月火水木金土日
Blender のスクリプトで拡散反射のベクトルを可視化する
diffuse反射はPhongの反射モデルの一部で、ADSのDの部分。やってることは面法線と光のベクトルの内積を光の強さとしているといっていい(だろう。たぶん。)。ベクトルの内積は、その角度が小さくなると大きくなり、角度が大きくなると小さくなる。
ただこの現象を文章で説明されてもぱっと思い浮かばないので可視化する
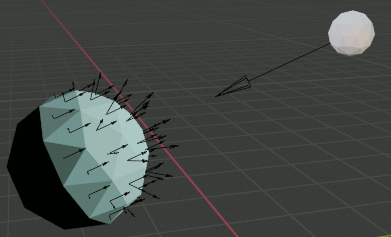
これは面ごとにEmissionで色を付けている。
角度が小さいほど明るい色になっている。
コード
実行すると、光源の位置に該当する球と、対象物に対する球、光源から物体の方向のArrowと各面の面法線、その位置からの光源へのベクトルが生成される。
import bpy import mathutils import numpy import math # @brief オブジェクトを指定座標へ向けるための回転軸と回転角を計算する # @param [in] オブジェクト # @param [in] 向ける方向(座標) # @return 回転軸,回転角(ラジアン) def calc_lookat_param(obj,lookat): # オブジェクトのローカルのZ軸のベクトルを取得 mat = obj.matrix_world localZ = mathutils.Vector((mat[0][2],mat[1][2],mat[2][2])) #print(localZ) va = mathutils.Vector(lookat) - obj.location vb = mathutils.Vector(localZ) va.normalize() vb.normalize() # 外積 axis = mathutils.Vector.cross(va,vb) axis.normalize() # 内積 th = mathutils.Vector.dot(va,vb) # 角度算出 rad = -math.acos( numpy.clip(th,-1.0,1.0) ) return axis , rad # @brief 任意軸回転 # @param [in,out] obj 回転するオブジェクト # @param [in] axis 回転軸 # @param [in] radian 回転角をラジアンで指定 # @return なし # @sa https://www.study.suzulang.com/bpy-calculation/bpy-arbitrary-axis-rotation def rotate_object(obj,axis,radian): rot_mat= mathutils.Matrix.Rotation( radian, 4, axis ) # decompose world_matrix's components, and from them assemble 4x4 matrices orig_loc, orig_rot, orig_scale = obj.matrix_world.decompose() # orig_loc_mat = mathutils.Matrix.Translation(orig_loc) orig_rot_mat = orig_rot.to_matrix().to_4x4() orig_scale_mat = (mathutils.Matrix.Scale(orig_scale[0],4,(1,0,0)) @ mathutils.Matrix.Scale(orig_scale[1],4,(0,1,0)) @ mathutils.Matrix.Scale(orig_scale[2],4,(0,0,1))) # # assemble the new matrix obj.matrix_world = orig_loc_mat @ rot_mat @ orig_rot_mat @ orig_scale_mat def fix_arrow_dir(aobj,_to): # 方向を一致させるためのパラメータ取得 axis , rad = calc_lookat_param(aobj,_to) # 回転 rotate_object(aobj,axis,rad) def fix_arrow_fromto(aobj,_from,_to): aobj.location=_from fix_arrow_dir(aobj,_to) aobj.location=_from # _from → _to の距離を計算 objlen = ( _from - _to ).length # 矢印の長さ==スケール aobj.scale[0] = objlen aobj.scale[1] = objlen aobj.scale[2] = objlen # @brief オブジェクトの指定したpolygonの法線を取得 # @param [in] obj オブジェクト # @param [in] polyIndex ポリゴン番号 # @return 法線(グローバル座標系) def get_polygon_normal(obj,polyIndex): # オブジェクトの行列を取得 local44 = obj.matrix_world ll_inv = local44.inverted() ll_inv_norm = ll_inv.transposed().to_3x3() vn = obj.data.polygons[polyIndex].normal return ll_inv_norm @ vn # @brief _fromから_toを指すEmptyArrowを作成 # @param [in] 矢印の根元の座標 # @param [in] 矢印の先端の座標 # @return 作成したオブジェクト def make_empty_arrow(_from,_to): # 新しいEmpty ObjectのArrowを作成 bpy.ops.object.empty_add(type="SINGLE_ARROW",location=_from) aobj = bpy.context.object fix_arrow_fromto(aobj,_from,_to) return aobj ##################################################### ##################################################### # 矢印一個のオブジェクト。 class Arrow: _from = mathutils.Vector((0,0,0)) _to = mathutils.Vector((0,0,0)) _object = None def __init__(self,name): exist = bpy.context.scene.objects.get(name) if exist is None: bpy.ops.object.empty_add(type="SINGLE_ARROW",location=(0,0,0)) self._object = bpy.context.object self._object.name = name else: self._object = exist #obj = bpy.context.active_object # オブジェクトのローカルのZ軸のベクトルを取得 mat = self._object.matrix_world localZ = mathutils.Vector((mat[0][2],mat[1][2],mat[2][2])) _to = localZ + self._object.location def get_direction(self,normalize): v = _to - _from if normalize == True: v.normalize return v def get_arrow(self,normalize): pos = get_direction(normalize) __to = _from+pos return _from , __to def set_arrow_from_to(self,_from,_to): fix_arrow_fromto(self._object,_from,_to) self._from = _from self._to = _to def get_vnorm(self): v = self._to - self._from v.normalize() return v def set_length(self,length): self._object.scale[0]=length self._object.scale[1]=length self._object.scale[2]=length ##################################################### ##################################################### class TheLight: light = None arrowToTarget = None def __init__(self,_pos): self.light = bpy.context.scene.objects.get('TheLight') if self.light is None: # 新しいEmpty ObjectのArrowを作成 bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_ico_sphere_add(location=_pos,radius =0.3) self.light = bpy.context.object self.light.name = 'TheLight' def update(self,target): self.arrowToTarget = Arrow('LightToTarget') self.arrowToTarget.set_arrow_from_to( self.light.location, target.target.location ) self.arrowToTarget.set_length(2) def get_location(self): return self.light.location ############################################### ############################################### # 各面ごとに、面法線と光源の方向を示すための矢印を定義する class Plane: normal = None material_name = None plane_index = 0 toLightArrow = None normalArrow_name = "" Ld = 0.0 def __init__(self,obj,pindex): self.normalArrow_name = 'PlaneNormal-' + str(pindex) self.normal = Arrow(self.normalArrow_name) mat_name = "mat" + str(pindex) self.material_name = mat_name mat = bpy.data.materials.get(mat_name) # マテリアルがなければ作成する if mat is None: mat = bpy.data.materials.new(mat_name) # マテリアルをオブジェクトに設定する obj.data.materials.append(mat) mat.use_nodes = True self.material_name = mat_name self.plane_index = pindex obj.data.polygons[pindex].material_index = pindex def update(self,origin,dir,light): self.normal.set_arrow_from_to( origin, origin+dir) # direction ldir = light.get_location()-origin ldir.normalize() # 面に光が当たったときの明るさを計算 # 面法線とライト方向へのベクトルの内積 Kd = 1.0 I = 1.0 self.Ld = Kd*I*numpy.dot( self.normal.get_vnorm(), -light.arrowToTarget.get_vnorm() ) if self.Ld < 0: self.Ld = 0 else: # arrow-to-line lightarrowname = self.normalArrow_name +'-tolight' self.toLightArrow = Arrow(lightarrowname) tolight = origin-light.arrowToTarget.get_vnorm() self.toLightArrow.set_arrow_from_to(origin,tolight) self.toLightArrow.set_length(0.3) self.normal.set_length(self.Ld*0.5) def set_material(self,polyindex): material =bpy.data.materials.get(self.material_name) material_output = material.node_tree.nodes.get('Material Output') #emission = new_mat.node_tree.nodes.get('ShaderNodeEmission') emission = material.node_tree.nodes.get('Emission') if emission is None: print( 'Emission:',emission ) emission = material.node_tree.nodes.new('ShaderNodeEmission') material.node_tree.links.new(material_output.inputs[0], emission.outputs[0]) ntree = material.node_tree#.new('ShaderNodeEmission') print( self.Ld ) material.node_tree.nodes["Emission"].inputs["Color"].default_value[0] = 0.5 * self.Ld material.node_tree.nodes["Emission"].inputs["Color"].default_value[1] = 0.9 * self.Ld material.node_tree.nodes["Emission"].inputs["Color"].default_value[2] = 0.8 * self.Ld ############################################### ############################################### class TheTarget: target = None # 光が当たるオブジェクト planes = [] # 各面の設定を面ごとに入れる def create_planes(self): mesh = self.target.data k = len(mesh.polygons) # 全てのポリゴンに対するループ for i in range(0,k): self.planes.append( Plane(self.target,i) ) def update(self,light): mesh = self.target.data vcoords = mesh.vertices # オブジェクトの行列を取得 local44 = self.target.matrix_world k = len(self.planes) for i in range(0,k): n = get_polygon_normal(self.target,i) ## origin of polygon grav = mathutils.Vector((0,0,0)) for v in mesh.polygons[i].vertices: # v はpolyの各頂点のID grav += vcoords[ v ].co # 頂点座標の合計を頂点数で割る grav /= len(mesh.polygons[i].vertices) origin = local44 @ grav self.planes[i].update( origin, n, light) self.planes[i].set_material(self.target) def __init__(self,_pos): self.target = bpy.context.scene.objects.get('TargetMesh') if self.target is None: #bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_plane_add(location=_pos) bpy.ops.mesh.primitive_ico_sphere_add( location=_pos, radius =1.0 ) self.target = bpy.context.object self.target.name = 'TargetMesh' self.create_planes() ############################################### ############################################### ############################################### def my_function(): target = TheTarget( (-1,2,1) ) thelight = TheLight( (1,5,5) ) thelight.update(target) target.update(thelight) ############################################### ############################################### ############################################### my_function()
