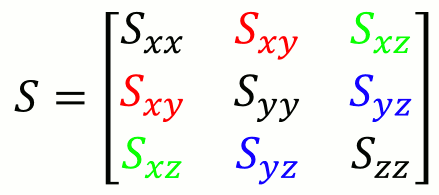WindowsからBMPファイルを出力
BMPファイル形式について
BMPはMicrosoftとIBMが開発したファイル形式で、Windows版とOS/2版がある。ここではWindows版の32bit,24bitしか考えない。
以下Wikipedia:
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windows_bitmap
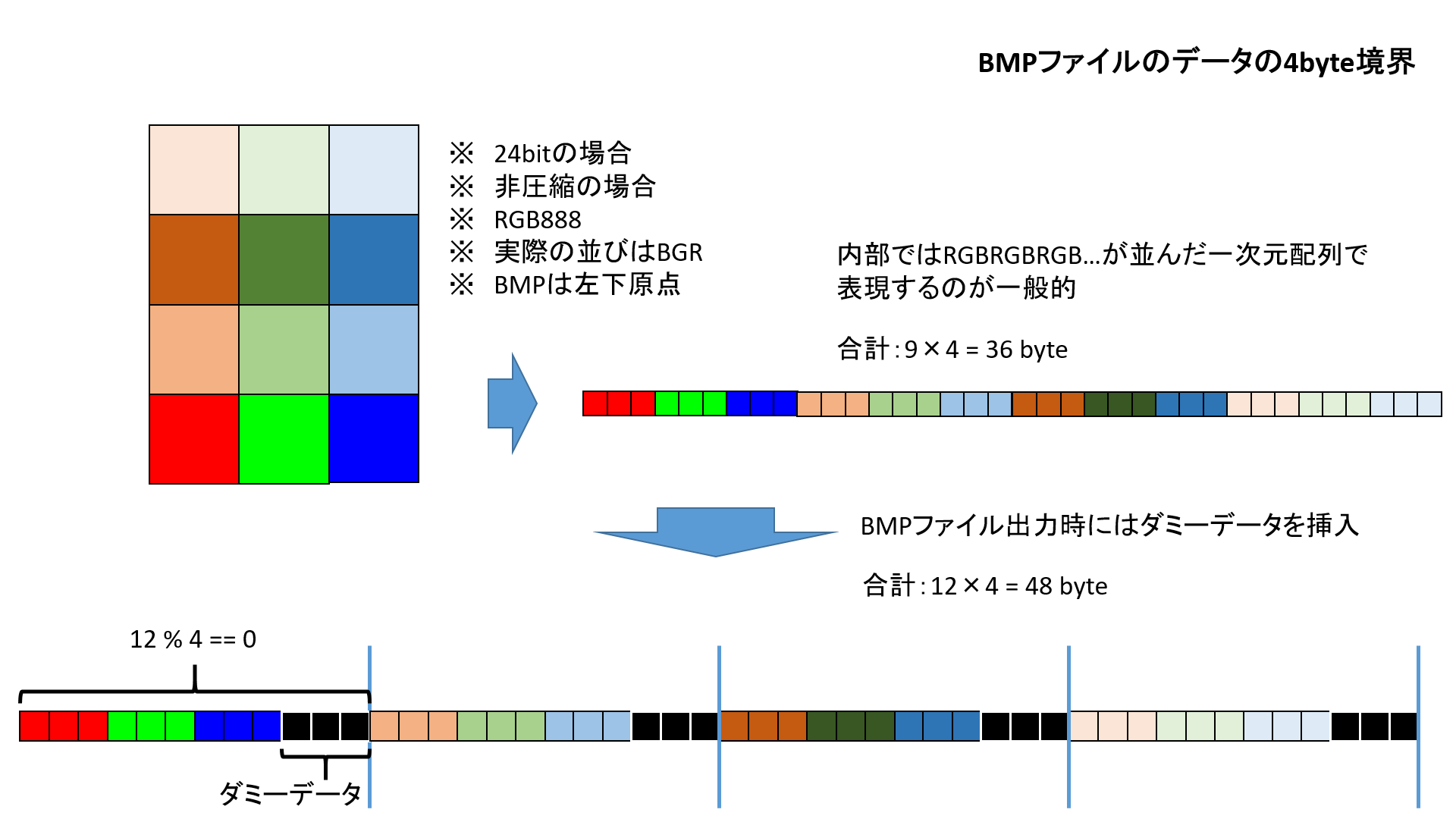
BMPファイルの4バイト境界について
BMPファイルは、横一行のデータのバイト数が4の倍数でなければいけないという制約がある。32bit BMPの場合は1画素が4バイトなので必ずこの条件を満たす。従って考える必要はない(考える必要がないだけで制約が取り払われているわけではない)。
問題は24bitの時で、例えば3×2の画像の一行の画素数は3なので、1行3×(24/8)=9バイトになる。9より大きいもっとも小さな4の倍数は12なので、10,11,12バイト目はダミーのデータで埋めてやる必要がある。
しかも、32bit BMPは24bit BMPに比べて扱えないソフトが多いとの理由で、.bmp形式なら24bit BMPが世の中では推奨されている。だから24bit BMPを無視できない。
BMPファイルの出力手順
1.データが4byte境界の条件を満たしていないなら、満たしているデータを作成する。
2.BITMAPFILEHEADER構造体に値を設定する
3.BITMAPINFO構造体に値を設定する
4.上記2,3をバイナリでファイルに書き出す
5.画像データをファイルに書き出す
BMPファイル形式はMicrosoftが考案した形式だが、Windowsに用意されているのはヘッダの構造体だけだ。データの4byte境界を修正する関数はおろかそのエラーチェックをする関数も用意されていない。圧縮もサポートしていると言ってもヘッダに圧縮状態のフラグを指定できるだけで、使いたかったら自分で圧縮しなければならない。ヘッダの出力もやってることはただのfwriteで、sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER)バイトだけ、sizeof(BITMAPINFO)バイトだけバイナリ出力しているに過ぎない。
サンプルコード
BMPwriter.hpp
#pragma once //! @brief 与えられた画素数がビットマップの要求する4byte境界に何バイト足りないかを返す //! @param [in] width 画素数 //! @param [in] pixelsize 1ピクセルのビット数 //! @return 足して4の倍数になる値 int getbmp4line_err(const unsigned int width, const unsigned int pixelbits); //! @brief 幅と高さと画素のビット数からビットマップデータにしたときに何バイトになるかを算出する //! @param [in] width 画像のピクセル数(幅) //! @param [in] height 画像のピクセル数(高さ) //! @param [in] pixelbit 1ピクセルのビット数 //! @return 4バイト境界に合わせたときのバイト数 unsigned int getbmpdata_memsize(const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height, const unsigned int pixelbits); //! @brief データをスキャンライン4倍バイトデータにしたものを作成 //! @param [out] dst 調整後の画素データの格納先アドレス //! @param [in] src 元データの先頭アドレス //! @param [in] width 画像幅(ピクセル) //! @param [in] height 画像高さ(ピクセル) //! @param [in] pixelbit 1ピクセルのビット数 //! @return そのままBMPにできるデータ配列 //! @note dstは確保済みの必要がある。このバイト数はgetbmpdatasizeで取得できる void data_to_bmp4lines(unsigned char* dst,const void* src, const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height, const unsigned int pixelbits); //! @brief ビットマップファイルを保存する //! @param [in] pathname ファイル名 //! @param [in] pixeldata 画像データの先頭ポインタ。4バイト境界に調整済みの必要がある //! @param [in] width 画像のピクセル幅 //! @param [in] height 画像のピクセル高さ //! @param [in] 1画素のビット数 //! @return なし void bmp_write(const wchar_t* pathname, const void* pixeldata, const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height, const unsigned int pixelbits); //! @brief ビットマップファイルを保存する関数のインタフェース //! @param [in] pathname ファイル名 //! @param [in] pixeldata 画像データの先頭ポインタ。4バイト境界の調整前のもの //! @param [in] width 画像のピクセル幅 //! @param [in] height 画像のピクセル高さ //! @param [in] 1画素のビット数 //! @return なし void call_bmp_write(const wchar_t* pathname, const void* pixeldata, const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height, const unsigned int pixelbits);
BMPWriter.cpp
#include "BMPwriter.hpp" #include <Windows.h> #include <vector>
int getbmp4line_err(const unsigned int width, const unsigned int pixelbits) { return (4 - (width * pixelbits /8) % 4) % 4; }
unsigned int getbmpdata_memsize(const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height, const unsigned int pixelbits) { unsigned int widthbytes = width * (pixelbits / 8) + getbmp4line_err(width, pixelbits); return widthbytes * height; }
void data_to_bmp4lines(unsigned char* dst, const void* src, const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height, const unsigned int pixelbits) { unsigned int pixelbytes = (pixelbits / 8); std::uint8_t * p = (std::uint8_t*)src; int err = getbmp4line_err(width, pixelbits);//4バイト境界に何バイト足りないかを算出 size_t pos=0; for (size_t h = 0; h < height; h++) { //一行コピー for (size_t x = 0; x < width * pixelbytes; x++) { dst[pos++] = *p; p++; } if (err != 0) { // width * pixelsizeが4になるようにデータを挿入 for (size_t k = 0; k < err; k++) { dst[pos++] = 0; } } } }
void bmp_write( const wchar_t* pathname, const void* pixeldata, const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height, const unsigned int pixelbits) { const unsigned long bytecount = pixelbits / 8; const unsigned long headSize = (sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER) + sizeof(BITMAPINFO)); //4バイト境界を考慮した1スキャンラインのバイト数 const unsigned long widthBytes = width * bytecount + getbmp4line_err(width, pixelbits); const unsigned long imageBytes = (widthBytes * height); // BITMAPFILEHEADERの初期化 BITMAPFILEHEADER bmpHead = { 0 }; bmpHead.bfType = 0x4D42; // "BM" bmpHead.bfSize = headSize + imageBytes; bmpHead.bfReserved1 = 0; bmpHead.bfReserved2 = 0; bmpHead.bfOffBits = headSize; // BITMAPINFOの初期化 BITMAPINFO bmpInfo = { 0 }; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biSize = sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER); bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biWidth = width; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biHeight = height; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biPlanes = 1; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biBitCount = pixelbits; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biCompression = BI_RGB; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biSizeImage = 0; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biXPelsPerMeter = 0; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biYPelsPerMeter = 0; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biClrUsed = 0; bmpInfo.bmiHeader.biClrImportant = 0; FILE * fp = _wfopen(pathname, L"wb" ); fwrite(&bmpHead, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, fp); fwrite(&bmpInfo, sizeof(BITMAPINFO), 1, fp); fwrite(pixeldata, 1 , imageBytes, fp); fclose(fp); }
void call_bmp_write(const wchar_t* pathname, const void* pixeldata, const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height, const unsigned int pixelbits) { //BMP保存時の画像のメモリサイズを求める int retsize = getbmpdata_memsize(width, height, pixelbits); std::vector<std::uint8_t> save; save.resize(retsize); //4バイト境界の条件を満たしたデータを作成する data_to_bmp4lines(&save[0], pixeldata, width, height, pixelbits); //BMPファイルに保存する bmp_write(pathname, &save[0], width, height, pixelbits); }
使用例
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include "BMPwriter.hpp" struct data32bit { unsigned char p[4]; data32bit() {} data32bit( unsigned char b, unsigned char g, unsigned char r, unsigned char u ) { p[0] = b; p[1] = g; p[2] = r; p[3] = u; } data32bit( unsigned char b, unsigned char g, unsigned char r ) { p[0] = b; p[1] = g; p[2] = r; p[3] = 0; } }; struct data24bit { unsigned char p[3]; data24bit() {} data24bit( unsigned char b, unsigned char g, unsigned char r ) { p[0] = b; p[1] = g; p[2] = r; } }; template<typename dtype> void create_data(std::vector<dtype>& img,int width,int height) { for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) { for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) { int pos = y * width + x; if (y == x) { img[pos] = dtype(255, 0, 0); } else { img[pos] = dtype(0, 0, 255); } if (x == width - 1) img[pos] = dtype(0, 255, 0); } } }
int main() { //画像データ std::vector<data24bit> img; unsigned int bits = 24; unsigned int width = 7; unsigned int height = 9; img.resize(width*height); create_data(img,width,height); std::cout << "scanline bytes % 4 = " << (width * bits / 8) % 4; call_bmp_write(L"C:\\data\\a.bmp",&img[0], width, height, bits); int k; std::cin >> k; }
Blender 2.8 How to Create the World in 1 Minute 抜粋 2-シェーダの設定 + 雲
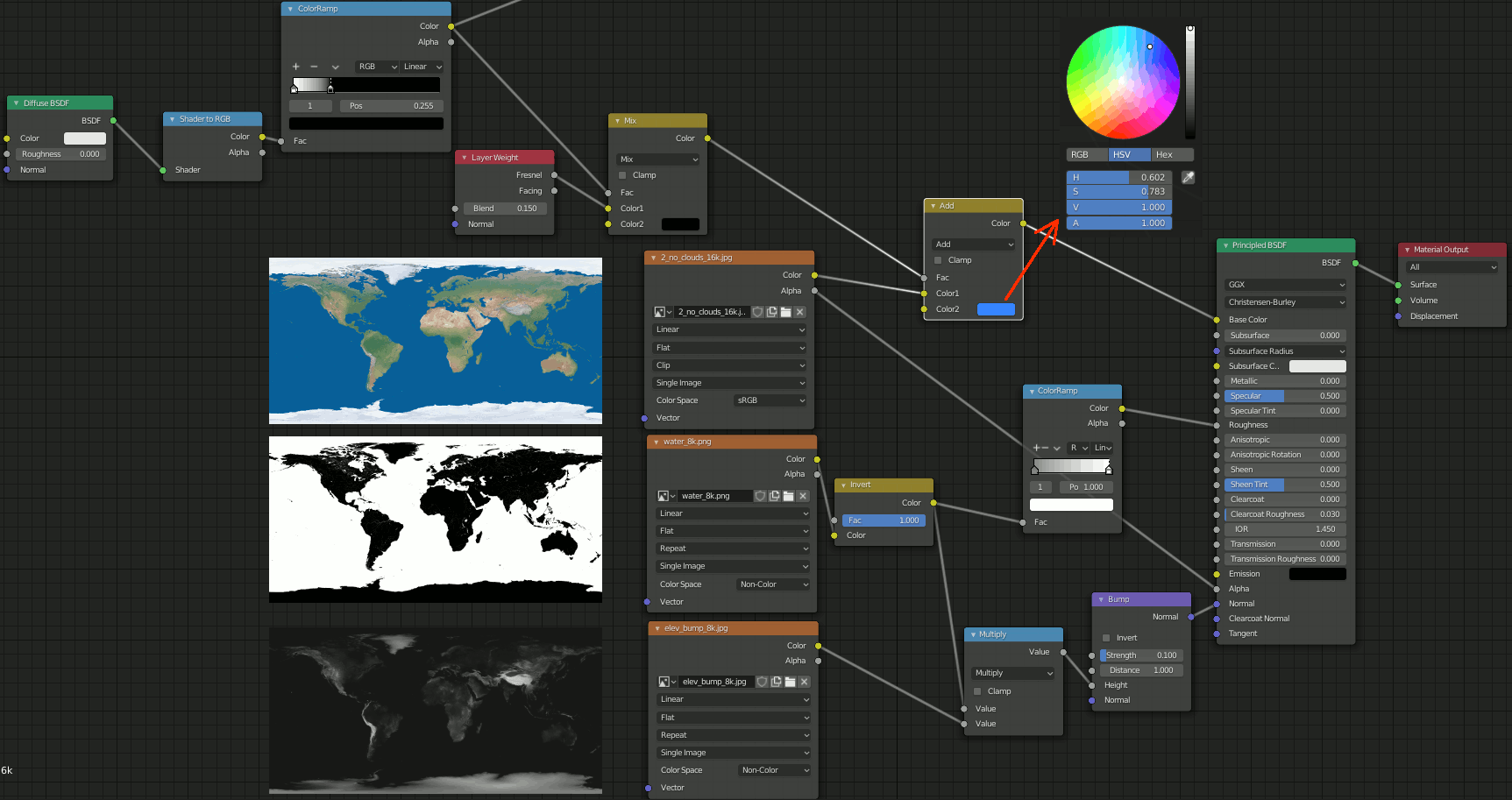
前回の続き。まずざっくり以下のようにノードを設定する。
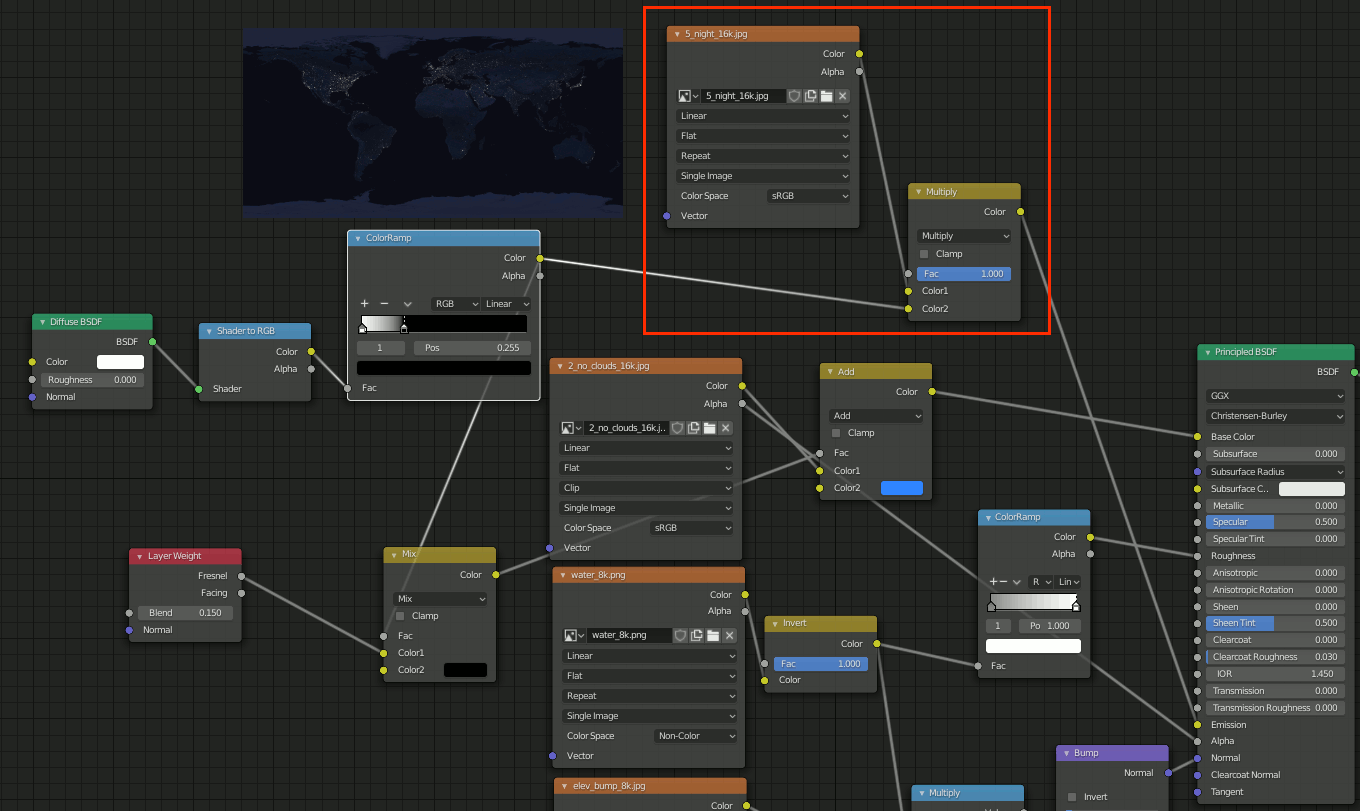
次に、夜景のテクスチャを追加し、Shader to RGBとMultiplyしてEmissionへつなげる
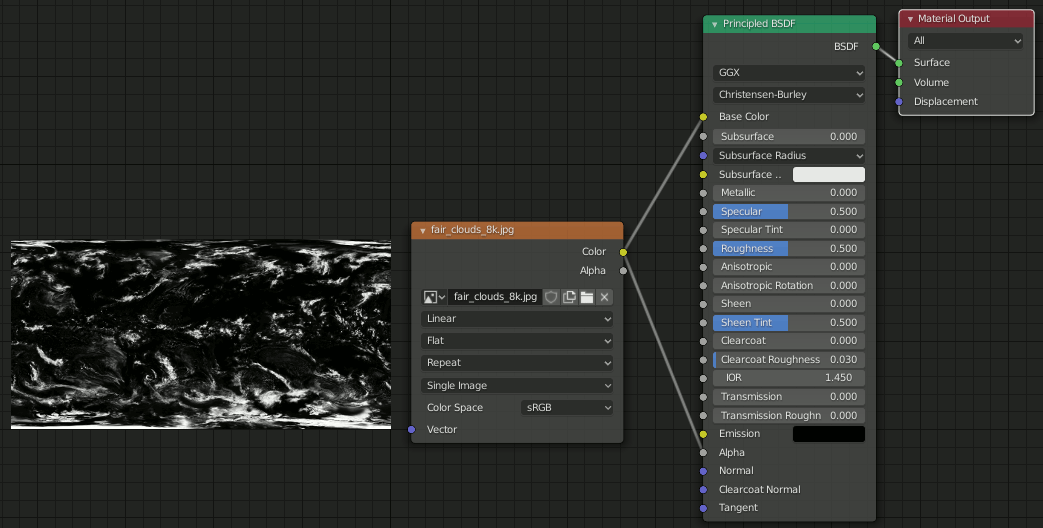
雲
[Shift+D]で地球を複製し、僅かに拡大する。このままだとマテリアルが共通なので、数字をクリックして新しいマテリアルを作成する。
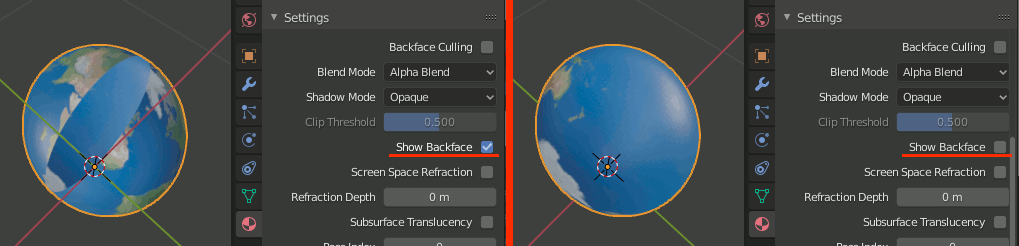
複製したほうの球体に対して雲のテクスチャを設定する。雲のテクスチャは恐らく雲=白、その他=黒になっているので、そのままAlphaに接続すると雲だけがレンダリングできる。
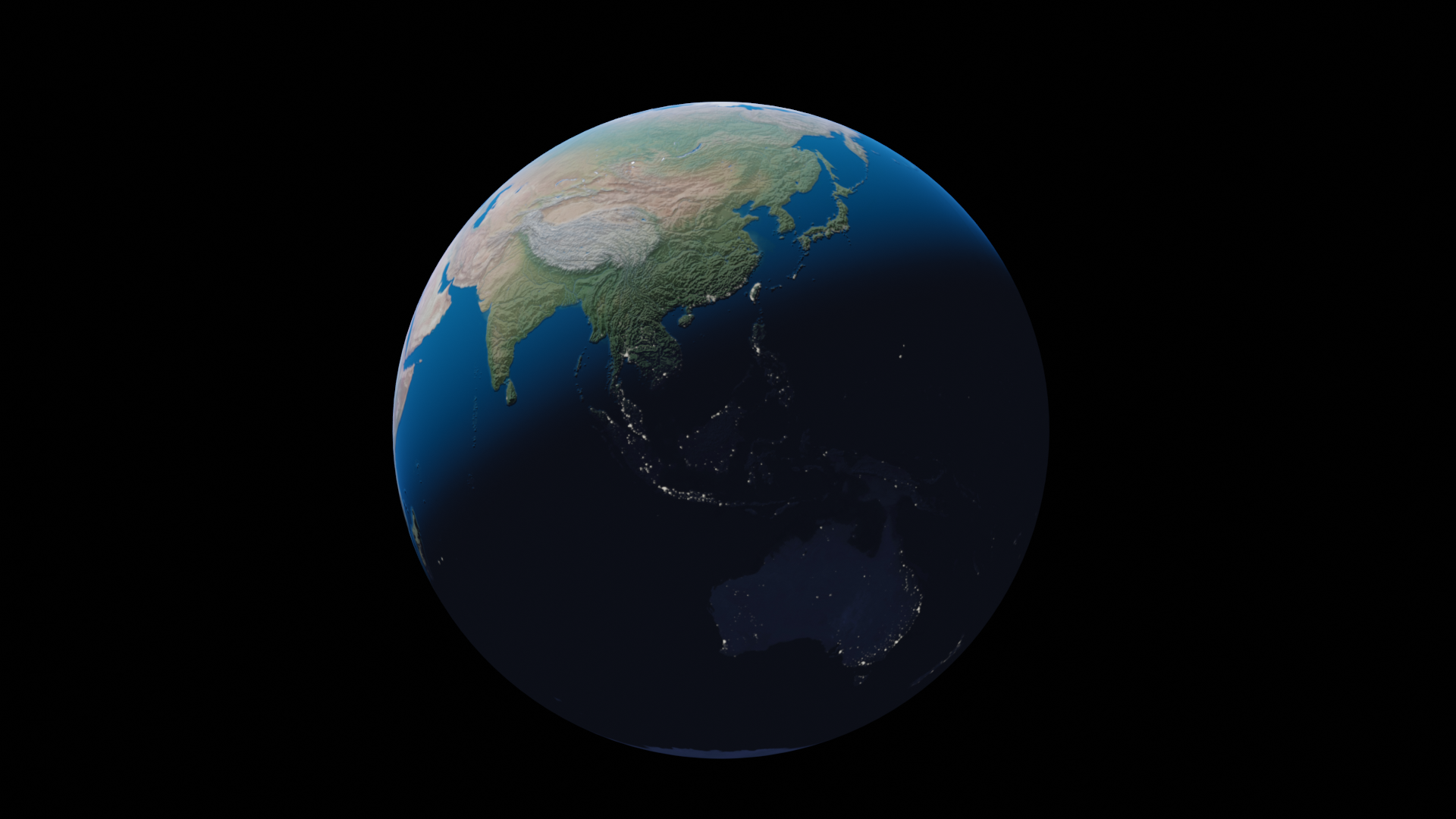
結果(アニメーションPng)
Blender 2.8 How to Create the World in 1 Minute 抜粋 1-モデル作成
使用テクスチャ
テクスチャ
http://www.shadedrelief.com/natural3/pages/textures.html
使用アドオン
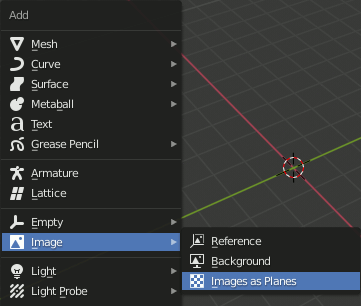
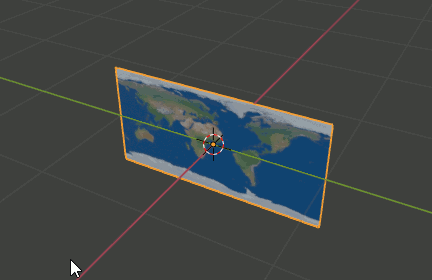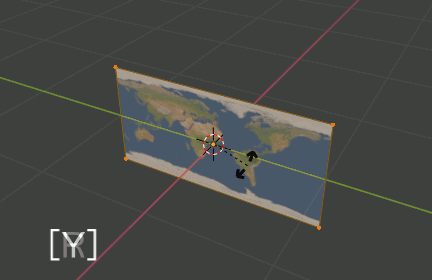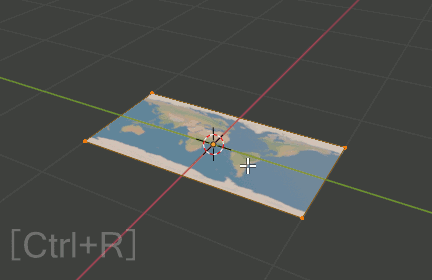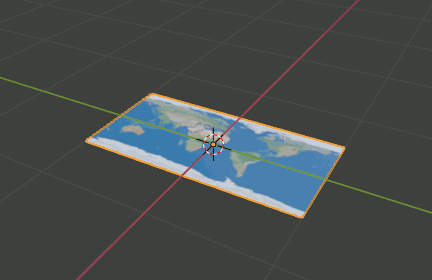
Planeを配置
1.Image as Planeで画像を貼り付けたPlaneを作成
2.Editモードへ移行し、[R][Y][90]でY軸に90度回転
3.Ctr+RでX軸に水平に一回ループカット
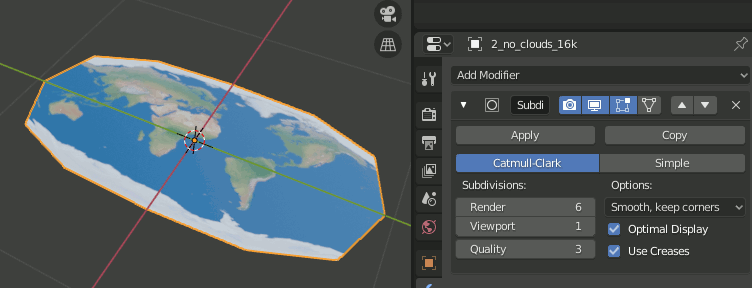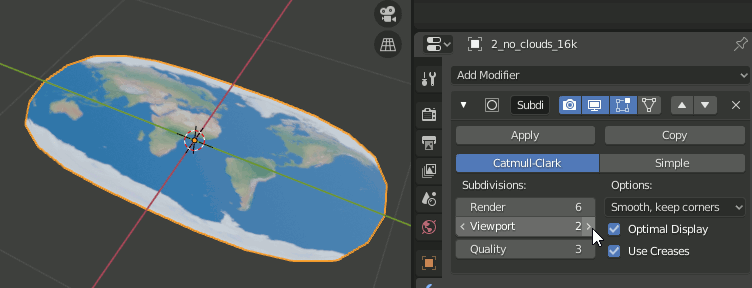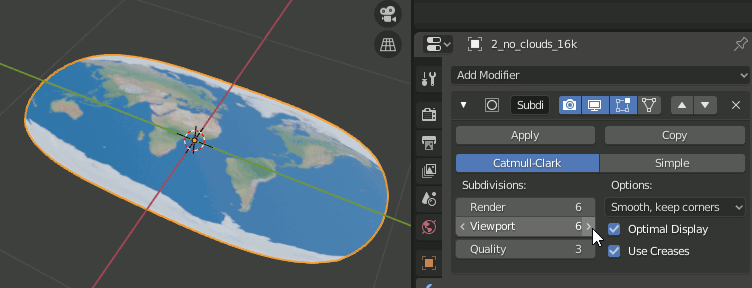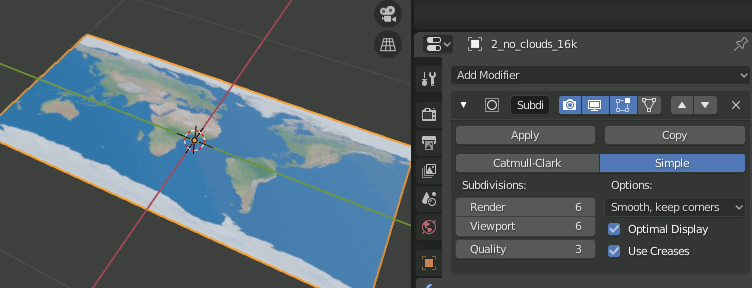
4.Subdivision Surfaceモディファイアを追加し6,simpleに設定
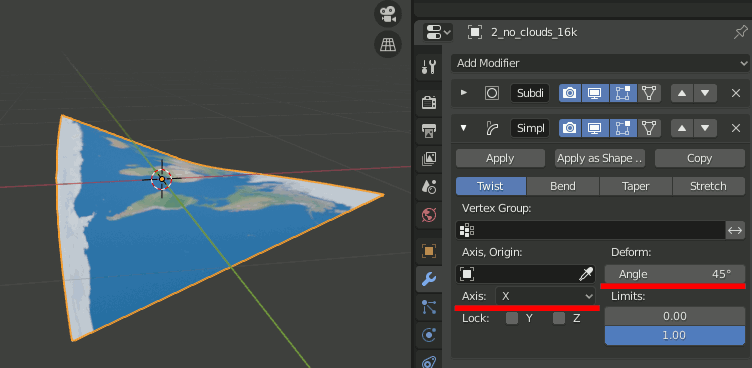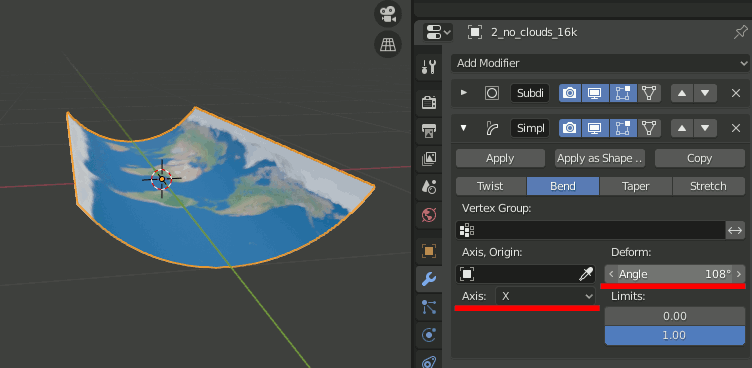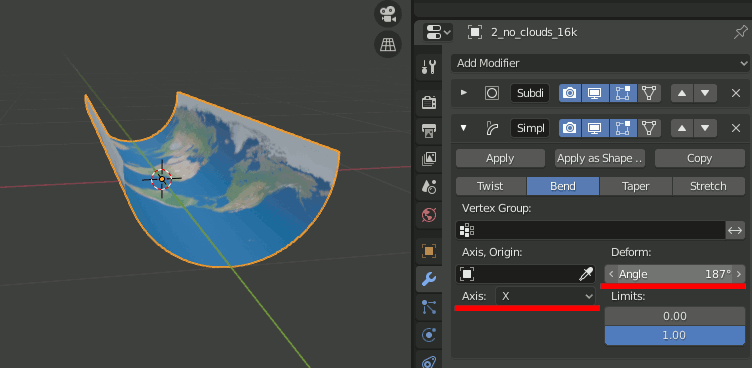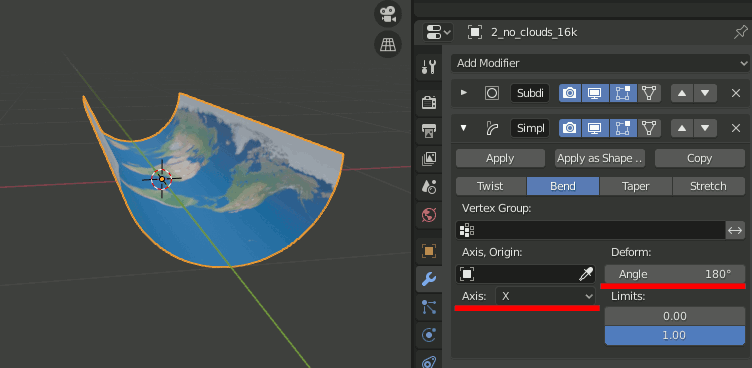
5.Simple Deformモディファイアを追加し、Bend,Axis = X,Angle=180
6.もう一つSimple Deformモディファイアを追加し、Bend,Axis=Z,Angle=360
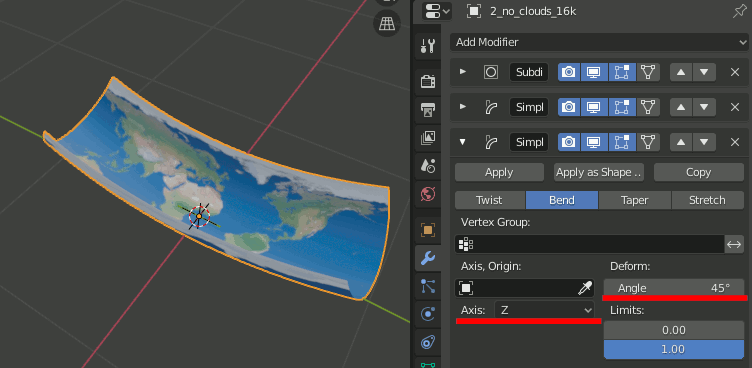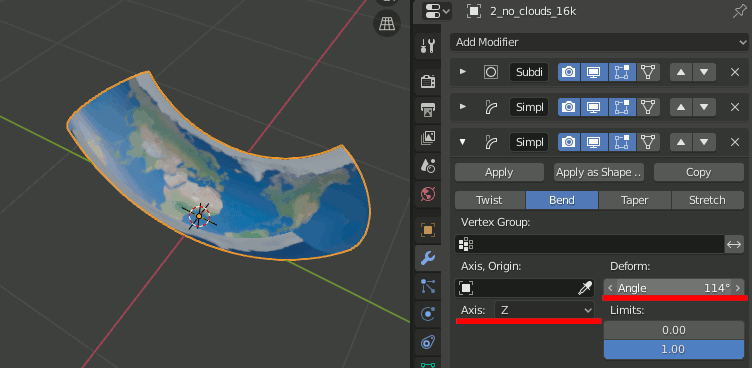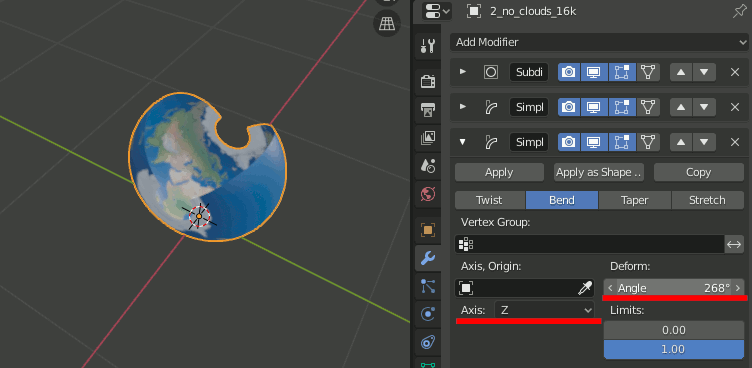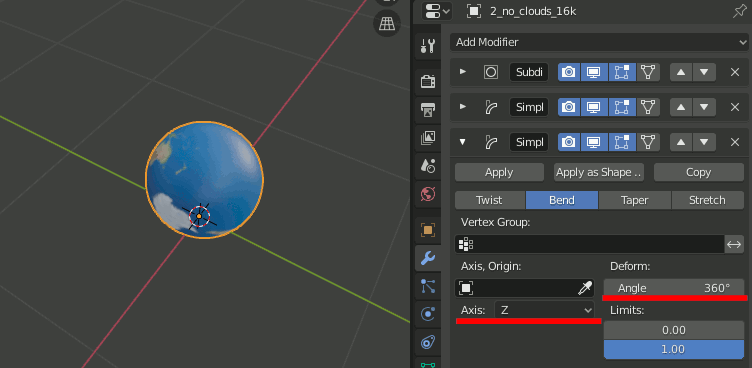
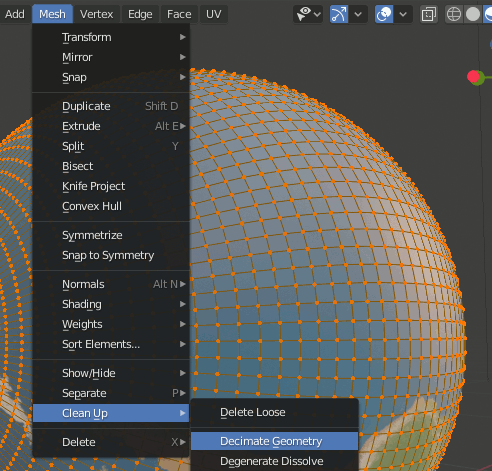
7.モディファイアを適用し、Editモードで[Mesh]→[Clean Up]→[Decimate Geometry]で重複点をmergeする。
続く
Blender で地面を作る(テクスチャ使用)
以下はHow to make Realistic Ground の内容。+α。
1.基本
1-1.テクスチャのダウンロード
まずテクスチャを準備する。わかりやすいように石が多いものがいい。また、displacementマップを持っている必要がある。
今回は以下を使用:
https://cc0textures.com/view?id=Ground022
1-2.Planeの設置
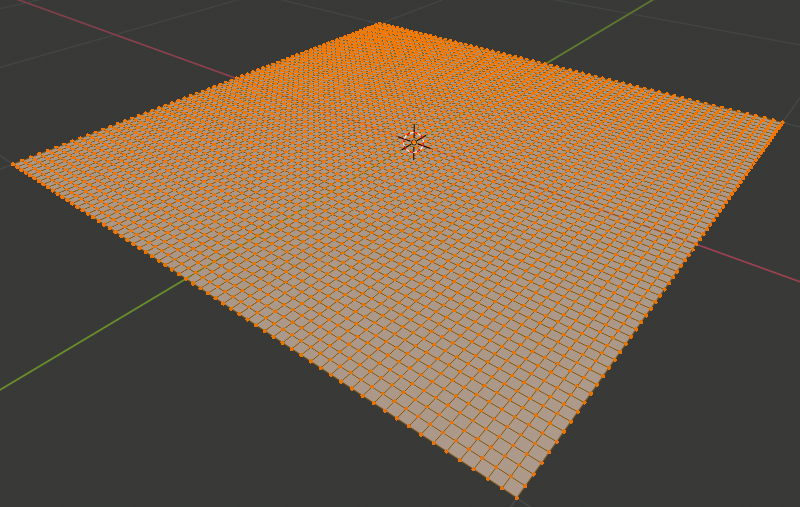
[Shift + A]→[Mesh]→[Plane]で平面を追加
[Tab]でエディットモードに入り、右クリック→[Subdivide]を6回ほど繰り返しPlaneを細かく分割する
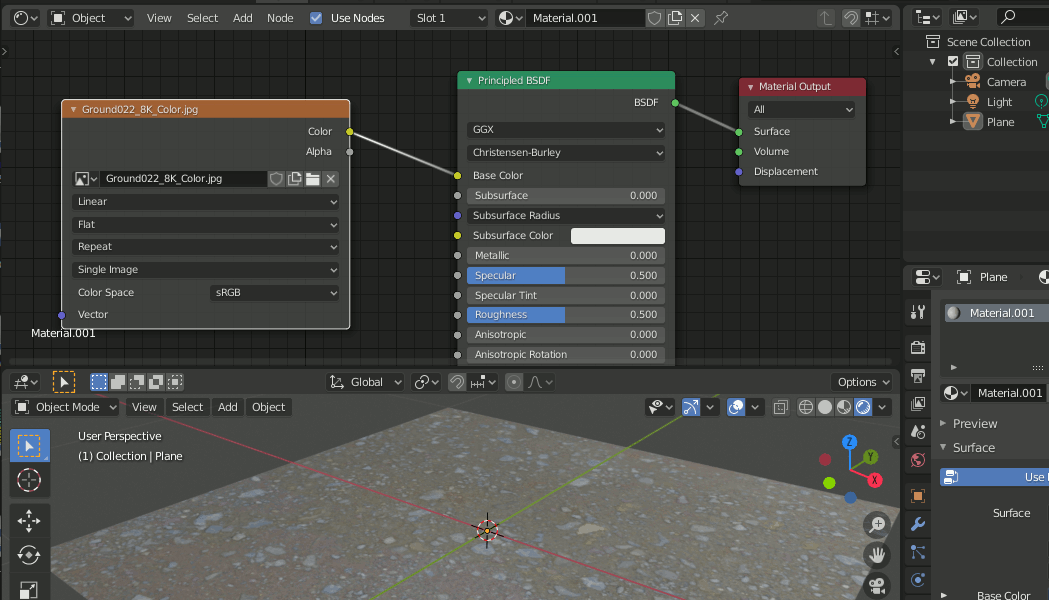
1-3.マテリアルの設定
[Shift+A]→[Texture]→[Image Texture]でテクスチャノードを追加し、カラー画像を設定する
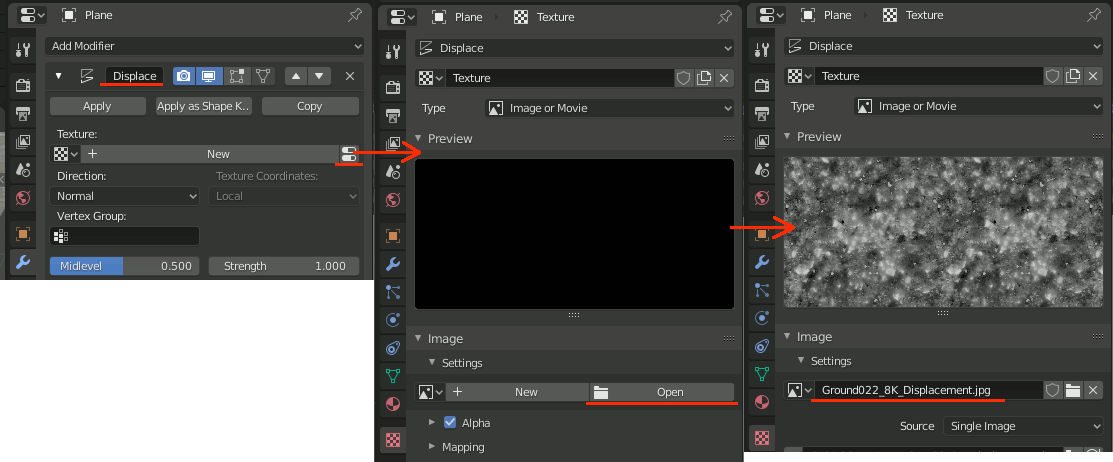
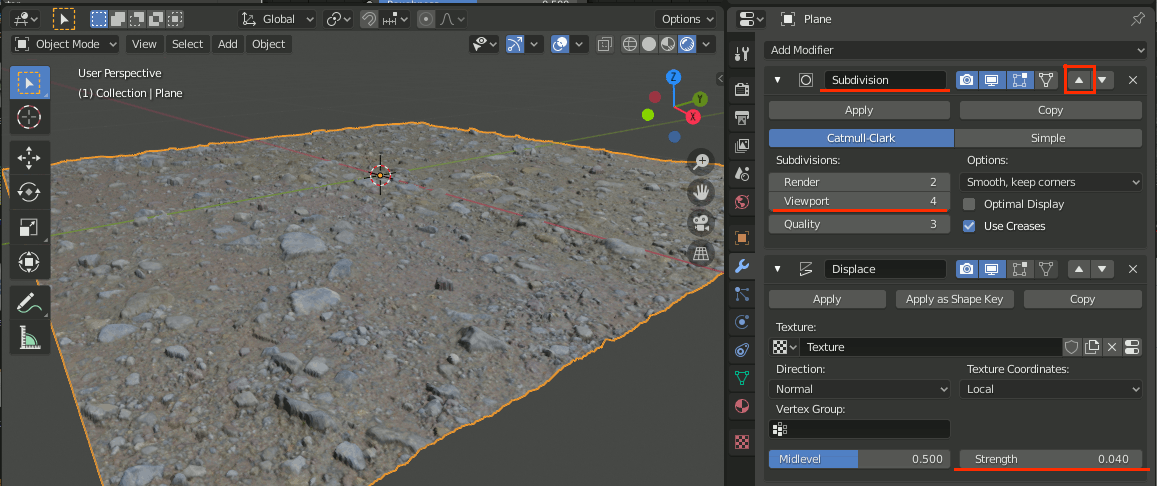
1-4.Displaceモディファイアの設定
1-4-1.テクスチャの設定
Displaceモディファイアを追加し、テクスチャに、マテリアルに設定したテクスチャのDisplacementテクスチャを追加する
1-4-2.調整、細分化
Displaceモディファイアの設定に戻り、Strengthを0.04程度にする。
さらにSubdivisionモディファイア追加し、Subdivisionsの設定を4等の大きい値にする。
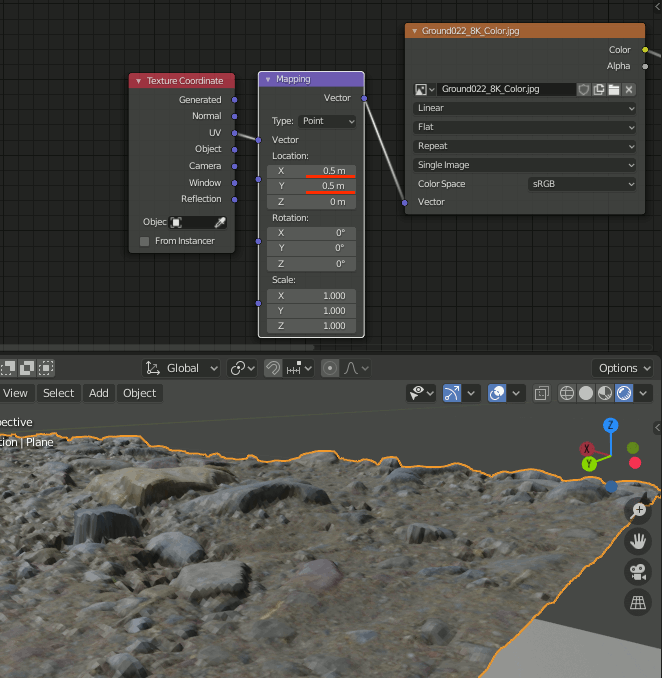
2.応用 拡大・縮小
2-1.displacementモディファイアの設定
この方法では、マテリアルに設定したカラーのテクスチャと、displaceモディファイアに設定したDisplacementテクスチャの座標系が1:1に対応していなければならない。マテリアル側とDisplace側で座標系がやや違うのでそれを考慮しながら作業する
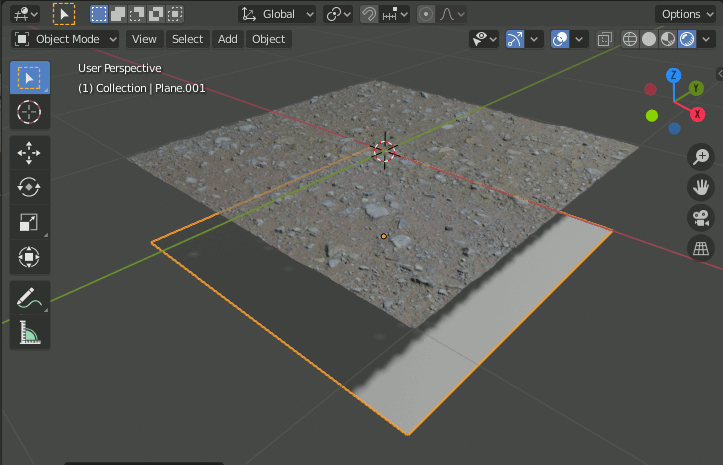
2-1-1.Planeの追加
[Shift+A]→[Mesh]→[Plane]でplaneを追加する(Plane.001)。X,Y方向の位置が重要になるので、適当に移動させずに、真下に移動させるか別コレクションとしておく
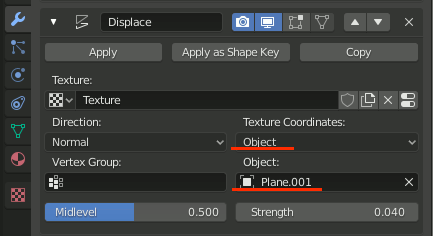
2-1-2.DisplaceモディファイアにPlane.001を設定
Displaceモディファイアの[Texture Coordinates]に追加したPlane.001を指定
このままPlane.001をスケーリングするとDisplaceも拡大縮小するが、スケーリングの中心がPlaneの中央になっている。テクスチャ側のスケーリング中心が左端なので合わせる必要がある。
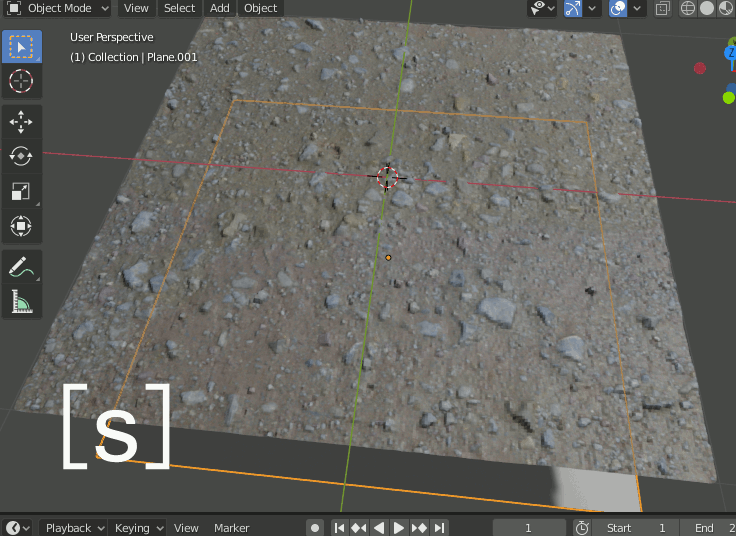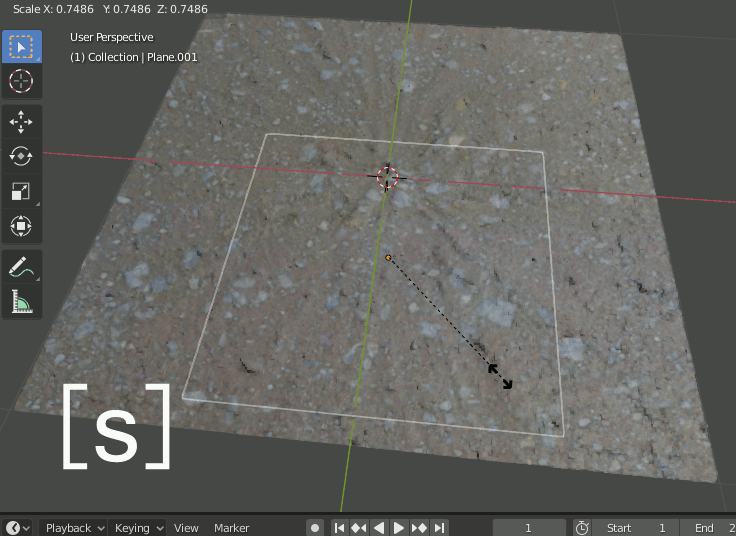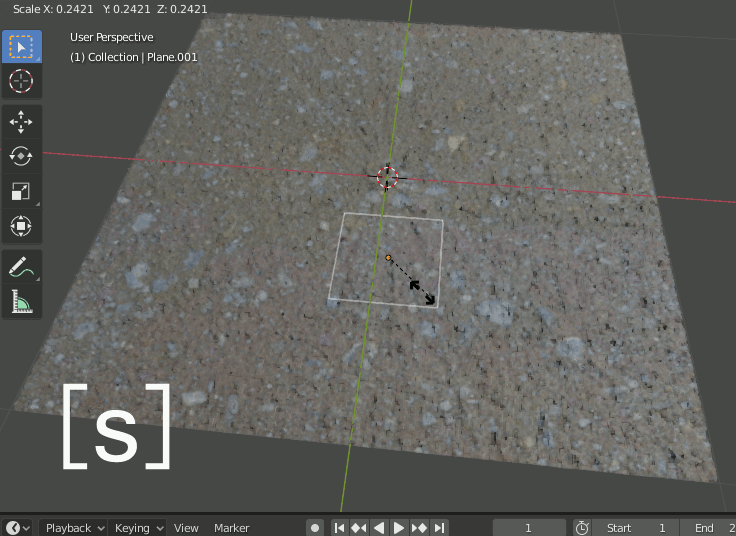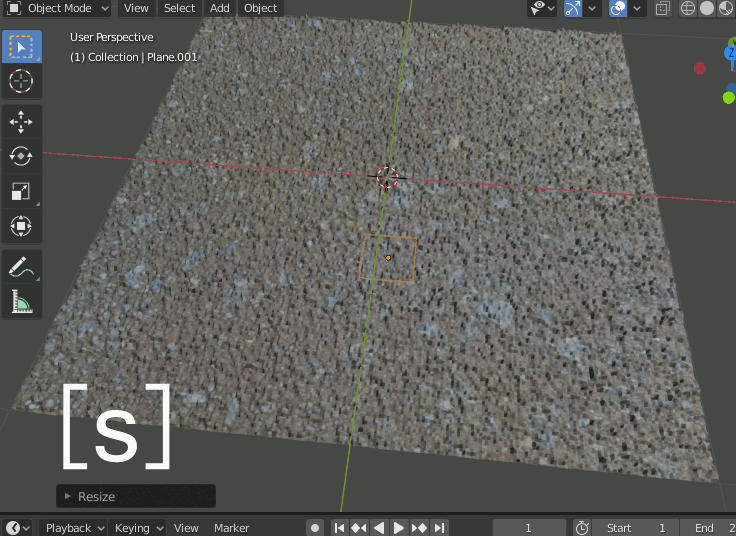
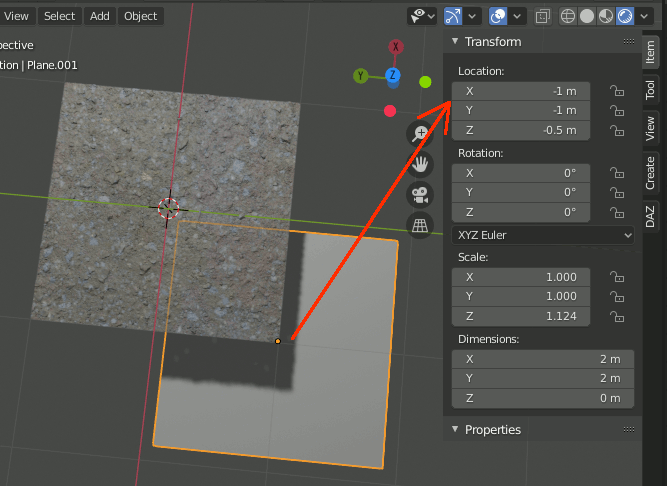
2-1-3.Plane.001を(-1,-1)へ移動
Plane.001を-1,-1へ移動する。z座標は邪魔にならなければいくつでも良い。
2-1-4.テクスチャの座標系を変更
[Shift+A]→[Vector]→[Mapping]を追加し、Locationを0.5,0.5に設定
Texture CoordinateはUVから繋いでおく。
これで、再びDisplaceモディファイアとカラーのテクスチャが一致するようになる
2-1-5.テクスチャとdisplaceをスケーリング
Plane.001側を0.5,0.5倍、テクスチャ側を2.0,2.0倍にする。
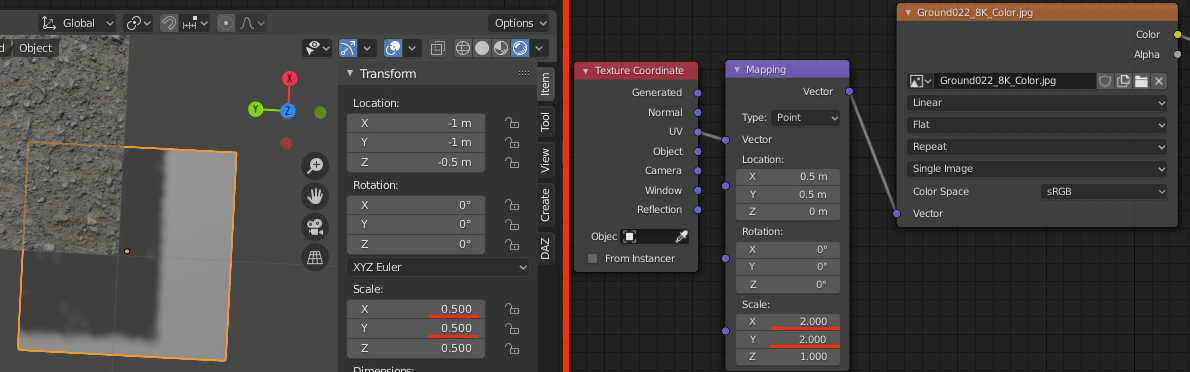
3.その他
Displaceモディファイアをもう一つ追加し、Cloudsなどを設定するとよりリアルな地形になる。
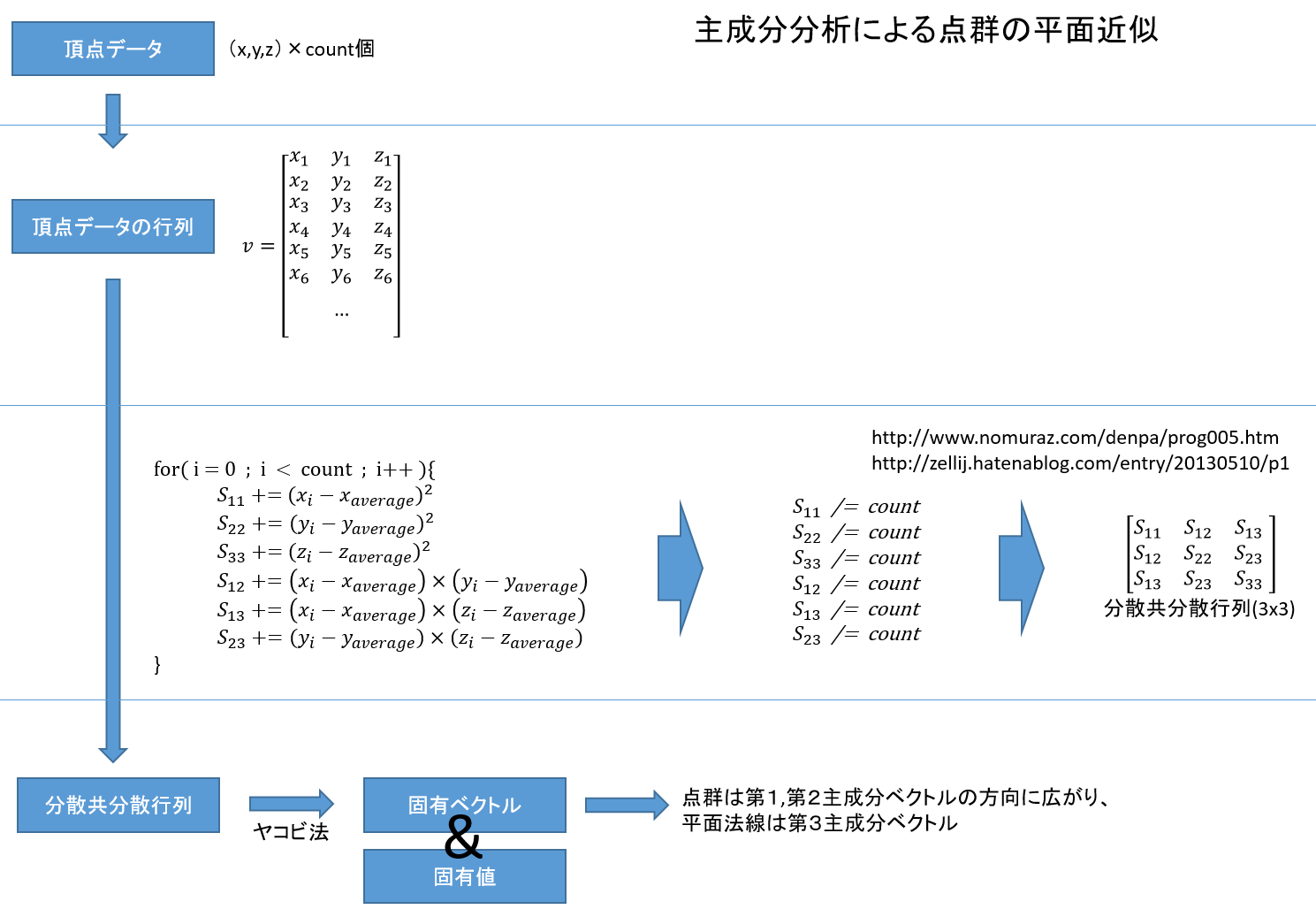
主成分分析で三次元点群から平面を求める – 2 – 固有ベクトルを求める
前回はデータから分散共分散行列を求めた。
分散共分散行列(3×3)に対してヤコビ法などを用いると、行列の固有値と固有ベクトルがそれぞれ3つずつ求まる。固有値が最も小さい固有ベクトルが面法線となる。
プログラム
リンク先、先頭のヤコビ法のプログラムをそのまま使用する
固有ベクトルと固有値
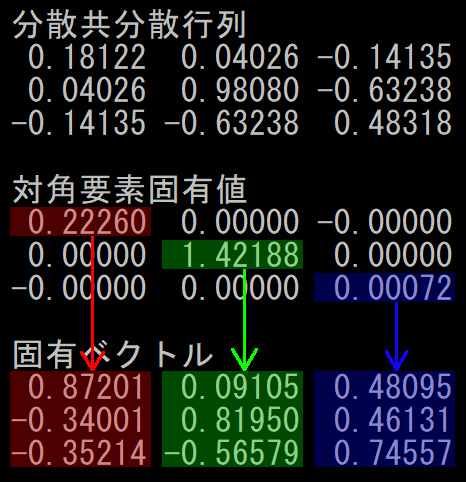
該当部分プログラム
printf("分散共分散行列\n"); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", Sxx, Sxy, Sxz); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", Sxy, Syy, Syz); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", Sxz, Syz, Szz); puts(""); float a[3 * 3] = { Sxx,Sxy,Sxz, Sxy,Syy,Syz, Sxz,Syz,Szz }; float v[3 * 3]; EigenJacobiMethod(a, v, 3); printf("対角要素固有値\n"); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", a[0], a[1], a[2]); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", a[3], a[4], a[5]); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", a[6], a[7], a[8]); puts(""); printf("固有ベクトル\n"); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", v[0], v[1], v[2]); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", v[3], v[4], v[5]); printf("% 1.5lf % 1.5lf % 1.5lf\n", v[6], v[7], v[8]);
面法線の選択
主成分分析で得られるベクトルは、データがどの方向にばらついているかを表していて、一番ばらつきが少ない方向が面法線という事になる
参考:
主成分分析の考え方
ので、一番小さい固有値に対応した固有ベクトルが面法線になる。
参考:
”主成分分析における固有値は、その固有ベクトルの方向に沿ったデータの分散の大きさに対応します。固有値が大きい固有ベクトルほど、データの分散をよく説明している、つまり、データの重要な特徴を捉えていると考えられます。なので、各固有値を固有値の合計で割ったものを寄与率と呼んだり、固有値(寄与率)が大きい主成分から順に、第1主成分(PC1)、第2主成分(PC2)……と呼んだりします。”
上記結果では固有値が0.00072のベクトル( 0.00957 , -0.00150 , 0.99995 )が答えになる。
面の特定
面はその面に含まれる一点と法線ベクトルがわかれば求められる。
面に含まれる一点・・・頂点群の重心
面法線・・・頂点群の主成分分析の結果の第三主成分
で面が決定できる。
プログラム全体
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <array> //! @struct point //! @brief 座標を表すデータ型 struct point { double p[3]; point(double x, double y, double z) { p[0] = x; p[1] = y; p[2] = z; } point() {} }; //! @brief 固有値・固有ベクトル struct eigen { double val; //!< 固有値 double vec[3];//!< 固有ベクトル }; int EigenJacobiMethod(float* a, float* v, int n, float eps = 1e-8, int iter_max = 100); void data(std::vector<point>& pt);
//! @brief データの平均を求める //! @param [in] vec データの配列 //! @return 各要素の平均 point Covariance_Ave(const std::vector<point>& vec) { // 初期化 point ave; ave.p[0] = 0; ave.p[1] = 0; ave.p[2] = 0; // 各要素平均 for (size_t i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) { ave.p[0] += vec[i].p[0]; ave.p[1] += vec[i].p[1]; ave.p[2] += vec[i].p[2]; } ave.p[0] /= vec.size(); ave.p[1] /= vec.size(); ave.p[2] /= vec.size(); return ave; }
//! @brief 共分散を求める //! @param [in] average 各要素の平均 //! @param [in] vec データ //! @param [in] param どの要素に対して求めるか。例えばxyzの時、x,yに対する共分散なら{0,1}を与える。 //! @return 偏差の積の和の要素数分の一 double Covariance(const point& average,const std::vector<point>& vec,const std::array<int,2>& param) { double sum = 0.0; for (size_t i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) { //指定したパラメータの偏差を求める point deviation; for (size_t j = 0; j < param.size(); j++) { int target = param[j]; deviation.p[target] = (vec[i].p[target] - average.p[target]); } //偏差の積 double product = 1.0; for (size_t j = 0; j < param.size(); j++) { int target = param[j]; product *= deviation.p[target]; } //偏差の積の和を更新 sum += product; } //偏差の積の和のN分の一 return 1.0 / vec.size() * sum; }
//! @brief データを主成分分析する //! @param [out] ev 固有値と固有ベクトル //! @param [in] average 全データの各要素の平均 //! @param [in] pt 三次元の座標値一覧 //! @return なし void eigen_vector(eigen* ev, point* average, const std::vector<point>& pt) { //各要素の平均を求める。 //これは共分散を求めるときに (x[i] - xの平均)×(y[i] - yの平均) 等の計算が必要なため *average = Covariance_Ave(pt); //共分散を求める //第三引数の{0,0}はxxを表す。xyなら{0,1}。これはデータがxyzの順に並んでいる事が前提。 double Sxx = Covariance(*average, pt, { 0, 0 }); double Sxy = Covariance(*average, pt, { 0, 1 }); double Sxz = Covariance(*average, pt, { 0, 2 }); double Syy = Covariance(*average, pt, { 1, 1 }); double Syz = Covariance(*average, pt, { 1, 2 }); double Szz = Covariance(*average, pt, { 2, 2 }); // 分散共分散行列 float a[3 * 3] = { Sxx,Sxy,Sxz, Sxy,Syy,Syz, Sxz,Syz,Szz }; float v[3 * 3]; EigenJacobiMethod(a, v, 3); ev[0].val = a[0]; //固有値 ev[0].vec[0] = v[0];//固有値に対応した固有ベクトル ev[0].vec[1] = v[3]; ev[0].vec[2] = v[6]; ev[1].val = a[4]; //固有値 ev[1].vec[0] = v[1];//固有値に対応した固有ベクトル ev[1].vec[1] = v[4]; ev[1].vec[2] = v[7]; ev[2].val = a[8]; //固有値 ev[2].vec[0] = v[2];//固有値に対応した固有ベクトル ev[2].vec[1] = v[5]; ev[2].vec[2] = v[8]; }
int main() { std::vector<point> pt; data( pt ); //データの準備 eigen ev[3]; point average; eigen_vector(ev, &average,pt); //固有値と固有ベクトルを表示 printf("[%lf] %lf %lf %lf\n", ev[0].val, ev[0].vec[0], ev[0].vec[1], ev[0].vec[2]); printf("[%lf] %lf %lf %lf\n", ev[1].val, ev[1].vec[0], ev[1].vec[1], ev[1].vec[2]); printf("[%lf] %lf %lf %lf\n", ev[2].val, ev[2].vec[0], ev[2].vec[1], ev[2].vec[2]); printf("\n重心\n"); printf("%.5lf %.5lf %.5lf\n", average.p[0], average.p[1], average.p[2]); int i; std::cin >> i; }
void data(std::vector<point>& pt) { pt.emplace_back(-0.9282366037368774, -4.60659646987915, 4.179419040679932); pt.emplace_back(-0.6398676633834839, -4.345795631408691, 3.8638782501220703); pt.emplace_back(-0.3469808101654053, -4.115365028381348, 3.5088584423065186); pt.emplace_back(-0.05463826656341553, -3.881274938583374, 3.1585941314697266); pt.emplace_back(0.2328449785709381, -3.614520311355591, 2.850792646408081); pt.emplace_back(-1.0035791397094727, -3.9636778831481934, 3.8052620887756348); pt.emplace_back(-0.7170133590698242, -3.690755844116211, 3.5054771900177); pt.emplace_back(-0.4283676743507385, -3.4318137168884277, 3.1875195503234863); pt.emplace_back(-0.13146033883094788, -3.2284107208251953, 2.7973649501800537); pt.emplace_back(0.15122388303279877, -2.929394483566284, 2.531501293182373); pt.emplace_back(-1.0883535146713257, -3.2573564052581787, 3.513524055480957); pt.emplace_back(-0.7981395721435547, -3.0089566707611084, 3.181861639022827); pt.emplace_back(-0.5119532346725464, -2.733482599258423, 2.88539457321167); pt.emplace_back(-0.21177172660827637, -2.5520896911621094, 2.466628313064575); pt.emplace_back(0.08094996213912964, -2.3205485343933105, 2.113051414489746); pt.emplace_back(-1.1616857051849365, -2.6279513835906982, 3.1217992305755615); pt.emplace_back(-0.8680680990219116, -2.402432918548584, 2.7603931427001953); pt.emplace_back(-0.5798090696334839, -2.140892267227173, 2.4458136558532715); pt.emplace_back(-0.2915937602519989, -1.87905752658844, 2.1316158771514893); pt.emplace_back(0.002897977828979492, -1.6594164371490479, 1.7625699043273926); pt.emplace_back(-1.2396777868270874, -1.967220664024353, 2.7707955837249756); pt.emplace_back(-0.9490185976028442, -1.7218148708343506, 2.43524169921875); pt.emplace_back(-0.6570032835006714, -1.4855259656906128, 2.087836503982544); pt.emplace_back(-0.36362549662590027, -1.2583959102630615, 1.7285257577896118); pt.emplace_back(-0.0764693021774292, -0.9894416332244873, 1.4235832691192627); }
/*! * Jacobi法による固有値の算出 * @param[inout] a 実対称行列.計算後,対角要素に固有値が入る * @param[out] v 固有ベクトル(aと同じサイズ) * @param[in] n 行列のサイズ(n×n) * @param[in] eps 収束誤差 * @param[in] iter_max 最大反復回数 * @return 反復回数 * @see http://www.slis.tsukuba.ac.jp/~fujisawa.makoto.fu/cgi-bin/wiki/index.php?%B8%C7%CD%AD%C3%CD/%B8%C7%CD%AD%A5%D9%A5%AF%A5%C8%A5%EB */ int EigenJacobiMethod(float* a, float* v, int n, float eps, int iter_max) { float* bim, * bjm; float bii, bij, bjj, bji; bim = new float[n]; bjm = new float[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { v[i * n + j] = (i == j) ? 1.0 : 0.0; } } int cnt = 0; for (;;) { int i, j; float x = 0.0; for (int ia = 0; ia < n; ++ia) { for (int ja = 0; ja < n; ++ja) { int idx = ia * n + ja; if (ia != ja && fabs(a[idx]) > x) { i = ia; j = ja; x = fabs(a[idx]); } } } float aii = a[i * n + i]; float ajj = a[j * n + j]; float aij = a[i * n + j]; float alpha, beta; alpha = (aii - ajj) / 2.0; beta = sqrt(alpha * alpha + aij * aij); float st, ct; ct = sqrt((1.0 + fabs(alpha) / beta) / 2.0); // sinθ st = (((aii - ajj) >= 0.0) ? 1.0 : -1.0) * aij / (2.0 * beta * ct); // cosθ // A = PAPの計算 for (int m = 0; m < n; ++m) { if (m == i || m == j) continue; float aim = a[i * n + m]; float ajm = a[j * n + m]; bim[m] = aim * ct + ajm * st; bjm[m] = -aim * st + ajm * ct; } bii = aii * ct * ct + 2.0 * aij * ct * st + ajj * st * st; bij = 0.0; bjj = aii * st * st - 2.0 * aij * ct * st + ajj * ct * ct; bji = 0.0; for (int m = 0; m < n; ++m) { a[i * n + m] = a[m * n + i] = bim[m]; a[j * n + m] = a[m * n + j] = bjm[m]; } a[i * n + i] = bii; a[i * n + j] = bij; a[j * n + j] = bjj; a[j * n + i] = bji; // V = PVの計算 for (int m = 0; m < n; ++m) { float vmi = v[m * n + i]; float vmj = v[m * n + j]; bim[m] = vmi * ct + vmj * st; bjm[m] = -vmi * st + vmj * ct; } for (int m = 0; m < n; ++m) { v[m * n + i] = bim[m]; v[m * n + j] = bjm[m]; } float e = 0.0; for (int ja = 0; ja < n; ++ja) { for (int ia = 0; ia < n; ++ia) { if (ia != ja) { e += fabs(a[ja * n + ia]); } } } if (e < eps) break; cnt++; if (cnt > iter_max) break; } delete[] bim; delete[] bjm; return cnt; }
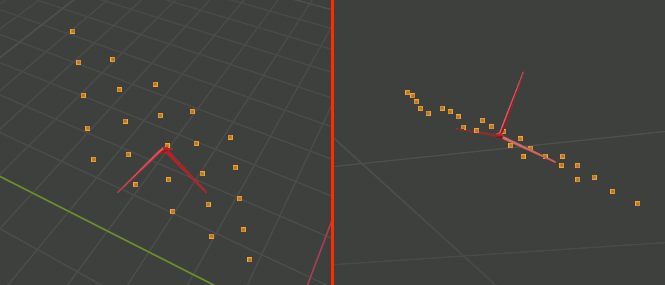
Blenderで可視化
もっと良いツールがあるのかもしれないがBlenderで重心から各主成分に線を伸ばしたものを作成して結果を確認する
主成分分析で三次元点群から平面を求める – 1 – 分散共分散行列を求める
まず、手順としては下の図のようになる。
頂点データを行列として扱う所は特に問題は無いが、行列が苦手な人(自分もだが)のためにコメントすると3×頂点数の行列ができる。つまり例えば3×50000の行列とかにする。コード的な視点から見るとわざわざ「行列型」にする必要はない。構造体の配列で問題ない。
その行列に対して処理をして、最終的に3×3の分散共分散行列を作成する。その行列の固有ベクトル( xyzのベクトルが三つ )を求めればいい。
データ
例えば以下のようなデータの場合、分散共分散行列は3x3の行列になる。
| x | y | z |
|---|---|---|
| -0.9282366037368774 | -4.60659646987915 | 4.179419040679932 |
| -0.6398676633834839 | -4.345795631408691 | 3.8638782501220703 |
| -0.3469808101654053 | -4.115365028381348 | 3.5088584423065186 |
| -0.05463826656341553 | -3.881274938583374 | 3.1585941314697266 |
| 0.2328449785709381 | -3.614520311355591 | 2.850792646408081 |
| -1.0035791397094727 | -3.9636778831481934 | 3.8052620887756348 |
| -0.7170133590698242 | -3.690755844116211 | 3.5054771900177 |
| -0.4283676743507385 | -3.4318137168884277 | 3.1875195503234863 |
| -0.13146033883094788 | -3.2284107208251953 | 2.7973649501800537 |
| 0.15122388303279877 | -2.929394483566284 | 2.531501293182373 |
| -1.0883535146713257 | -3.2573564052581787 | 3.513524055480957 |
| -0.7981395721435547 | -3.0089566707611084 | 3.181861639022827 |
| -0.5119532346725464 | -2.733482599258423 | 2.88539457321167 |
| -0.21177172660827637 | -2.5520896911621094 | 2.466628313064575 |
| 0.08094996213912964 | -2.3205485343933105 | 2.113051414489746 |
| -1.1616857051849365 | -2.6279513835906982 | 3.1217992305755615 |
| -0.8680680990219116 | -2.402432918548584 | 2.7603931427001953 |
| -0.5798090696334839 | -2.140892267227173 | 2.4458136558532715 |
| -0.2915937602519989 | -1.87905752658844 | 2.1316158771514893 |
| 0.002897977828979492 | -1.6594164371490479 | 1.7625699043273926 |
| -1.2396777868270874 | -1.967220664024353 | 2.7707955837249756 |
| -0.9490185976028442 | -1.7218148708343506 | 2.43524169921875 |
| -0.6570032835006714 | -1.4855259656906128 | 2.087836503982544 |
| -0.36362549662590027 | -1.2583959102630615 | 1.7285257577896118 |
| -0.0764693021774292 | -0.9894416332244873 | 1.4235832691192627 |
分散共分散行列
分散共分散行列の形
データがx,y,zの場合、以下のような形をしている
問題はこのSxx,Sxy,Sxz,...をどうやって求めるかなのだが、このSxyは「xとyの共分散」である。
だから「xとxの共分散(=xの分散)」、「xとyの共分散」、...を求める。では共分散はどうやって求めるのか。
共分散の求め方
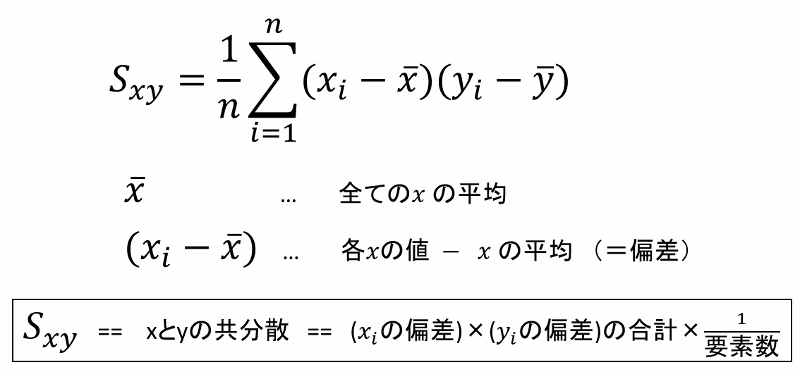
当然だが、Sxxの場合、「Sxx = (x[i]の偏差)の二乗の合計×(1/要素数)」になる。
偏差の求め方がわかれば共分散が求められ、共分散を求めることができれば分散共分散行列を組み立てることができる。
Excelで動作確認
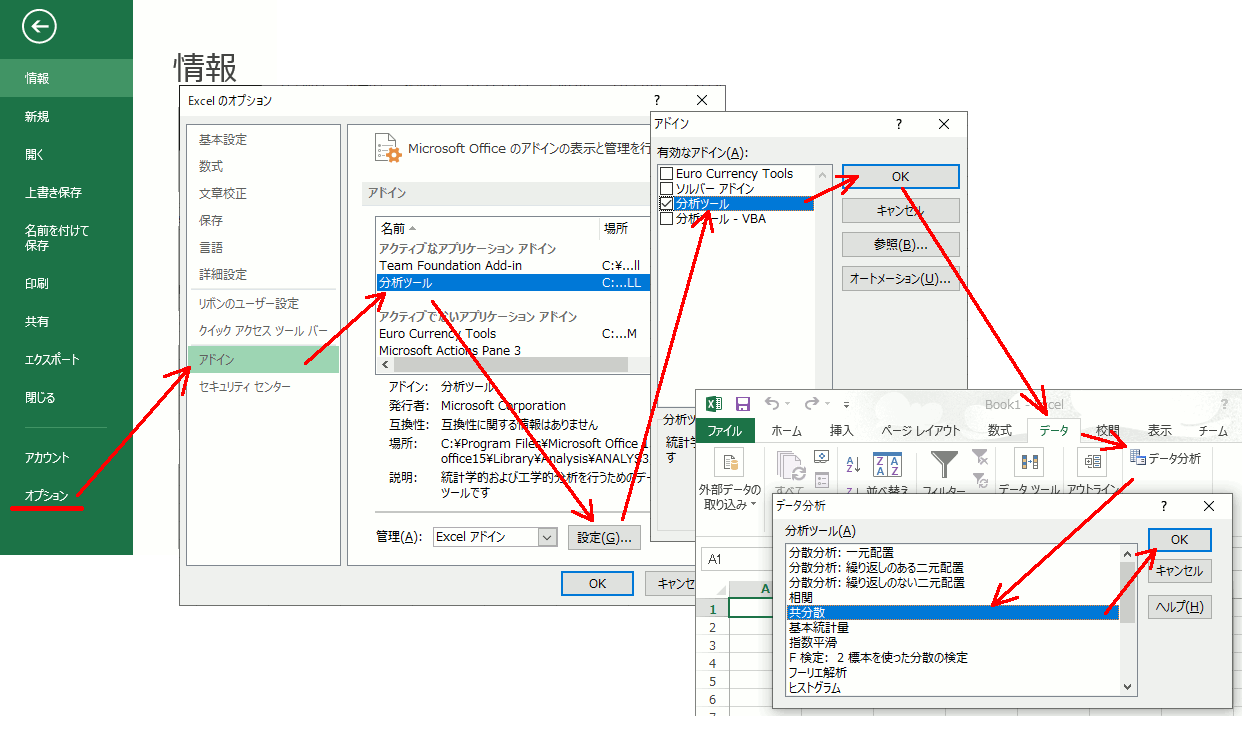
分析ツールの追加
プログラムに起こしたので、Excelに同じデータを入れて正しい答えが出ているかを確認する。
で分析ツールを追加し、データ→データ分析→共分散と操作する。
Excelによる計算結果
自作コードでの計算結果

ソースコード
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <array> //! @brief 座標を表すデータ型 struct point { double p[3]; point(double x, double y, double z) { p[0] = x; p[1] = y; p[2] = z; } point() {} };
//! @brief データの平均を求める //! @param [in] vec データの配列 //! @return 各要素の平均 point Covariance_Ave(const std::vector<point>& vec) { // 初期化 point ave; ave.p[0] = 0; ave.p[1] = 0; ave.p[2] = 0; // 各要素平均 for (size_t i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) { ave.p[0] += vec[i].p[0]; ave.p[1] += vec[i].p[1]; ave.p[2] += vec[i].p[2]; } ave.p[0] /= vec.size(); ave.p[1] /= vec.size(); ave.p[2] /= vec.size(); return ave; }
//! @brief 共分散を求める //! @param [in] average 各要素の平均 //! @param [in] vec データ //! @param [in] param どの要素に対して求めるか。例えばxyzの時、x,yに対する共分散なら{0,1}を与える。 //! @return 偏差の積の和の要素数分の一 double Covariance(const point& average,const std::vector<point>& vec,const std::array<int,2>& param) { double sum = 0.0; for (size_t i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) { //指定したパラメータの偏差を求める point deviation; for (size_t j = 0; j < param.size(); j++) { int target = param[j]; deviation.p[target] = (vec[i].p[target] - average.p[target]); } //偏差の積 double product = 1.0; for (size_t j = 0; j < param.size(); j++) { int target = param[j]; product *= deviation.p[target]; } //偏差の積の和を更新 sum += product; } //偏差の積の和のN分の一 return 1.0 / vec.size() * sum; }
void data(std::vector<point>& pt);
int main() { std::vector<point> pt; data( pt ); //データの準備 //各要素の平均を求める。 //これは共分散を求めるときに (x[i] - xの平均)×(y[i] - yの平均) 等の計算が必要なため point average = Covariance_Ave(pt); //共分散を求める //第三引数の{0,0}はxxを表す。xyなら{0,1}。これはデータがxyzの順に並んでいる事が前提。 double Sxx = Covariance(average, pt, { 0, 0 }); double Sxy = Covariance(average, pt, { 0, 1 }); double Sxz = Covariance(average, pt, { 0, 2 }); double Syy = Covariance(average, pt, { 1, 1 }); double Syz = Covariance(average, pt, { 1, 2 }); double Szz = Covariance(average, pt, { 2, 2 }); // 分散共分散行列を表示 printf("分散共分散行列\n"); printf("%.5lf %.5lf %.5lf\n", Sxx, Sxy, Sxz); printf("%.5lf %.5lf %.5lf\n", Sxy, Syy, Syz); printf("%.5lf %.5lf %.5lf\n", Sxz, Syz, Szz); int i; std::cin >> i; }
void data(std::vector<point>& pt) { pt.emplace_back(-0.9282366037368774, -4.60659646987915, 4.179419040679932); pt.emplace_back(-0.6398676633834839, -4.345795631408691, 3.8638782501220703); pt.emplace_back(-0.3469808101654053, -4.115365028381348, 3.5088584423065186); pt.emplace_back(-0.05463826656341553, -3.881274938583374, 3.1585941314697266); pt.emplace_back(0.2328449785709381, -3.614520311355591, 2.850792646408081); pt.emplace_back(-1.0035791397094727, -3.9636778831481934, 3.8052620887756348); pt.emplace_back(-0.7170133590698242, -3.690755844116211, 3.5054771900177); pt.emplace_back(-0.4283676743507385, -3.4318137168884277, 3.1875195503234863); pt.emplace_back(-0.13146033883094788, -3.2284107208251953, 2.7973649501800537); pt.emplace_back(0.15122388303279877, -2.929394483566284, 2.531501293182373); pt.emplace_back(-1.0883535146713257, -3.2573564052581787, 3.513524055480957); pt.emplace_back(-0.7981395721435547, -3.0089566707611084, 3.181861639022827); pt.emplace_back(-0.5119532346725464, -2.733482599258423, 2.88539457321167); pt.emplace_back(-0.21177172660827637, -2.5520896911621094, 2.466628313064575); pt.emplace_back(0.08094996213912964, -2.3205485343933105, 2.113051414489746); pt.emplace_back(-1.1616857051849365, -2.6279513835906982, 3.1217992305755615); pt.emplace_back(-0.8680680990219116, -2.402432918548584, 2.7603931427001953); pt.emplace_back(-0.5798090696334839, -2.140892267227173, 2.4458136558532715); pt.emplace_back(-0.2915937602519989, -1.87905752658844, 2.1316158771514893); pt.emplace_back(0.002897977828979492, -1.6594164371490479, 1.7625699043273926); pt.emplace_back(-1.2396777868270874, -1.967220664024353, 2.7707955837249756); pt.emplace_back(-0.9490185976028442, -1.7218148708343506, 2.43524169921875); pt.emplace_back(-0.6570032835006714, -1.4855259656906128, 2.087836503982544); pt.emplace_back(-0.36362549662590027, -1.2583959102630615, 1.7285257577896118); pt.emplace_back(-0.0764693021774292, -0.9894416332244873, 1.4235832691192627); }
参考
https://sci-pursuit.com/math/statistics/covariance.html
http://www.geisya.or.jp/~mwm48961/statistics/syuseibun1.htm
http://www.it.is.tohoku.ac.jp/lecture/pattern/pdf/2012/slide3.pdf
http://www.nomuraz.com/denpa/prog005.htm
http://sysplan.nams.kyushu-u.ac.jp/gen/edu/Algorithms/PlaneFitting/index.html
次回
固有ベクトルを求めるのだけれど、いかんせんヤコビ法が全く分からないので、その部分はコピペで済ます。
可変長テンプレートとテンプレートテンプレートパラメータ
まず、私はこれがモダンなC++の標準機能なのかは知らない。ただ、VC++2017で以下のようにやって動いた、という話。
テンプレートテンプレートパラメータをパラメータパック
例えば以下はエラー。
template< class Container, class Type > struct MyVector { Container<Type> o; };
int main() { MyVector<std::vector, int> mv; mv.o.push_back(1); }
あるクラスに、コンテナとその内容の型を別々に渡したいときは、以下のようにする。
template< class Type , template<class, class ___ALLCATOR = std::allocator<Type> > class Container > struct MyVector { Container<Type> o; };
int main() { MyVector<int, std::vector> mv; mv.o.push_back(1); }
ここで、template<class,class>は相手がvectorならよいが、unordered_mapなどを入れると互換性がないといわれる。
template< class Type, template<class, class ___ALLCATOR = std::allocator<Type> > class Container > struct MyVector { Container<Type> o; };
int main() { MyVector<int, std::unordered_map> mv; mv.o.push_back(1); }
クラス テンプレート 'std::unordered_map' 用テンプレート パラメーター リストがテンプレート パラメーター 'Container' 用テンプレート パラメーター リストと一致しません。
そこで、テンプレートテンプレートパラメータのほうのパラメータリストをパックする
template< template<class ...Args> class Container, class Type> struct MyVector { Container<Type> o; };
int main() { MyVector<std::vector,int> mv; mv.o.push_back(1); }
結論
テンプレートテンプレートパラメータをパックできるので、コンテナに与える型もパックしてやると、色々なコンテナに対応したテンプレートクラスを作成できる。
template< template<class ...Args> class Container, class ...Type> struct MyVector { Container<Type...> o; };
int main() { MyVector< std::unordered_map, int, float> cm; MyVector< std::vector, float> cv; cm.o[100] = 50.3f; cv.o.push_back(30.0f); std::cout << "map " << cm.o[100] << std::endl; std::cout << "vec " << cv.o[0] << std::endl; int i; std::cin >> i; }
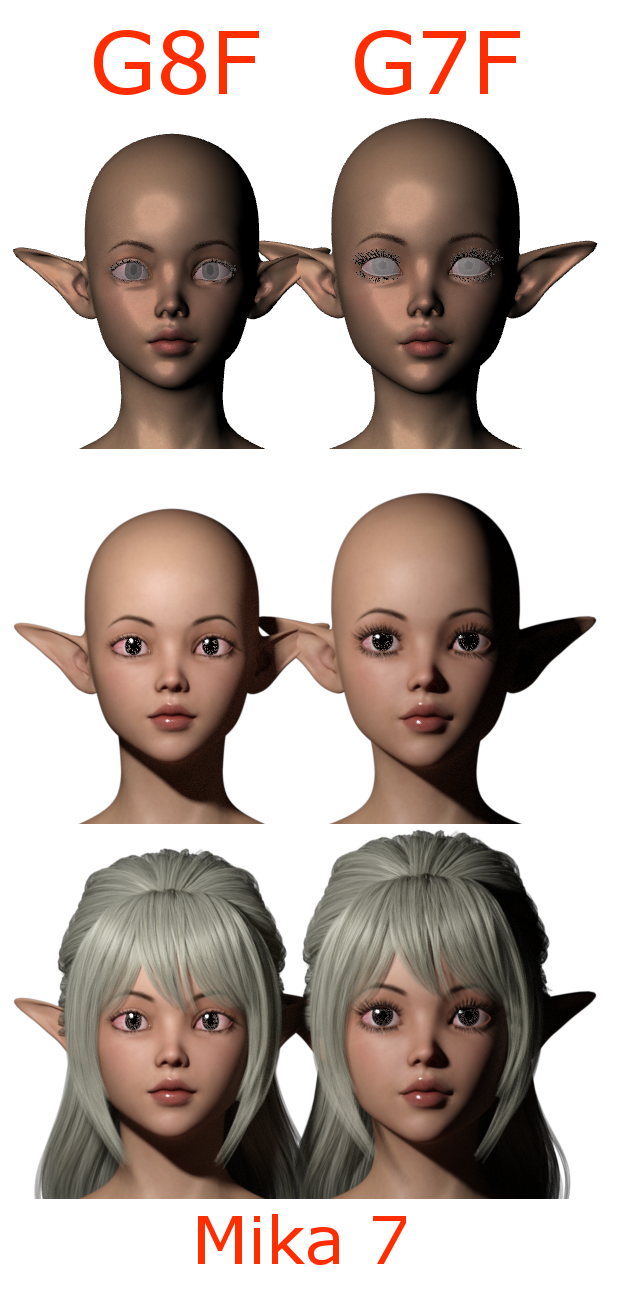
Daz Character Converter G3F to G8F (2) – 変換精度
Mika 7
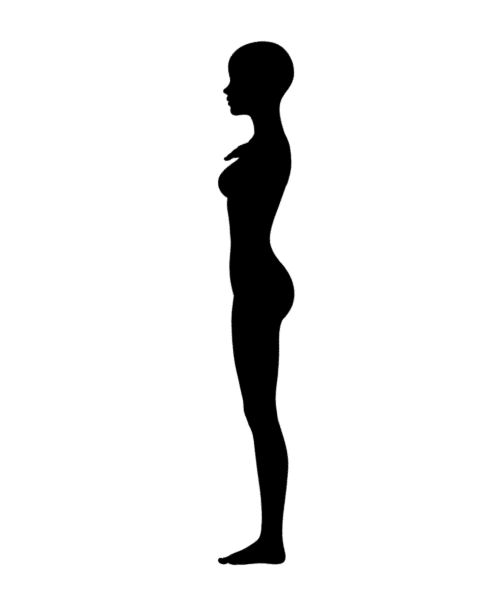
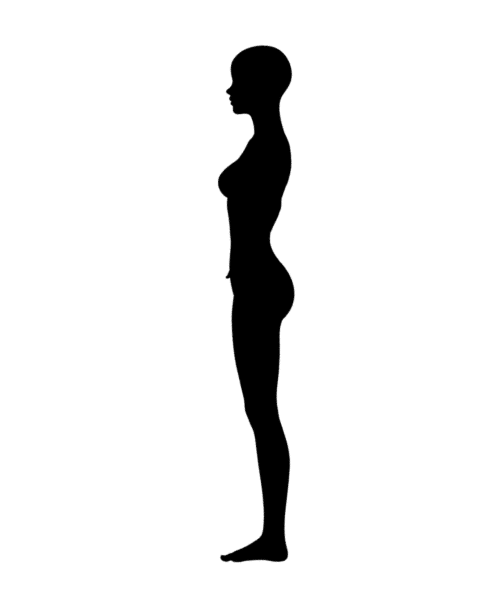
以下はG3F のMika 7を変換した結果。なお全て平行投影。
※あと、G7Fとあるけど実際にはG3Fです。Genesis 3 Femaleです。間違えました
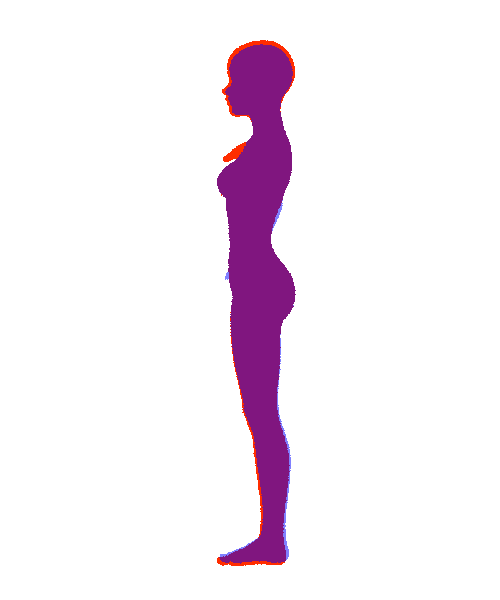
好みの差が出てくるくらいの違いは確認できる。
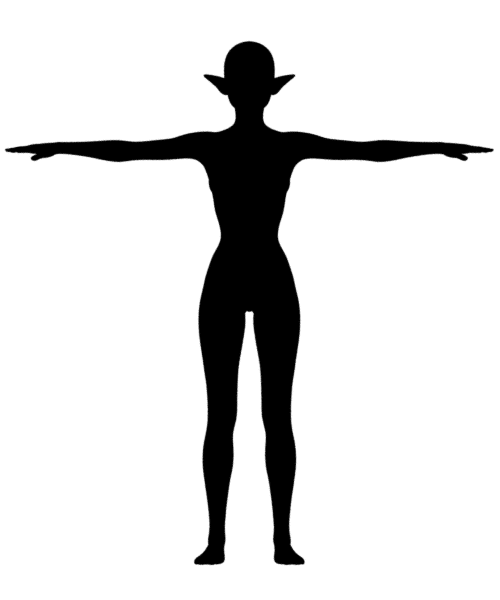
以下、正面から見た場合のシルエット。初期の姿勢が変わっているのは仕方が無い。
横から見た図
Star 2.0
むしろこういう特殊なキャラクタこそちゃんと変換して欲しい気がするのだが、とにかく時間がかかった割に黒い線が入ったりしている。

Daz Character Converter G3F to G8F (1) – 使い方
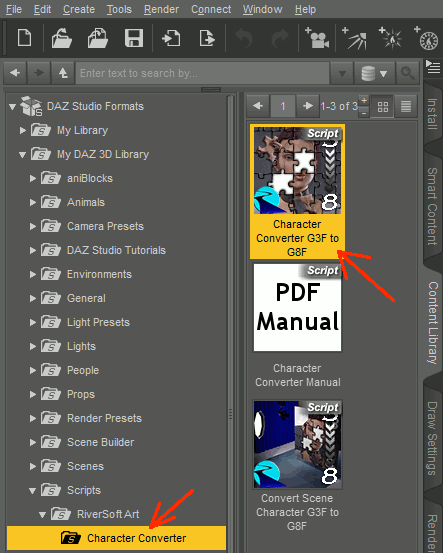
Character Converter G3F to G8Fの使い方について。日本語の情報があまりなかったので。
Character Converter G3F to G8F
https://www.daz3d.com/character-converter-from-genesis-3-female-to-genesis-8-female
1.DAZ Install ManagerからインストールするとCharacter Converterの中に入っている。
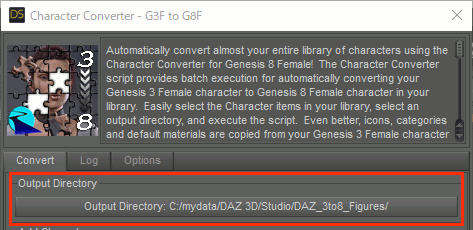
2.Output Directoryに変換後のデータを入れるディレクトリを指定。上書を避けるためにMy Daz 3D Library以外が推奨されている。
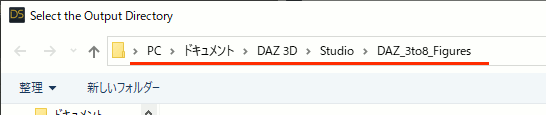
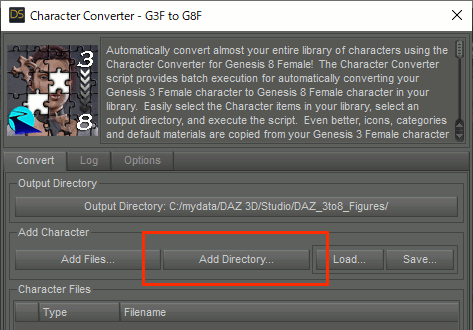
3.Genesis 3 Femaleのキャラクタの入っているディレクトリを指定する。
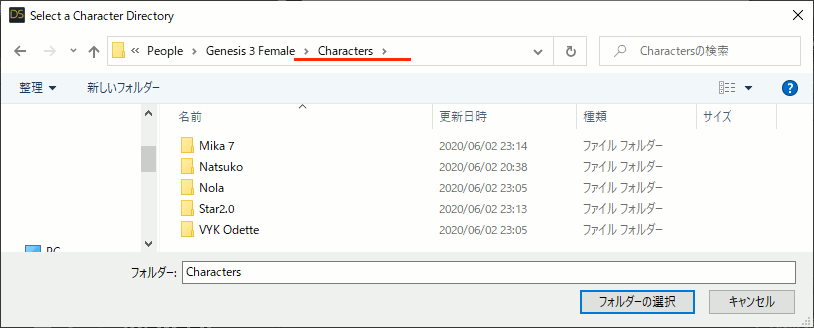
各キャラクタのディレクトリが入っているディレクトリを指定。
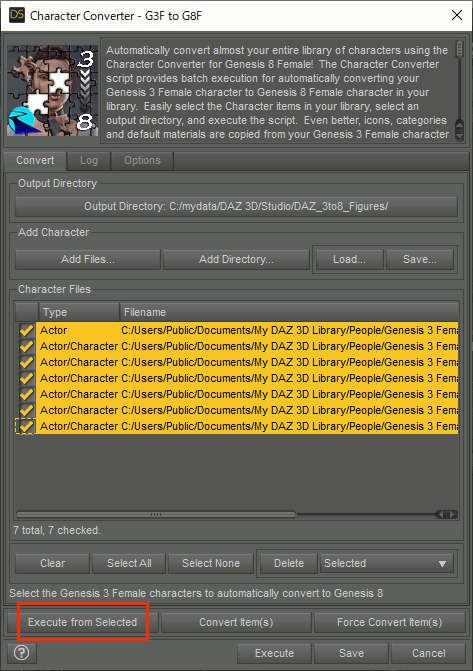
変換したいキャラがチェックされている状態で、Execute from Selectedをクリック。
ものによってものすごく時間がかかることがある。Star 2.0とか、50分かかった。そのうえ失敗する。
変換精度の話
次回へ続く。
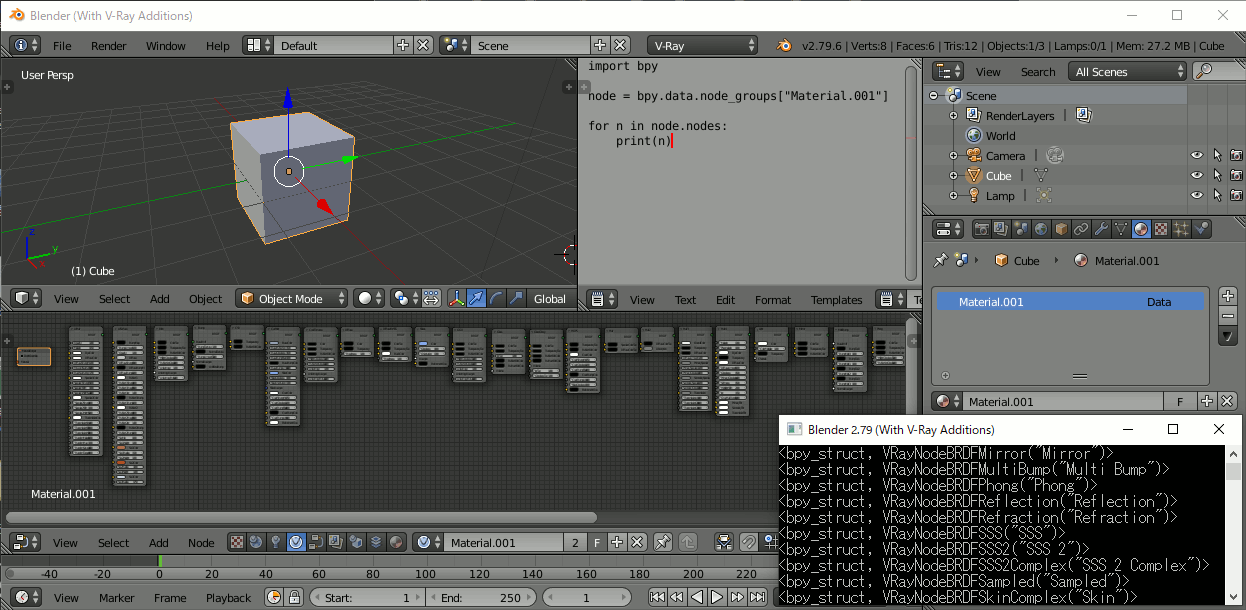
Blender PythonからVRayのノードを追加する
ノードを追加
import bpy node = bpy.data.node_groups["Material.001"] node.nodes.new(type='VRayNodeMetaStandardMaterial')
Material
| Material Output | VRayNodeOutputMaterial |
| Standard Material | VRayNodeMetaStandardMaterial |
| Two Sided | VRayNodeMtl2Sided |
| Angle Blend | VRayNodeMtlAngleBlend |
| Diffuse | VRayNodeMtlDiffuse |
| Double Sided | VRayNodeMtlDoubleSided |
| GLSL | VRayNodeMtlGLSL |
| Material ID | VRayNodeMtlMaterialID |
| Object Bounding | VRayNodeMtlObjBBox |
| Override | VRayNodeMtlOverride |
| Render Stats | VRayNodeMtlRenderStats |
| Rounded Corners | VRayNodeMtlRoundEdges |
| Single | VRayNodeMtlSingleBRDF |
| Streak Fade | VRayNodeMtlStreakFade |
| Toon | VRayNodeMtlToon |
| VRmat | VRayNodeMtlVRmat |
| Wrapper | VRayNodeMtlWrapper |
| Multi ID | VRayNodeMtlMulti |
| OSL Material | VRayNodeMtlOSL |
BRDF
| AlHair | VRayNodeBRDFAlHair |
| Material Output | VRayNodeOutputMaterial |
| AlSurface | VRayNodeBRDFAlSurface |
| Blinn | VRayNodeBRDFBlinn |
| Bump | VRayNodeBRDFBump |
| CSV | VRayNodeBRDFCSV |
| Car Paint | VRayNodeBRDFCarPaint |
| Cook Torrance | VRayNodeBRDFCookTorrance |
| Diffuse | VRayNodeBRDFDiffuse |
| Diffuse For SSS | VRayNodeBRDFDiffuse_forSSS |
| Flakes | VRayNodeBRDFFlakes |
| GGX | VRayNodeBRDFGGX |
| Glass | VRayNodeBRDFGlass |
| Glass Glossy | VRayNodeBRDFGlassGlossy |
| HOPS | VRayNodeBRDFHOPS |
| Hair | VRayNodeBRDFHair |
| Hair 2 | VRayNodeBRDFHair2 |
| Hair 3 | VRayNodeBRDFHair3 |
| Hair 4 | VRayNodeBRDFHair4 |
| Light | VRayNodeBRDFLight |
| Mirror | VRayNodeBRDFMirror |
| Multi Bump | VRayNodeBRDFMultiBump |
| Phong | VRayNodeBRDFPhong |
| Reflection | VRayNodeBRDFReflection |
| Refraction | VRayNodeBRDFRefraction |
| SSS | VRayNodeBRDFSSS |
| SSS 2 | VRayNodeBRDFSSS2 |
| SSS 2 Complex | VRayNodeBRDFSSS2Complex |
| Sampled | VRayNodeBRDFSampled |
| Skin | VRayNodeBRDFSkinComplex |
| Stochastic Flakes | VRayNodeBRDFStochasticFlakes |
| VRayMtl | VRayNodeBRDFVRayMtl |
| Ward | VRayNodeBRDFWard |
| Point Particle | VRayNodeBSDFPointParticle |
| Layered | VRayNodeBRDFLayered |
Textures
| Image File | VRayNodeMetaImageTexture |
| Color | VRayNodeTexAColor |
| Bercon Distortion | VRayNodeTexBerconDistortion |
| Bercon Grad | VRayNodeTexBerconGrad |
| Bercon Noise | VRayNodeTexBerconNoise |
| Bercon Tile | VRayNodeTexBerconTile |
| Bercon Wood | VRayNodeTexBerconWood |
| Bifrost VV Mix | VRayNodeTexBifrostVVMix |
| Bulge | VRayNodeTexBulge |
| Cellular | VRayNodeTexCellular |
| Checker | VRayNodeTexChecker |
| Cloth | VRayNodeTexCloth |
| Curvature | VRayNodeTexCurvature |
| Dirt | VRayNodeTexDirt |
| Distance | VRayNodeTexDistance |
| Distance Between | VRayNodeTexDistanceBetween |
| Edges | VRayNodeTexEdges |
| Falloff | VRayNodeTexFalloff |
| Float | VRayNodeTexFloat |
| Fresnel | VRayNodeTexFresnel |
| Gradient Ramp | VRayNodeTexGradRamp |
| Gradient | VRayNodeTexGradient |
| Granite | VRayNodeTexGranite |
| Grid | VRayNodeTexGrid |
| HSV To RGB | VRayNodeTexHSVToRGB |
| Hair Sampler | VRayNodeTexHairSampler |
| ICC | VRayNodeTexICC |
| Int | VRayNodeTexInt |
| Leather | VRayNodeTexLeather |
| Luminance | VRayNodeTexLuminance |
| Lut | VRayNodeTexLut |
| Marble | VRayNodeTexMarble |
| Mesh Map Channel | VRayNodeTexMeshVertexColorChannel |
| Motion Occlusion | VRayNodeTexMotionOcclusion |
| Multi Float | VRayNodeTexMultiFloat |
| Noise | VRayNodeTexNoise |
| Noise (3ds Max) | VRayNodeTexNoiseMax |
| Noise (Maya) | VRayNodeTexNoiseMaya |
| OCIO | VRayNodeTexOCIO |
| OpenVDB | VRayNodeTexOpenVDB |
| Ptex | VRayNodeTexPtex |
| Ray Switch | VRayNodeTexRaySwitch |
| Rock | VRayNodeTexRock |
| Sampler | VRayNodeTexSampler |
| Noise (Simplex) | VRayNodeTexSimplexNoise |
| Sky | VRayNodeTexSky |
| Smoke | VRayNodeTexSmoke |
| Snow | VRayNodeTexSnow |
| Soft Box | VRayNodeTexSoftbox |
| Speckle | VRayNodeTexSpeckle |
| Splat | VRayNodeTexSplat |
| Stencil | VRayNodeTexStencil |
| Stucco | VRayNodeTexStucco |
| Surface Luminance | VRayNodeTexSurfaceLuminance |
| Swirl | VRayNodeTexSwirl |
| Temperature | VRayNodeTexTemperature |
| Thickness | VRayNodeTexThickness |
| Tiles | VRayNodeTexTiles |
| TriPlanar | VRayNodeTexTriPlanar |
| UVW | VRayNodeTexUVW |
| User Color | VRayNodeTexUserColor |
| User Scalar | VRayNodeTexUserScalar |
| Voxel Data | VRayNodeTexVoxelData |
| Water | VRayNodeTexWater |
| Wood | VRayNodeTexWood |
| Layered | VRayNodeTexLayered |
| Multi ID | VRayNodeTexMulti |
| OSL Texture | VRayNodeTexOSL |
確認方法
ノードを手動で追加し、以下のスクリプトで表示させている。
import bpy node = bpy.data.node_groups["Material.001"] for n in node.nodes: print(n)