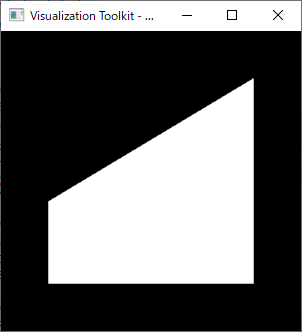
vtk 9.0 で表示(4) ポリゴンを表示
//VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> #include <vtkPoints.h> // vtkPoints用 #include <vtkPolygon.h> // vtkPolygon用 #include <vtkPolyData.h> //vtkPolyData用 #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonCore-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingCore-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkInteractionStyle-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkFiltersSources-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonExecutionModel-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonDataModel-9.0.lib ") // ポリゴン用 //必須 #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingOpenGL2-9.0.lib") //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle); int main(int /*argc*/, char ** /*argv*/) { ////////////////////////////////////// vtkSmartPointer < vtkPoints > points = vtkSmartPointer < vtkPoints >::New(); points->InsertNextPoint(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); points->InsertNextPoint(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); points->InsertNextPoint(1.0, 1.0, 0.0); points->InsertNextPoint(0.0, 0.4, 0.0); ////////////////////////////////////// vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolygon> polygon = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolygon>::New(); polygon->GetPointIds()->SetNumberOfIds(4);//4頂点 polygon->GetPointIds()->SetId(0, 0); polygon->GetPointIds()->SetId(1, 1); polygon->GetPointIds()->SetId(2, 2); polygon->GetPointIds()->SetId(3, 3); ////////////////////////////////////// vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> polylist = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); polylist->InsertNextCell(polygon); ////////////////////////////////////// vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polydata = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polydata->SetPoints(points); polydata->SetPolys(polylist); ////////////////////////////////////// // Create a mapper and actor vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); //mapper->SetInputConnection(cylinderSource->GetOutputPort()); mapper->SetInputData(polydata); vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(actor); renderer->ResetCamera(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); //vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); renderWindow->SetInteractor(interactor); renderWindow->Render(); interactor->Start(); //イベントループへ入る return 0; }
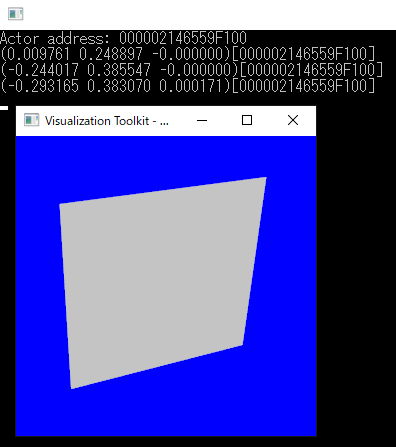
vtk 9.0 で表示(3) マウスピック
マウスクリックされたオブジェクトを特定する。
参考: https://vtk.org/Wiki/VTK/Examples/Cxx/Interaction/Picking
ソースコード
//VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> #include <vtkInteractorStyleImage.h> #include <vtkPropPicker.h>// ピックに必要 #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #include <vtkPlaneSource.h> #ifdef _DEBUG #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonCore-9.0d.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingCore-9.0d.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkInteractionStyle-9.0d.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkFiltersSources-9.0d.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonExecutionModel-9.0d.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingOpenGL2-9.0d.lib") #else #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonCore-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingCore-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkInteractionStyle-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkFiltersSources-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonExecutionModel-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingOpenGL2-9.0.lib") #endif //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle); ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 参考:
// https://vtk.org/Wiki/VTK/Examples/Cxx/Interaction/Picking
// Handle mouse events class MouseInteractorStyle2 : public vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera { public: static MouseInteractorStyle2* New(); vtkTypeMacro(MouseInteractorStyle2, vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera); virtual void OnLeftButtonDown() { int* clickPos = this->GetInteractor()->GetEventPosition(); // ピック下オブジェクトを取得 auto picker = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPropPicker>::New(); picker->Pick(clickPos[0], clickPos[1], 0, this->GetDefaultRenderer()); // オブジェクトがクリックされていたら位置とアドレスを出力 if (picker->GetActor() != nullptr) { double* pos = picker->GetPickPosition(); printf("(%lf %lf %lf)[%p]\n", pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], picker->GetActor()); } // Forward events vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera::OnLeftButtonDown(); } private: };
vtkStandardNewMacro(MouseInteractorStyle2); // Execute application. int main(int, char *[]) { auto planeSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPlaneSource>::New(); planeSource->Update(); // Create a polydata object vtkPolyData* polydata = planeSource->GetOutput(); // Create a mapper auto mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputData(polydata); // Create an actor auto actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); std::cout << "Actor address: " << actor << std::endl; // A renderer and render window auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); auto renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); // An interactor auto renderWindowInteractor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); renderWindowInteractor->SetRenderWindow(renderWindow); // Set the custom stype to use for interaction. auto style = vtkSmartPointer<MouseInteractorStyle2>::New(); style->SetDefaultRenderer(renderer); renderWindowInteractor->SetInteractorStyle(style); // Add the actors to the scene renderer->AddActor(actor); renderer->SetBackground(0, 0, 1); // Render and interact renderWindow->Render(); renderWindowInteractor->Initialize(); renderWindowInteractor->Start(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
vtk 9.0 で表示(2) Cylinder表示
//VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> //円筒とその表示に必要 #include <vtkCylinderSource.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonCore-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingCore-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkInteractionStyle-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkFiltersSources-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonExecutionModel-9.0.lib") //必須 #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingOpenGL2-9.0.lib") //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle); int main(int /*argc*/, char ** /*argv*/) { ////////////////////////////////////// // Create a vtkCylinderSource vtkSmartPointer<vtkCylinderSource> cylinderSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCylinderSource>::New(); cylinderSource->SetCenter(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); cylinderSource->SetRadius(5.0); cylinderSource->SetHeight(7.0); cylinderSource->SetResolution(100); ////////////////////////////////////// // Create a mapper and actor vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputConnection(cylinderSource->GetOutputPort()); vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(actor); renderer->ResetCamera(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); renderWindow->SetInteractor(interactor); renderWindow->Render(); interactor->Start(); //イベントループへ入る return 0; }
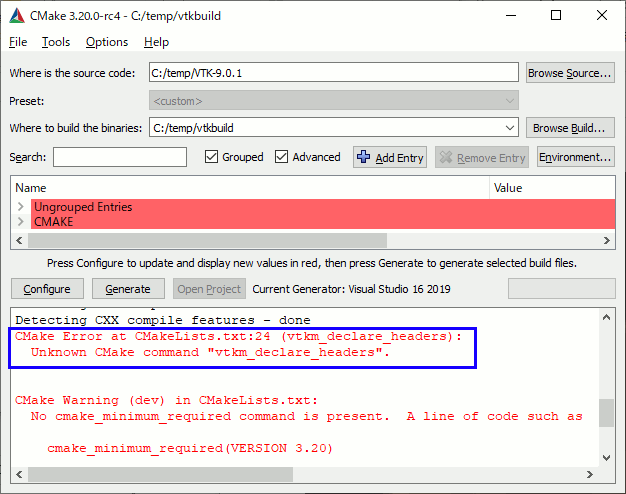
VTKをCMakeしたらUnknown CMake command “vtkm_declare_headers”
投稿順を間違えた。なお、以下のディレクトリ設定さえ間違えなければwarning一つでないほど綺麗にCMakeできる。
VTKをCMakeしようとして失敗
VTK-9.0.1をCMakeしようとしたら以下のようなエラーが出た。
Unknown CMake command "vtkm_declare_headers".
原因は以下のディレクトリをWhere is the source codeに指定したことによる。
解凍したフォルダの一番上の階層にあるCMakeListではなく、その一つ下のVTK-9.0.1ディレクトリを指定しなければならない。
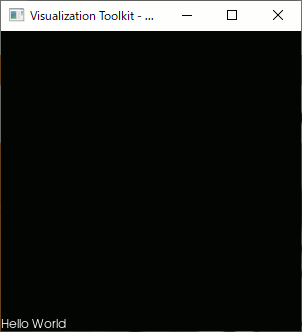
vtk 9.0 で表示(1) Hello World
// VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkTextActor.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonCore-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingCore-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkInteractionStyle-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkFiltersSources-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkCommonExecutionModel-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingOpenGL2-9.0.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"vtkRenderingFreeType-9.0.lib") VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingFreeType); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle); int main(int /*argc*/, char ** /*argv*/) { auto textActor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkTextActor>::New(); textActor->SetInput("Hello World"); auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(textActor); renderer->ResetCamera(); auto interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); auto renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); renderWindow->SetInteractor(interactor); renderWindow->Render(); interactor->Start(); return 0; }
PythonでOpen3dを使う(PointCloud作成)。あとPythonの配列もちょっと。
PointCloudのサンプルは沢山あるのだがランダム頂点を表示するような物ばかりで、任意の頂点を追加する方法がわからず一月近く調べていた。Pythonは普段使わないのでそういうことになったのだが以下がとりあえずの答。
import open3d import numpy # 点群型データ作成 pcd = open3d.geometry.PointCloud() # 座標設定 pcd.points.append([0.0,0.0,0.0]) pcd.points.append([1.0,1.0,1.0]) pcd.points.append([1.0,2.0,0.0]) # 色設定 pcd.colors.append([1.0,0.0,0.0]); pcd.colors.append([0.0,1.0,0.0]); pcd.colors.append([0.0,0.0,1.0]); # 法線設定 pcd.normals.append([1.0,0.0,0.0]); pcd.normals.append([0.0,1.0,0.0]); pcd.normals.append([0.0,0.0,1.0]); open3d.visualization.draw_geometries( [pcd], width=400, height=400, point_show_normal = True )
調べた手順
一応、私のように必要に迫られてPythonやってる人のためにどうやって調べたかを書いておくと、以下のプログラムを書いて走らせる。
import open3d pcd = open3d.io.read_point_cloud("bun000.ply") print( type ( pcd.points ) ) print( type ( pcd.points[0] ) )
すると以下のような結果を得られる。
<class 'open3d.cpu.pybind.utility.Vector3dVector'>
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>これでどうやらVector3dVectorという型が頂点リストになっているらしいので以下を検索する。
http://www.open3d.org/docs/release/python_api/open3d.utility.Vector3dVector.html
append(self: open3d.cpu.pybind.utility.Vector3dVector, x: numpy.ndarray[float64[3, 1]])
するとappendぽい関数がある。この読み方、
引数名:データ型 , 引き数名:データ型 , ...
となっているらしい。で、pythonのselfはC++におけるthisなので無視して、与えるのがxでその型がnumpy.ndarrayだと言うのでndarrayについて調べる。
受け手側がndarrayなので、ndarrayには普通の配列[x,y,z]などをそのまま入れられるらしい?ので、最初のコードになる。
AnacondaでPythonを使う(目的 Open3d)
前置き
普段はC++からOpen3d使っているのだがひょんなことからPythonから使わざるを得なくなった。色々詰まったので流れをメモしておきたい。
なおAnacondaを使う。初めて使うので設定からやる。Anacondaは開発環境を切り替えて使うためのソフトである。つまり、
・このスクリプトはnumpy 0.5+open3d 0.3以外では動かない。
・別のはnumpy 1.19+open3d 1.12以外では動かない。
・でもどちらも頻繁に使う
みたいな状況で簡単に環境を切り替えるのに便利だという事(らしい)。
環境
Windows 10
Anaconda
インストール
https://www.anaconda.com/products/individualから、一番下の方にある「Anaconda Installers」の64-Bit Graphical Installer (457 MB)あたりをクリックしてダウンロード・インストールする
参考:https://www.python.jp/install/anaconda/windows/install.html
仮想環境構築
まず仮想環境を作り、その環境に必要なライブラリをインストールする。
AnacondaをインストールするとAnaconda PowerShell Prompt(Anaconda 3)というのがスタートメニューに追加されるので起動する。
あるいはAnaconda Promptの方でもいい。lsとかが使えなくてやや面倒だが、activateを何もしなくても使えるメリットがある。
1.環境作成
conda create -n 環境名
例(環境名devo3dを作成):
conda create -n devo3d
環境が作成できたか確認:
conda info -e
作成した環境(devo3d)へ移行:
Anaconda Promptを使っているなら以下のactivateで環境を移行できるが、PowerShellを使っている場合はactivateがそのままでは動かないのでもう一手間必要になる
activate devo3d
※PowerShellを使っている場合はactivateの前に以下を実行。ただし何をやっているのか著者は理解していないのでちゃんと調べてからやった方が良い。
conda install -n root -c pscondaenvs pscondaenvs
参考:
https://qiita.com/nabehide/items/097553ccd51543ee31fb
(2022年12月 情報更新記事)
以下の内容は古い上にcondaとpipを併用する悪い方法なのでインストールは別記事を参照
condaでopen3dをインストールする(改)
以下、古い記事
2.Open3d インストール
open3dのPythonモジュールをインストールする。
conda install -c open3d-admin open3d
参考:http://www.open3d.org/docs/release/getting_started.html
3.バージョン確認
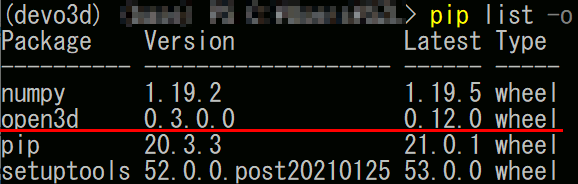
インストールされたバージョンによってはサンプルが全く動かないので、バージョンを確認する。pip list で-oオプションを付けると、バージョンアップの必要なライブラリの一覧だけを見られる。
pip list -o
明らかにバージョンが低い場合はアップデートする
pip install -U open3d
参考:https://qiita.com/HyunwookPark/items/242a8ceea656416b6da8
4.稼働確認
importだけ実行してみてエラーが出なければ(無言なら)成功している。
python -c "import open3d"
別ファイルのBlender Pythonスクリプトをimportして使い回す
一つのファイルに全ての関数やクラスを入れてしまうとあまりに見通しが悪くなるのでファイルを分けたい。
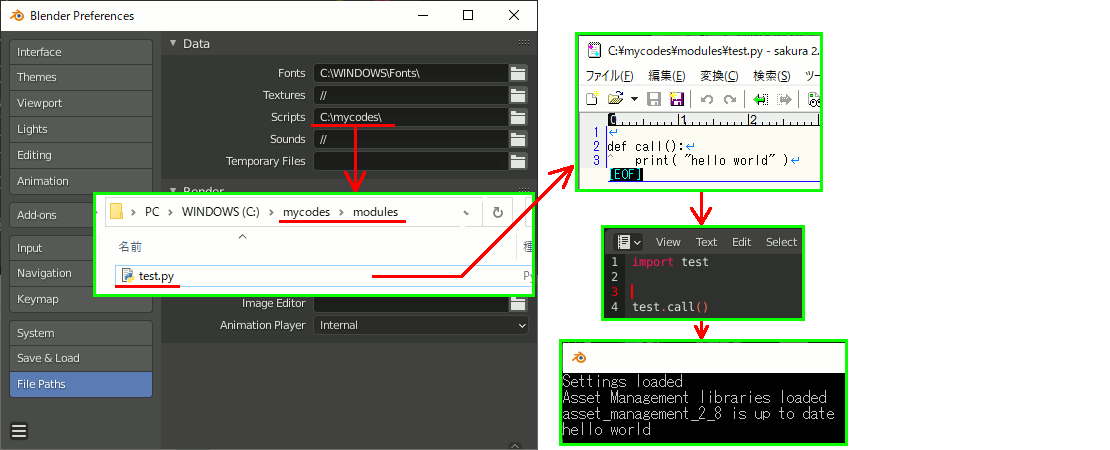
自分のスクリプトを入れるディレクトリの設定
Edit → Preference → File Paths → Data → Scripts にディレクトリを設定する。注意点はディレクトリ名が\modules , \addons ... でなければいけない。
ここではimportしたいので、\modulesディレクトリを作り、そのディレクトリの親ディレクトリを指定する。
\modules\ ディレクトリの中のファイル名(拡張子除)がモジュール名になり、これをimportすれば中の関数を呼び出すことができる。
外部にモジュールを置き、blenderスクリプトから呼び出す
import test test.call()
更新できるようにする(メインのファイル)
このままだと、上記test.pyを更新する度にBlenderを再起動しなければならない。実行する度に再読み込みを行うには再読み込み命令をスクリプトに書く必要がある。importlib.reload( モジュール名 )を呼び出す。
import test ############################# ## リロード import importlib importlib.reload(test) #モジュール名を指定 ## ############################# test.call()
更新できるようにする(関連するファイル)
上記test.pyがさらに内部で別のモジュールをimportしていた場合、それらは更新されない。これを更新するためには、testモジュール内部で使用する外部モジュールをimportlib.reloadする必要がある。
modules/test.py
import neighbour # 別ファイル neighbour.py import importlib # reload用 # blenderから呼ばれる def call(): importlib.reload(neighbour) # neighbour.pyの再ロード neighbour.hello()
modules/neighbour.py
def hello(): print("neighbour.py is updated")
freeglutのコールバック関数でメンバ変数を呼び出す
freeglutをカプセル化できる。glutSetWindowDataにthisポインタを渡し、コールバック関数内でglutGetWindowDataでthisを取得しそのメンバを呼び出す。
#include <Windows.h> #include <gl/GL.h> #include <gl/freeglut.h> #include <cstdio> #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"freeglut.lib") class CfreeglutWindow {
// コールバック関数から呼ばれるメンバ関数群 ////////////////////////// static void mouse_callback(int button, int state, int x, int y) { CfreeglutWindow* pwin = (CfreeglutWindow*)glutGetWindowData(); pwin->mouse(button, state, x, y); } static void motion_callback(int x, int y) { CfreeglutWindow* pwin = (CfreeglutWindow*)glutGetWindowData(); pwin->motion(x, y); } static void mouseWheel_callback(int button, int dir, int x, int y) { CfreeglutWindow* pwin = (CfreeglutWindow*)glutGetWindowData(); pwin->mouse(button, dir, x, y); } static void disp_callback() { CfreeglutWindow* pwin = (CfreeglutWindow*)glutGetWindowData(); pwin->disp(); } static void key_callback(unsigned char key, int x, int y) { CfreeglutWindow* pwin = (CfreeglutWindow*)glutGetWindowData(); pwin->key(key,x,y); }
//普通のメンバ変数 int width; int height; float xpos,ypos; public: CfreeglutWindow() { xpos = 0.0; ypos = 0.0; } void init(int argc, char** argv, const char* title) { glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitWindowPosition(100, 50); glutInitWindowSize(400, 300); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGBA); width = 400; height = 300; glutCreateWindow(title); glutDisplayFunc(disp_callback); glutMouseFunc(mouse_callback); glutMotionFunc(motion_callback); glutMouseWheelFunc(mouseWheel_callback); glutKeyboardFunc(key_callback); glutSetWindowData(this); } void loop() { glutMainLoop(); }
// 描画 void disp(void) { glClearColor(0, 0, 0, 0); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glViewport(0, 0, width, height); float v = 0.7; glPushMatrix(); glLoadIdentity(); glTranslatef(xpos, ypos, 0.0); glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES); glColor3d(1, 1, 1); glVertex2f(-v, -v); glColor3d(0, 1, 1); glVertex2f( v, -v); glColor3d(0, 0, 1); glVertex2f( v, v); glEnd(); glPopMatrix(); glFlush(); glutSwapBuffers(); }
// 普通キーの入力 void key(unsigned char key, int x, int y) { if (key == 'a') { xpos -= 0.2; } if (key == 's') { xpos += 0.2; } glutPostRedisplay(); }
// クリック void mouse(int button, int state, int x, int y) { if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) { ypos += 0.2; } if (button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) { ypos -= 0.2; } glutPostRedisplay(); }
//ドラッグ void motion(int x, int y){}
// ホイール void mouseWheel(int button, int dir, int x, int y) { if (dir > 0){} else{} return; }
}; int main(int argc, char** argv) { CfreeglutWindow cfw; cfw.init(argc, argv, "freeglut"); cfw.loop(); return 0; }
GLSLを試す (9) Geometry Shader(5)- 三角形一枚から三角形二枚
前回のプログラム
https://suzulang.com/glsl-9-geometry-shader-4-triangle-to-triangle
の、C++側をそのままにして、ジオメトリシェーダを以下のものに置き換える。
#version 460 layout (triangles) in; //入力は三角形 layout (triangle_strip) out; //出力も三角形 layout (max_vertices = 4) out; //四点出力 //geometry shaderへの入力は配列で受け取らなければいけない //ただし名前はvertex shader側のoutと一致させる in vec4 vertexColor[]; // 出力は普通。名前はfragment shader側のinと一致させる out vec4 vColor; void main() {
gl_Position = gl_in[0].gl_Position; vColor = vertexColor[0]; EmitVertex();
gl_Position = gl_in[1].gl_Position; vColor = vertexColor[1]*0.2; EmitVertex();
gl_Position = gl_in[2].gl_Position; vColor = vertexColor[2]*0.2; EmitVertex();
//第四頂点 gl_Position = vec4(-0.8,0.8,0,1); vColor = vec4(1,1,1,1); EmitVertex();
EndPrimitive(); }
実行結果
C++側では三頂点しか指定していないのに三角形が二枚出力されている。
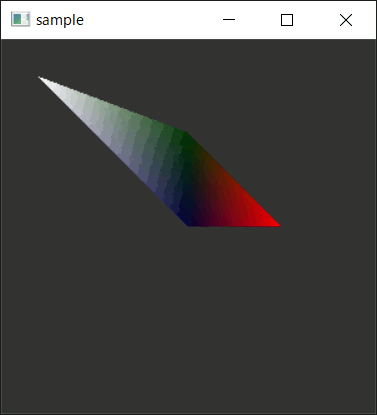
疑問
GL_GEOMETRY_VERTICES_OUTはジオメトリシェーダから出力する可能性のある最大長点数を指定するはずだが、なぜか前回の
をそのままにしておいても四つ目の頂点を出力できた。何か意味を取り違えているのだろうか。