VTKでポリゴンにテクスチャを貼ってみる
MyTexture.hpp
#pragma once #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkTexture.h> #include <vtkImageData.h>
//! @brief 指定サイズの矩形を作成 //! @note テクスチャ座標設定済み //! @param width 幅(ピクセル) //! @param height 高さ(ピクセル) //! @return 矩形ポリゴンのvtkPolyData vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> MakeScreenAlignedQuad(float width, float height);
//! @brief 矩形ポリゴンのサイズを変更 //! @param quad 矩形ポリゴンのvtkPolyData //! @param newWidth 新しい幅(ピクセル) //! @param newHeight 新しい高さ(ピクセル) //! @return なし void ResizeQuad(vtkPolyData* quad, float newWidth, float newHeight);
//! @brief vtkTextureにvtkImageDataをセット //! @param texture テクスチャオブジェクト //! @param image 画像データオブジェクト //! @return なし void SetTextureImage(vtkTexture* texture, vtkImageData* image);
//! @brief 画像配列から vtkImageData を生成 //! @param pixels 画像ピクセル配列(RGBAまたはRGB) //! @param width 画像幅(ピクセル) //! @param height 画像高さ(ピクセル) //! @param numComponents ピクセルあたりの成分数(3または4) vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageData> MakeImageDataFromBuffer( const unsigned char* pixels, int width, int height, int numComponents );
MyTexture.cpp
#include "MyTexture.hpp" #include <vtkFloatArray.h> #include <vtkPointData.h>
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> MakeScreenAlignedQuad(float width, float height) { vtkNew<vtkPoints> pts; pts->SetNumberOfPoints(4); pts->SetPoint(0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); pts->SetPoint(1, width, 0.0, 0.0); pts->SetPoint(2, width, height, 0.0); pts->SetPoint(3, 0.0, height, 0.0); vtkNew<vtkCellArray> polys; vtkIdType ids[4] = { 0,1,2,3 }; polys->InsertNextCell(4, ids); vtkNew<vtkFloatArray> tcoords; tcoords->SetName("TCoords"); tcoords->SetNumberOfComponents(2); tcoords->InsertNextTuple2(0.f, 0.f); // 左下 tcoords->InsertNextTuple2(1.f, 0.f); // 右下 tcoords->InsertNextTuple2(1.f, 1.f); // 右上 tcoords->InsertNextTuple2(0.f, 1.f); // 左上 vtkNew<vtkPolyData> pd; pd->SetPoints(pts); pd->SetPolys(polys); pd->GetPointData()->SetTCoords(tcoords); return pd; }
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageData> MakeImageDataFromBuffer( const unsigned char* pixels, int width, int height, int numComponents ) { vtkNew<vtkImageData> img; img->SetDimensions(width, height, 1); img->AllocateScalars(VTK_UNSIGNED_CHAR, numComponents); const int stride = numComponents; auto* dst = static_cast<unsigned char*>(img->GetScalarPointer()); std::memcpy(dst, pixels, static_cast<size_t>(width) * height * stride); return img; }
void ResizeQuad(vtkPolyData* quad, float newWidth, float newHeight) { auto* pts = quad->GetPoints(); pts->SetPoint(0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); pts->SetPoint(1, newWidth, 0.0, 0.0); pts->SetPoint(2, newWidth, newHeight, 0.0); pts->SetPoint(3, 0.0, newHeight, 0.0); pts->Modified(); quad->Modified(); }
void SetTextureImage(vtkTexture* texture, vtkImageData* image) { texture->SetInputData(image); texture->InterpolateOn(); // バイリニア補間 texture->RepeatOff(); // 画像外は伸ばさない texture->EdgeClampOn(); texture->Modified(); }
使用例
// 画像生成 std::vector<unsigned char> MakeCheckerRGBA(int w, int h, int block = 16) { std::vector<unsigned char> buf(static_cast<size_t>(w) * h * 4); for (int y = 0; y < h; ++y) { for (int x = 0; x < w; ++x) { bool on = ((x / block) + (y / block)) % 2 == 0; unsigned char c = on ? 230 : 60; size_t idx = (static_cast<size_t>(y) * w + x) * 4; buf[idx + 0] = c; buf[idx + 1] = c; buf[idx + 2] = c; buf[idx + 3] = 255; } } return buf; }
// テクスチャオブジェクト作成 /////////////// vtkNew<vtkTexture> texture; // 画像データ作成 /////////////////////////// std::vector<unsigned char> pixels = MakeCheckerRGBA(256, 256, 32); // 画像データをvtkImageDataに変換 /////////// vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageData> imgdata = MakeImageDataFromBuffer(pixels.data(), 256, 256, 4); // テクスチャに画像データをセット /////////// SetTextureImage(texture, imgdata); // ポリゴン作成 ///////////////////////////// auto poly_quad = MakeScreenAlignedQuad(100, 200); vtkNew<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper; mapper->SetInputData(poly_quad); vtkNew<vtkActor> actor; actor->SetMapper(mapper); actor->SetTexture(texture); auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(actor);
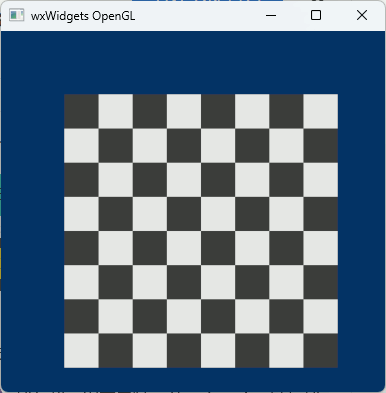
Win32APIでCEFのオフスクリーンレンダリング コード整頓
Win32APIからCEFを使用するコードを書きたかったので前に書いたものを整頓した。
実行には.exeファイルと同じ場所
cef_binary_138.0.15+gd0f1f64+chromium-138.0.7204.50_windows64\Resources\
の内容(localesフォルダなど)をコピーする。
#include "MyCEFControl.hpp" #include <Windows.h> #include <windowsx.h>
void OnPaint(HWND hwnd, HDC hdc) { MyHandler* handler = (MyHandler*)GetWindowLongPtr(hwnd, GWLP_USERDATA); if (handler) { CefRefPtr<CefRenderHandler> baseRenderHandler = handler->GetRenderHandler(); MyRenderHandler* renderHandler = static_cast<MyRenderHandler*>(baseRenderHandler.get()); RGBAImage img = renderHandler->m_browserImage; if (img.buffer.size() > 0) { // ビットマップ情報の設定 BITMAPINFO bmi; ZeroMemory(&bmi, sizeof(BITMAPINFO)); bmi.bmiHeader.biSize = sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER); bmi.bmiHeader.biWidth = img.width; bmi.bmiHeader.biHeight = -img.height; // 上下反転 bmi.bmiHeader.biPlanes = 1; bmi.bmiHeader.biBitCount = 24; // RGB24ビット bmi.bmiHeader.biCompression = BI_RGB; // 画像データを描画 SetDIBitsToDevice( hdc, 0, 0, // 描画位置 img.width, img.height, // 描画サイズ 0, 0, // ソースの開始位置 0, img.height, // ソースの開始ラインとライン数 img.buffer.data(), // ピクセルデータ &bmi, DIB_RGB_COLORS // カラーテーブルの使用方法 ); } } }
void OnMouseMove(HWND hwnd, int x, int y) { MyHandler* handler = (MyHandler*)GetWindowLongPtr(hwnd, GWLP_USERDATA); if (handler) { CefMouseEvent mouse_event; mouse_event.x = x; mouse_event.y = y; mouse_event.modifiers = 0; handler->GetBrowser()->GetHost()->SendMouseMoveEvent(mouse_event, false); InvalidateRect(hwnd, NULL, FALSE); } }
void OnLButtonDown(HWND hwnd, int x, int y) { MyHandler* handler = (MyHandler*)GetWindowLongPtr(hwnd, GWLP_USERDATA); if (handler) { CefMouseEvent mouse_event; mouse_event.x = x; mouse_event.y = y; mouse_event.modifiers = 0; handler->GetBrowser()->GetHost()->SendMouseClickEvent(mouse_event, cef_mouse_button_type_t::MBT_LEFT, false, 1); InvalidateRect(hwnd, NULL, FALSE); } }
void OnLButtonUp(HWND hwnd, int x, int y) { MyHandler* handler = (MyHandler*)GetWindowLongPtr(hwnd, GWLP_USERDATA); if (handler) { CefMouseEvent mouse_event; mouse_event.x = x; mouse_event.y = y; mouse_event.modifiers = 0; handler->GetBrowser()->GetHost()->SendMouseClickEvent(mouse_event, cef_mouse_button_type_t::MBT_LEFT, true, 1); InvalidateRect(hwnd, NULL, FALSE); } }
void OnClose(HWND hwnd) { MyHandler* handler = (MyHandler*)GetWindowLongPtr(hwnd, GWLP_USERDATA); if (handler) { handler->CloseAllBrowsers(true); } }
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wp, LPARAM lp) { MyHandler* handler = nullptr; LPCREATESTRUCT pcs; PAINTSTRUCT ps; HDC hdc; switch (msg) { case WM_CLOSE: OnClose(hwnd); DestroyWindow(hwnd); return 0; case WM_PAINT: hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps); OnPaint(hwnd, hdc); EndPaint(hwnd, &ps); return 0; case WM_CREATE: return 0; case WM_DESTROY: //CefQuitMessageLoop(); PostQuitMessage(0); return 0; case WM_MOUSEMOVE: OnMouseMove(hwnd, GET_X_LPARAM(lp), GET_Y_LPARAM(lp)); return 0; case WM_LBUTTONDOWN: OnLButtonDown(hwnd, GET_X_LPARAM(lp), GET_Y_LPARAM(lp)); return 0; case WM_LBUTTONUP: OnLButtonUp(hwnd, GET_X_LPARAM(lp), GET_Y_LPARAM(lp)); return 0; } return DefWindowProc(hwnd, msg, wp, lp); }
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow) { HWND hwnd; MSG msg; WNDCLASS winc; winc.style = CS_HREDRAW | CS_VREDRAW; winc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc; winc.cbClsExtra = winc.cbWndExtra = 0; winc.hInstance = hInstance; winc.hIcon = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION); winc.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW); winc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)GetStockObject(WHITE_BRUSH); winc.lpszMenuName = NULL; winc.lpszClassName = TEXT("SZL-WND"); if (!RegisterClass(&winc)) return -1; ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// CefRefPtr<MyHandler> g_handler = MyInitCEF(hInstance); if (!g_handler) { return -1; } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// hwnd = CreateWindow( TEXT("SZL-WND"), TEXT("CEF test"), WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW | WS_VISIBLE, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, 500, 500, NULL, NULL, hInstance, nullptr ); if (hwnd == NULL) return -1; ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// SetWindowLongPtr(hwnd, GWLP_USERDATA, (LONG_PTR)(g_handler.get())); ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// MyRenderSetting(hwnd,g_handler); ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // メッセージループ CefRunMessageLoop(); // CEFのシャットダウン CefShutdown(); return 0; }
MyCEFControl.hpp
#pragma once #include <include/cef_app.h> struct RGBAImage { int width; int height; std::vector<unsigned char> buffer; // RGBAの生データ }; RGBAImage FromRGBA(const unsigned char* rgba_buffer, int width, int height); class MyRenderHandler : public CefRenderHandler { public: HWND m_pCanvasWindow = nullptr; RGBAImage m_browserImage; // GetViewRect() をoverrideする // 必須:ビューポートのサイズを返す void GetViewRect(CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> browser, CefRect& rect) override; // 必須:レンダリング結果がここに来る void OnPaint(CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> browser, PaintElementType type, const RectList& dirtyRects, const void* buffer, int width, int height) override; // サイズを外から設定 void SetSize(int w, int h); private: IMPLEMENT_REFCOUNTING(MyRenderHandler); }; class MyHandler : public CefClient, public CefLifeSpanHandler { CefRefPtr<CefRenderHandler> renderHandler_; public: MyHandler(CefRefPtr<CefRenderHandler> renderHandler) : renderHandler_(renderHandler) { } CefRefPtr<CefRenderHandler> GetRenderHandler() override; CefRefPtr<CefLifeSpanHandler> GetLifeSpanHandler() override; void OnAfterCreated(CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> browser) override; void OnBeforeClose(CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> browser) override; void CloseAllBrowsers(bool force_close); CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> GetBrowser(); IMPLEMENT_REFCOUNTING(MyHandler); private: CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> m_Browser; }; CefRefPtr<MyHandler> MyInitCEF(HINSTANCE hInstance); void MyRenderSetting(HWND window, CefRefPtr<MyHandler> ghandler);
MyCEFControl.cpp
#include "MyCEFControl.hpp" void MyRenderHandler::GetViewRect(CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> browser, CefRect& rect){ // ビューポートのサイズを返す rect = CefRect(0, 0, m_browserImage.width, m_browserImage.height); } // 必須:レンダリング結果がここに来る void MyRenderHandler::OnPaint(CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> browser, PaintElementType type, const RectList& dirtyRects, const void* buffer, int width, int height) { // ※ buffer は 32bit BGRA フォーマット m_browserImage = FromRGBA(static_cast<const unsigned char*>(buffer), width, height); InvalidateRect(m_pCanvasWindow, NULL, FALSE); } // サイズを外から設定 void MyRenderHandler::SetSize(int w, int h) { m_browserImage.buffer.resize(w * h * 4); m_browserImage.width = w; m_browserImage.height = h; } //============================================================= CefRefPtr<CefRenderHandler> MyHandler::GetRenderHandler() { return renderHandler_; } CefRefPtr<CefLifeSpanHandler> MyHandler::GetLifeSpanHandler() { return this; } void MyHandler::OnAfterCreated(CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> browser) { m_Browser = browser; } void MyHandler::OnBeforeClose(CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> browser) { m_Browser = nullptr; CefQuitMessageLoop(); } void MyHandler::CloseAllBrowsers(bool force_close) { if (m_Browser) { m_Browser->GetHost()->CloseBrowser(force_close); } } CefRefPtr<CefBrowser> MyHandler::GetBrowser() { return m_Browser; } //============================================================= RGBAImage FromRGBA(const unsigned char* rgba_buffer, int width, int height) { // wxImage用にRGBを抜き出す // 既存の生配列からstd::vectorへの変換例 std::vector<unsigned char> rgb_data(rgba_buffer, rgba_buffer + width * height * 3); for (int i = 0; i < width * height; ++i) { rgb_data[i * 3 + 0] = rgba_buffer[i * 4 + 0]; rgb_data[i * 3 + 1] = rgba_buffer[i * 4 + 1]; rgb_data[i * 3 + 2] = rgba_buffer[i * 4 + 2]; } RGBAImage img; img.width = width; img.height = height; img.buffer = std::move(rgb_data); return img; } CefRefPtr<MyHandler> MyInitCEF(HINSTANCE hInstance) { CefMainArgs main_args(hInstance); int exit_code = CefExecuteProcess(main_args, nullptr, nullptr); if (exit_code >= 0) return nullptr; // CEFの設定 CefSettings settings; settings.no_sandbox = true; // マルチスレッドメッセージループを無効にする // オフスクリーンレンダリングでは false必須 settings.multi_threaded_message_loop = false; CefInitialize(main_args, settings, nullptr, nullptr); ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// CefRefPtr<MyRenderHandler> renderHandler = new MyRenderHandler(); CefRefPtr<MyHandler> g_handler = CefRefPtr<MyHandler>(new MyHandler(renderHandler)); return g_handler; } void MyRenderSetting(HWND window, CefRefPtr<MyHandler> ghandler) { // MyRenderHandlerを取得 CefRefPtr<CefRenderHandler> baseRenderHandler = ghandler->GetRenderHandler(); CefRefPtr<MyRenderHandler> renderHandler = static_cast<MyRenderHandler*>(baseRenderHandler.get()); renderHandler->m_pCanvasWindow = window; renderHandler->SetSize(400, 400); // ビューポートのサイズを設定 CefBrowserSettings browser_settings; CefWindowInfo window_info; CefRect cefRect( 0, 0, 800, 600); // オフスクリーンレンダリング window_info.SetAsWindowless(nullptr); CefBrowserHost::CreateBrowser( window_info, ghandler, "https://www.google.com", browser_settings, nullptr, nullptr); }
VTKのオブジェクトをスレッドで生成・追加
actorなどの生成まではスレッドでできるが、Render()関数などの呼び出しはメインスレッドで行わなければいけない。
VTKのメッセージループを使う限りはシグナルを送ったりということが簡単にできないので、OnTimerで定期的にRender()をする。
#include <iostream> #include <thread> //VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #include <vtkSphereSource.h> #include <vtkCallbackCommand.h> #include <vtkCamera.h> #include <vtkActor.h> // #include "createpoly.hpp" //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
// 定期的に Render する void OnTimer(vtkObject* /*caller*/, unsigned long /*eventId*/, void* clientData, void* /*callData*/) { auto renderWindow = static_cast<vtkRenderWindow*>(clientData); if (renderWindow) { renderWindow->Render(); } }
// 停止フラグ std::atomic<bool> g_stop{ false };
// スレッド void work(vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer> renderer) { for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++) { // 乱数 double x = (std::rand() % 100) / 10.0 - 5.0; double y = (std::rand() % 100) / 10.0 - 5.0; double z = (std::rand() % 100) / 10.0 - 5.0; // 球体 vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource> sphereSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource>::New(); sphereSource->SetCenter(x,y,z); sphereSource->SetRadius(5.0); sphereSource->Update(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputConnection(sphereSource->GetOutputPort()); actor->SetMapper(mapper); renderer->AddActor(actor); std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1)); if(g_stop) break; } }
int main(int /*argc*/, char** /*argv*/) { auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->ResetCamera(); renderer->GetActiveCamera()->SetPosition(0, 0, 100); ////////////////////////////////////// auto interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); renderWindow->SetInteractor(interactor); renderWindow->Render(); auto cb = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCallbackCommand>::New(); cb->SetClientData(renderWindow); cb->SetCallback(OnTimer); interactor->AddObserver(vtkCommand::TimerEvent, cb); interactor->Initialize(); interactor->CreateRepeatingTimer(10); std::thread t1(work, renderer); interactor->Start(); //イベントループへ入る g_stop = true; t1.join(); return 0; }
Blender 4.5.3 Geometry Nodeの実体化
Group Outputの前に Realize Instancesを入れることで、モディファイアの設定からapplyができるようになる。
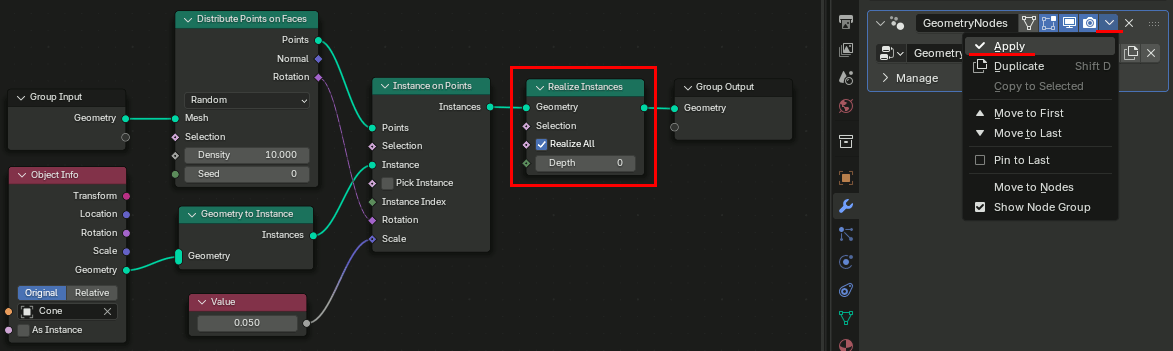
オブジェクトの分離
結果が全て一つのオブジェクトになっているので、個別のオブジェクトにするには By Loose Parts で分離する。
Mesh → Separate → By Loose Parts
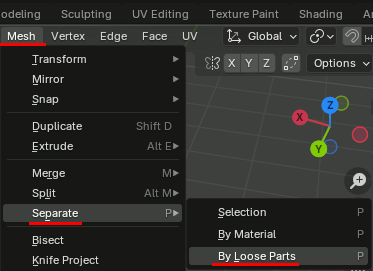
ただし、 By Loose Partsは頂点が繋がっていなければ纏まってくれないので、連続していないパーツが一つのオブジェクトになっている場合はどこかでつなげておかないといけない
pythonとyfinanceで株価取得
諸事情によりPythonで株価を取得するコードを書いた。
株価を取得するAPIは有料から無料までいろいろあるが今回はただ呼び出せば使える yfinance をつかう。
yfinanceでデータを取得してグラフ表示
################################### # 株価取得 ################################### import yfinance as yf df = yf.download("AAPL", start="2020-01-01", interval="1d") ################################### # 終値をグラフ表示 ################################### import matplotlib.pyplot as plt df["Close"].plot(title="AAPL Closing Price") plt.show()
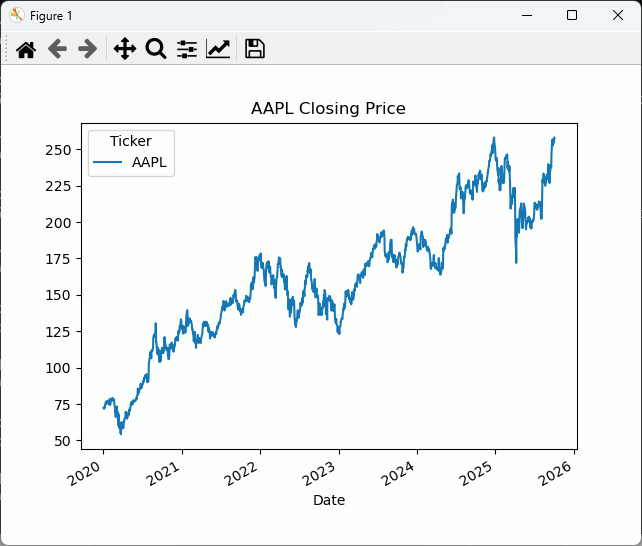
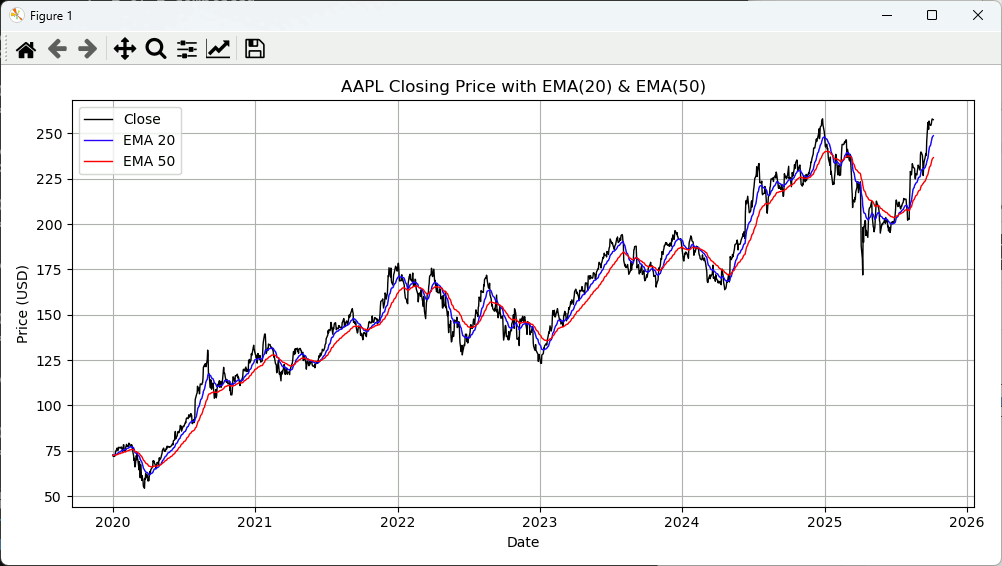
EMAを計算して同時に表示
import yfinance as yf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # データ取得 df = yf.download("AAPL", start="2020-01-01", interval="1d") # EMA(指数移動平均)を計算 df["EMA20"] = df["Close"].ewm(span=20, adjust=False).mean() # 20日EMA df["EMA50"] = df["Close"].ewm(span=50, adjust=False).mean() # 50日EMA # 終値とEMAを同じグラフに描画 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) plt.plot(df.index, df["Close"], label="Close", color="black", linewidth=1) plt.plot(df.index, df["EMA20"], label="EMA 20", color="blue", linewidth=1) plt.plot(df.index, df["EMA50"], label="EMA 50", color="red", linewidth=1) plt.title("AAPL Closing Price with EMA(20) & EMA(50)") plt.xlabel("Date") plt.ylabel("Price (USD)") plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
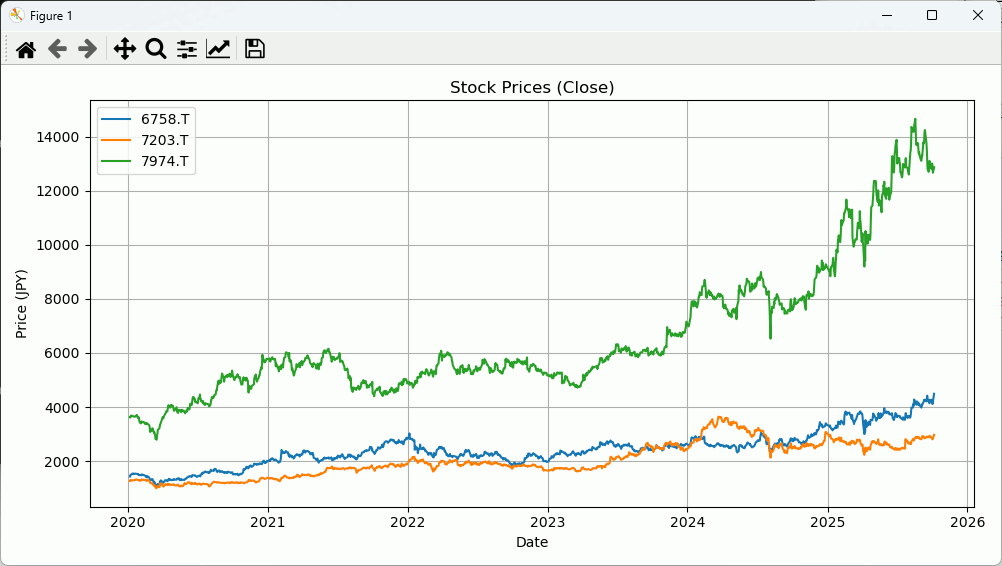
日本株の場合
日本株は銘柄の後に.Tをつけるといいらしい。
import yfinance as yf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt tickers = ["7203.T", "6758.T", "7974.T"] # 一括取得 df = yf.download(tickers, start="2020-01-01", interval="1d")["Close"] # DataFrame の確認 print(df.head()) print("==========================") # 銘柄 for symbol in df.columns: print(df[symbol]) print("==========================") # グラフ描画 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) for symbol in df.columns: plt.plot( df.index, # 横軸 日付 df[symbol], # 縦軸 価格 label=symbol # 凡例のラベル ) print("==========================") plt.title("Stock Prices (Close)") plt.xlabel("Date") plt.ylabel("Price (JPY)") plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
VTK 9.5.1 で .vtkhdf 形式でファイル保存/読み込み(vtkMultiBlockDataSet)
.vtkhdf形式は複数のオブジェクトを一つのファイルにまとめて保存できる。
ただしバイナリ形式なのと、保存形式が複数あるのでややこしい。今回はvtkMultiBlockDataSet形式で保存する。
saveMultiblock.hpp
vtkhdfで保存・読み込みを行う。データはvtkMultiBlockDataSetで保存する
#pragma once #include "createpoly.hpp" #include <vtkDataArraySelection.h> ///////////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////////// // 保存コード ///////////////////////////////////////// /////////////////////////////////////////
void save_as_Multiblock() { vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polypoints = createPoints(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polycone = createCone(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyline = createPolyLine(); auto mb = vtkSmartPointer<vtkMultiBlockDataSet>::New(); mb->SetNumberOfBlocks(3); mb->SetBlock(0, polypoints); mb->SetBlock(1, polycone); mb->SetBlock(2, polyline); auto w = vtkSmartPointer<vtkHDFWriter>::New(); w->SetInputData(mb); w->SetFileName("scene.vtkhdf"); w->Write(); }
/////////////////////////////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////
// 読み込みコード
/////////////////////////////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////
std::vector< vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> > load_as_Multiblock() { std::vector< vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> > polyvec; auto reader = vtkSmartPointer<vtkHDFReader>::New(); reader->SetFileName("scene.vtkhdf"); reader->GetPointDataArraySelection()->EnableAllArrays(); reader->GetCellDataArraySelection()->EnableAllArrays(); reader->Update(); //vtkDataObject* out = reader->GetOutput(); vtkDataObject* out = reader->GetOutputDataObject(0); auto mb = vtkMultiBlockDataSet::SafeDownCast(out); std::cout << "MultiBlock with " << mb->GetNumberOfBlocks() << " blocks\n"; // 各ブロックを処理 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < mb->GetNumberOfBlocks(); i++) { vtkPolyData* poly = vtkPolyData::SafeDownCast(mb->GetBlock(i)); if (poly) { // RGB配列があればアクティブにする例 if (poly->GetPointData()->HasArray("RGB")) { poly->GetPointData()->SetActiveScalars("RGB"); } } polyvec.push_back(poly); } return polyvec; }
createpoly.hpp
データを作成する。
#pragma once #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkDoubleArray.h> #include <vtkPointData.h> #include <vtkConeSource.h> #include <vtkCellArray.h> #include <vtkPoints.h> #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #include <vtkProperty.h> #include <vtkUnsignedCharArray.h> #include <array> #include <vtkCellData.h>
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> createPoints() { // 頂点配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); // 色情報の配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkUnsignedCharArray> colors = vtkSmartPointer<vtkUnsignedCharArray>::New(); colors->SetNumberOfComponents(3); colors->SetName("RGB"); // 頂点インデクスの配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> cells = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); for (size_t i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { double x = (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; double y = (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; double z = (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; points->InsertNextPoint(x, y, z); // 座標追加 unsigned char r = static_cast<unsigned char>(x * 255.0); unsigned char g = static_cast<unsigned char>(y * 255.0); unsigned char b = static_cast<unsigned char>(z * 255.0); colors->InsertNextTypedTuple(std::array<unsigned char, 3>{r, g, b}.data()); cells->InsertNextCell(1); // 要素数 cells->InsertCellPoint(i); // 頂点インデックスを追加 } // --- vtkPolyData作成 --- auto polydata = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polydata->SetPoints(points); polydata->SetVerts(cells); polydata->GetPointData()->SetScalars(colors); polydata->GetPointData()->SetActiveScalars("RGB"); return polydata; }
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> createCone() { vtkSmartPointer<vtkConeSource> coneSource; coneSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkConeSource>::New(); coneSource->SetHeight(1.0); coneSource->SetRadius(0.2); coneSource->SetResolution(10); coneSource->Update(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> conePolyData = coneSource->GetOutput(); return conePolyData; }
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> createPolyLine() { // VTKのデータ構造で W の形状を作成 // 頂点配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); // 色情報の配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkUnsignedCharArray> colors = vtkSmartPointer<vtkUnsignedCharArray>::New(); colors->SetNumberOfComponents(3); colors->SetName("RGB"); // 頂点インデクスの配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> cells = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); // 頂点追加 points->InsertNextPoint(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); // 0 colors->InsertNextTypedTuple(std::array<unsigned char, 3>{255,0,0}.data()); points->InsertNextPoint(0.5, 1.0, 0.0); // 1 colors->InsertNextTypedTuple(std::array<unsigned char, 3>{0,255, 0}.data()); points->InsertNextPoint(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); // 2 colors->InsertNextTuple3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); colors->InsertNextTypedTuple(std::array<unsigned char, 3>{0, 0, 255}.data()); points->InsertNextPoint(1.5, 1.0, 0.0); // 3 colors->InsertNextTypedTuple(std::array<unsigned char, 3>{255, 255, 0}.data()); points->InsertNextPoint(2.0, 0.0, 0.0); // 4 colors->InsertNextTypedTuple(std::array<unsigned char, 3>{255, 0, 255}.data()); // 頂点インデクス追加 cells->InsertNextCell(5); // 要素数 cells->InsertCellPoint(0); cells->InsertCellPoint(1); cells->InsertCellPoint(2); cells->InsertCellPoint(3); cells->InsertCellPoint(4); // --- vtkPolyData作成 --- auto polydata = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polydata->SetPoints(points); polydata->SetLines(cells); polydata->GetPointData()->SetScalars(colors); return polydata; }
VTK from Open3D (LineSet)
#pragma once #include <vtkCellArray.h> #include <vtkPoints.h> #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <vtkDoubleArray.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkPointData.h> #include <vtkProperty.h> #include <vtkLine.h> #include "vtkFromO3dCommon.hpp" #include <open3d/Open3D.h> namespace vtko3d {
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> toLineSetPolyData(const open3d::geometry::LineSet& linesegments, USEVALUE usedata) { // 頂点の作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); // 色情報の配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray> colors = vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray>::New(); colors->SetNumberOfComponents(3); colors->SetName("Colors"); for (size_t i = 0; i < linesegments.points_.size(); i++) { double x = linesegments.points_[i].x(); double y = linesegments.points_[i].y(); double z = linesegments.points_[i].z(); points->InsertNextPoint(x, y, z); if (usedata & POINT_RGB) { double r = linesegments.colors_[i].x(); double g = linesegments.colors_[i].y(); double b = linesegments.colors_[i].z(); colors->InsertNextTuple3(r, g, b); // 色情報追加 } } // 線分(Cell)を定義 vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> lines = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); for (size_t i = 0; i < linesegments.lines_.size(); i++) { size_t v1 = linesegments.lines_[i].x(); size_t v2 = linesegments.lines_[i].y(); // 線分を作成 auto line = vtkSmartPointer<vtkLine>::New(); line->GetPointIds()->SetId(0, v1); // 始点 line->GetPointIds()->SetId(1, v2); // 終点 lines->InsertNextCell(line); } // PolyDataへ格納 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(points); polyData->SetLines(lines); polyData->GetPointData()->SetScalars(colors); return polyData; }
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> toLineSegmentsActor(vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper, std::optional< std::array<double, 3> > single_color = std::nullopt, int line_width = 1) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); if (single_color.has_value()) { actor->GetProperty()->SetColor(single_color.value()[0], single_color.value()[1], single_color.value()[2]); } else { actor->GetProperty()->SetColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); // デフォルトは白色 } if (line_width > 0) { actor->GetProperty()->SetLineWidth(line_width); // 線の太さ } return actor; }
std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::LineSet> createSampleLineSegments() { auto linesets = std::make_shared<open3d::geometry::LineSet>(); for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < 100; j++) { double x1 = (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; double y1 = (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; double z1 = 0.0;// (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; double x2 = x1; double y2 = y1; double z2 = 1.0;// (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; linesets->points_.emplace_back(x1, y1, z1); linesets->points_.emplace_back(x2, y2, z2); linesets->colors_.emplace_back(x1, y1, z1); // 赤色のライン linesets->colors_.emplace_back(x2, y2, z2); // 青色のライン linesets->lines_.emplace_back(i * 2, i * 2 + 1); // ラインセグメントのインデックス } } return linesets; }
}
使用例
auto linesegments = vtko3d::createSampleLineSegments(); auto polyData = vtko3d::toLineSetPolyData(*linesegments, vtko3d::POINT_RGB); auto mapper = vtko3d::toMapper(polyData); auto actor = vtko3d::toLineSegmentsActor(mapper, std::nullopt, 2);
Open3D の LineSetの使用例
#include <open3d/Open3D.h> #include <Eigen/Dense> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <memory> #pragma comment(lib, "opengl32.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "glew32s.lib") using namespace open3d;
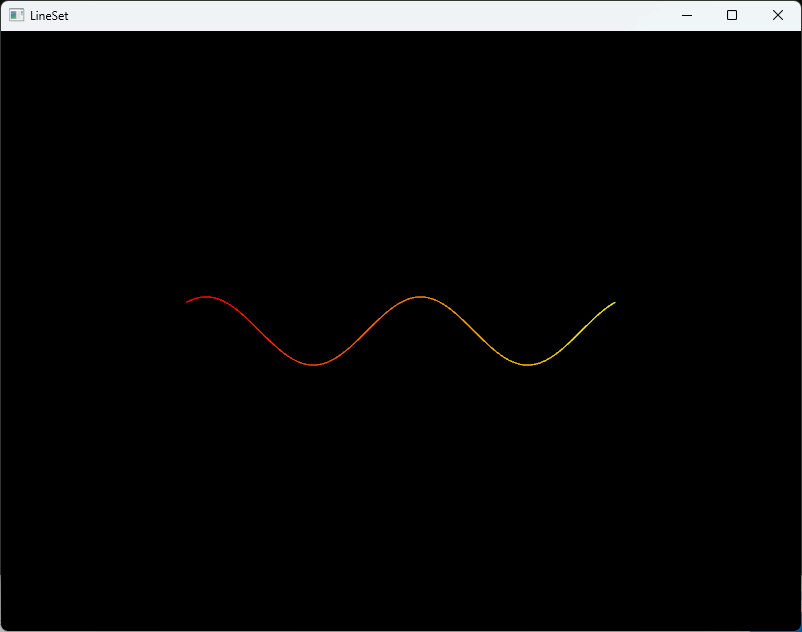
std::shared_ptr<geometry::LineSet> MakePolyline() { const double x0 = -2.0 * 3.14159; const double x1 = 2.0 * 3.14159; const double amplitude = 1.0; // 振幅 const double frequency = 1.0; // 周波数 const double phase = 1.0; // 位相 const int samples = 400; ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////// auto lineset = std::make_shared<geometry::LineSet>(); // 頂点作成 const double step = (x1 - x0) / (samples - 1); for (int i = 0; i < samples; ++i) { double x = x0 + step * i; double y = amplitude * std::sin(frequency * x + phase); lineset->points_.emplace_back(Eigen::Vector3d(x, y, 0.0)); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 頂点インデックスの組み合わせで線分を作成 for (size_t i = 0; i < samples-1; ++i){ lineset->lines_.emplace_back( (int)i, (int)(i + 1) ); // 線分に対する色を設定 lineset->colors_.emplace_back(Eigen::Vector3d(1.0, i/float(samples), 0.0)); } return lineset; }
int main() { auto sine_ls = MakePolyline(); visualization::Visualizer vis; vis.CreateVisualizerWindow("LineSet", 800, 600); vis.AddGeometry(sine_ls); auto& opt = vis.GetRenderOption(); opt.line_width_ = 2.0; opt.background_color_ = { 0, 0, 0 }; vis.Run(); vis.DestroyVisualizerWindow(); return 0; }
VTK from Open3D (PointCloud)
#pragma once #include <vtkCellArray.h> #include <vtkPoints.h> #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <vtkDoubleArray.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkPointData.h> #include <vtkProperty.h> #include <open3d/Open3D.h> #include <open3d/geometry/PointCloud.h> #include <Eigen/Core> #include "vtkFromO3dCommon.hpp" namespace vtko3d {
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> toCloudPolyData(const open3d::geometry::PointCloud& cloud, USEVALUE usedata=POINT_RGB) { // 頂点配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); // 色情報の配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray> colors = vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray>::New(); colors->SetNumberOfComponents(3); colors->SetName("Colors"); auto normals = vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray>::New(); normals->SetNumberOfComponents(3); // x, y, z normals->SetName("Normals"); // 頂点インデクスの配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> cells = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud.points_.size(); i++) { double x = cloud.points_[i].x(); double y = cloud.points_[i].y(); double z = cloud.points_[i].z(); points->InsertNextPoint(x, y, z); // 座標追加 if (usedata & POINT_RGB) { double r = cloud.colors_[i].x(); double g = cloud.colors_[i].y(); double b = cloud.colors_[i].z(); colors->InsertNextTuple3(r, g, b); // 色情報追加 } if (usedata & POINT_NORMAL) { double nx = cloud.normals_[i].x(); double ny = cloud.normals_[i].y(); double nz = cloud.normals_[i].z(); normals->InsertNextTuple3(nx, ny, nz); // 法線ベクトル追加 } cells->InsertNextCell(1); // 要素数 cells->InsertCellPoint(i); // 頂点インデックスを追加 } // --- vtkPolyData作成 --- auto polydata = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polydata->SetPoints(points); polydata->SetVerts(cells); if (usedata & POINT_RGB) { polydata->GetPointData()->SetScalars(colors); } if (usedata & POINT_NORMAL) { polydata->GetPointData()->SetNormals(normals); } return polydata; }
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> toCloudActor(vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper, int point_size = 1,std::optional< std::array<double, 3> > single_color = std::nullopt) { auto actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); if (single_color.has_value()) { mapper->SetScalarVisibility(false); // 頂点ごとの色情報を無視 } actor->SetMapper(mapper); if (mapper->GetScalarVisibility() == false) { if (single_color.has_value()) { actor->GetProperty()->SetColor(single_color.value()[0], single_color.value()[1], single_color.value()[2]); // 単色(R, G, B)を指定 } } actor->GetProperty()->SetPointSize(point_size); // 頂点サイズを5に設定(ピクセル単位) actor->GetProperty()->SetLighting(false); return actor; }
std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::PointCloud> createSampleCloud() { auto pointcloud = std::make_shared<open3d::geometry::PointCloud>(); for (size_t i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { double x = (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; double y = (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; double z = (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX; pointcloud->points_.emplace_back(x, y, z); // 座標追加 pointcloud->colors_.emplace_back(x, y, z); // 色情報追加 pointcloud->normals_.emplace_back(x, y, z); // 法線ベクトル追加 } return pointcloud; }
}
使用例
auto cloud = vtko3d::createSampleCloud(); auto polyData = vtko3d::toCloudPolyData(*cloud, vtko3d::POINT_RGB); auto mapper = vtko3d::toMapper(polyData); auto actor = vtko3d::toCloudActor(mapper,3);
VTK from Open3D (Mesh)
open3dのメッシュを可視化するためのコードを纏めておく。
vtkFromO3dMesh.hpp
#pragma once #include <vtkTriangle.h> #include <vtkProperty.h> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <open3d/Open3D.h> #include <open3d/geometry/PointCloud.h> #include <Eigen/Core> #include "vtkFromO3dCommon.hpp" namespace vtko3d {
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> toMeshPolyData(const open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh& mesh, USEVALUE usedata, bool withpoints = false) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> triangles = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> vertices = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); // 色情報の配列 vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray> colors = vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray>::New(); colors->SetNumberOfComponents(3); colors->SetName("Colors"); vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray> normals = vtkSmartPointer<vtkDoubleArray>::New(); normals->SetNumberOfComponents(3); normals->SetName("Normals"); for (size_t i = 0; i < mesh.vertices_.size(); ++i) { double x = mesh.vertices_[i].x(); double y = mesh.vertices_[i].y(); double z = mesh.vertices_[i].z(); vtkIdType pid = points->InsertNextPoint(x, y, z); if (withpoints) { vertices->InsertNextCell(1, &pid); } if (usedata & POINT_RGB) { double r = mesh.vertex_colors_[i].x(); double g = mesh.vertex_colors_[i].y(); double b = mesh.vertex_colors_[i].z(); colors->InsertNextTuple3(r, g, b); // 色情報追加 } if (usedata & POINT_NORMAL) { double nx = mesh.vertex_normals_[i].x(); double ny = mesh.vertex_normals_[i].y(); double nz = mesh.vertex_normals_[i].z(); normals->InsertNextTuple3(nx, ny, nz); } } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// for (size_t i = 0; i < mesh.triangles_.size(); ++i) { size_t p1 = mesh.triangles_[i](0); size_t p2 = mesh.triangles_[i](1); size_t p3 = mesh.triangles_[i](2); // 三角形1 (p1, p2, p3) vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle> tri = vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle>::New(); tri->GetPointIds()->SetId(0, p1); tri->GetPointIds()->SetId(1, p2); tri->GetPointIds()->SetId(2, p3); triangles->InsertNextCell(tri); } // vtkPolyData の作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(points); if (withpoints) { polyData->SetVerts(vertices); } polyData->SetPolys(triangles); // 三角形セルを設定 if(usedata & POINT_RGB) { polyData->GetPointData()->SetScalars(colors); } if (usedata & POINT_NORMAL) { polyData->GetPointData()->SetNormals(normals); } return polyData; }
struct wireframe_option { bool show_faces = false; float line_width = 1.2f; std::array<double, 3> line_color = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 }; };
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> toMeshActor( vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper, bool usephong=false, std::optional<wireframe_option> wireopt = std::nullopt, std::optional< std::array<double, 3> > single_color = std::nullopt, int point_size = 5 ) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); if (single_color.has_value()) { actor->GetProperty()->SetColor(single_color.value()[0], single_color.value()[1], single_color.value()[2]); } else { actor->GetProperty()->SetColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); // デフォルトは白色 } vtkPolyData* poly = mapper->GetInput(); if (poly->GetVerts()->GetNumberOfCells() > 0) { actor->GetProperty()->SetPointSize(point_size); // 点のサイズを設定 } if (usephong) { actor->GetProperty()->SetInterpolationToPhong(); // またはSetInterpolationToGouraud() } if (wireopt.has_value()) { if (wireopt->show_faces) { actor->GetProperty()->SetRepresentationToSurface(); actor->GetProperty()->EdgeVisibilityOn(); actor->GetProperty()->SetEdgeColor( wireopt->line_color.data() ); // エッジ色 actor->GetProperty()->SetLineWidth(wireopt->line_width); } else { actor->GetProperty()->SetRepresentationToWireframe(); actor->GetProperty()->SetLineWidth(wireopt->line_width); actor->GetProperty()->SetLighting(false); actor->GetProperty()->BackfaceCullingOff(); actor->GetProperty()->FrontfaceCullingOff(); } } return actor; }
// テスト用のメッシュを作成 std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> createSampleMesh() { std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> mesh = std::make_shared<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh>(); int xcount = 20; int ycount = 20; float width = 1.0f; float height = 1.0f; float depth = 0.1f; float density = 10.0f; // 頂点の登録 for (int i = 0; i < xcount; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < ycount; ++j) { double x = -0.5 + 1.0 * i / (xcount - 1); double y = -0.5 + 1.0 * j / (ycount - 1); double z = sin(x * density) * depth + sin(y * density) * depth; mesh->vertices_.emplace_back(x, y, z); mesh->vertex_colors_.emplace_back(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, z + 0.5); } } // メッシュ(三角形)の作成 for (int i = 0; i < xcount - 1; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < ycount - 1; ++j) { // 四角形を2つの三角形に分割 int p1 = i * ycount + j; // 左下 int p2 = (i + 1) * ycount + j; // 右下 int p3 = i * ycount + (j + 1); // 左上 int p4 = (i + 1) * ycount + (j + 1); // 右上 mesh->triangles_.emplace_back(Eigen::Vector3i(p1, p2, p3)); mesh->triangles_.emplace_back(Eigen::Vector3i(p2, p4, p3)); } } return mesh; } }
vtkFromO3dCommon.hpp
#pragma once #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> namespace vtko3d { enum USEVALUE { POINT_XYZ = 0b0001, POINT_RGB = 0b0010, POINT_NORMAL = 0b0100, POINT_RGBNORMAL = POINT_RGB | POINT_NORMAL, }; vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> toMapper(vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polydata) { auto mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputData(polydata); return mapper; } }
使用例
auto mesh = vtko3d::createSampleMesh(); mesh->ComputeVertexNormals(); // 法線ベクトルを計算 auto polyData = vtko3d::toMeshPolyData(*mesh, vtko3d::POINT_RGBNORMAL,false); auto mapper = vtko3d::toMapper(polyData); auto actor = vtko3d::toMeshActor(mapper, true, vtko3d::wireframe_option{ false }); auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(actor);