = 0 for e in edges: dic[e.vertices[0]] += 1 dic[e.vertices[1]] += 1 ends = [] for i in range(len(dic)): if dic[ i ] == 1: ends.append( i ) return ends[target] ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief vtxを持つエッジのリストを取得 # @param [in] edges エッジリスト # @param [in] vtx 頂点index # @return エッジindexの配列 def get_edge_by_point(edges,vtx): edgelist = [] for e in _edges: if e.vertices[0] == vtx or e.vertices[1] ==vtx: edgelist.append(e.index) return edgelist ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief V1を持ち、V2を持たないエッジ # @param [in] V1 頂点index(持つ頂点) # @param [in] v2 頂点index(持たない頂点) # @return 見つかったエッジindex # @retval None そのようなエッジはなかった def get_edge_V1_but_V2(edges,V1,V2): for e in _edges: if e.vertices[0] == V1 and e.vertices[1] != V2: return e.index if e.vertices[1] == V1 and e.vertices[0] != V2: return e.index return None ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief edgeを構成する2頂点のうち、vertexでないほうの頂点を返す # @param [in] edge エッジリスト # @param [in] vertex 基準となる頂点のIndex # @return 頂点番号 def get_another_point_on_edge(edge,vertex): if edge.vertices[0] == vertex: return edge.vertices[1] if edge.vertices[1] == vertex: return edge.vertices[0] ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief 一直線に連続した順番の頂点一覧を取得 # @param [in] verts 頂点リスト # @param [in] edges エッジリスト # @param [in] order 端点のどちら側から探索するか(0 or 1) # @return 頂点一覧 def get_connected_vertex_list(verts,edges,order): # 結果の格納先 vlist = [] # 最初の頂点を取得。「端点」は二つだけ存在するので # 結果は二つ求まる(0,1)。そのうちのorder番を取得 EP = get_end_points(verts,edges,order) vlist.append(EP) #その要素が結果の一番目 edgeidxlist = get_edge_by_point(edges,EP)# EPを持つエッジの一覧。要素数1の配列になるはず # エッジ最初の頂点を持つエッジ endpointedge = edges[edgeidxlist[0]] #EP(最初の端点)でない方の頂点を取得 another = get_another_point_on_edge( endpointedge , EP ) # 端点を持つエッジの、端点でないほうの頂点は、二番目の頂点 vlist.append(another) # 無限ループを使うのでループ上限を設けておく looplimit = 100 while True: # 前回の前回見つけた頂点 before = vlist[len(vlist)-2] # 前回見つけた頂点。この頂点の次の頂点を探したい now = vlist[len(vlist)-1] #nowを持ち、beforeを持たないエッジを検索 nextedge = get_edge_V1_but_V2(edges,now,before) # 端点には「nowを持ち、beforeを持たないエッジ」がないので、Noneが入っている if nextedge is None: break #nextedgeの、nowでない方の頂点を取得 next = get_another_point_on_edge( edges[nextedge] , now ) vlist.append(next) looplimit -= 1 if looplimit == 0: break return vlist
# 頂点群を取得 ret = select_object() _verts = ret[0] _edges = ret[1] # 頂点番号のテキストオブジェクトを追加 add_text_numbers(_verts) vtx_c_list = get_connected_vertex_list(_verts,_edges,0) print(vtx_c_list)
結果
Blender Python Meshオブジェクトの頂点のIndexをText objectで追加する
まだやってなかったと思う。多分。
import bpy
###################################################### # textオブジェクトの追加 def add_text_numbers(vertexes): # 新しいCollrectionを作成 newCol = bpy.data.collections.new('Vertex Numbers') # 現在のシーンにコレクションをリンク bpy.context.scene.collection.children.link(newCol) for v in range(len(vertexes)): fontCurve1 = bpy.data.curves.new(type="FONT",name="fontCurve1") obj = bpy.data.objects.new("vert[ "+str(v)+" ]",fontCurve1) obj.data.body = "" + str(v) # textオブジェクトの内容 obj.location.x=vertexes[v].co.x obj.location.y=vertexes[v].co.y obj.location.z=vertexes[v].co.z obj.scale=[0.5,0.5,0.5] newCol.objects.link(obj)
###################################################### # 現在選択中のオブジェクトを取得 def select_object(): ob = bpy.context.active_object if ob.type != 'MESH': raise TypeError("Active object is not a Mesh") mesh = ob.data #print( len(mesh.edges) ) #print( len(mesh.vertices) ) return mesh.vertices
# 頂点群を取得 verts = select_object() # 頂点番号のテキストオブジェクトを追加 add_text_numbers(verts)
Unreal Engine 4 ブループリント(6)クリックした三次元座標を取得
クリック位置の検出はPlayerControlのブループリントでGet Hit Result Under Cursor by Channelノードを追加しHit ResultからBreak Hit Resultを見れば取り出せる。
作業
まず以前やった方法でアクタのクリックの検出をできるようにする。
https://suzulang.com/unrealengine4-blueprint-4-actorclickevent/
アクタのクリック検出にはPlayerControlのオーバーライドが必要なので、この作業で必然的にPlayerControlのブループリントができたことになる。これをMyPlayerControlとして、以下のように設定する
テスト
クリック位置にオブジェクトをスポーンする