partitionを使ってクイックセレクト関数を書く
partitionを使い、quick selectアルゴリズムを書く。quick selectでは「配列がソートされたときに、n番目に来る値」を取得できる。これを利用して中央値を取得できる。n番目の要素を特定するのに必要な処理が完了したらクイックソートを中断することで実現するので、データの順番が入れ替わるが、全部ソートするほどの時間はかからない。
C++でpartitionするプログラムを変更して[pivot未満][pivot][pivotより大きい]の領域に分割する
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include "partition_3area.hpp"
void quick_select(std::vector<PairTypeFloat>& arr,size_t low,size_t high, size_t target_index) { size_t nlow = low; size_t nhigh = high; size_t tmp_pivot_index = low + (nhigh - nlow) / 2; //なにかしらpivotを決める // pivotでパーティション PartitionFuncFloat cond(arr, tmp_pivot_index); std::array<int64_t, 3> ret= partition_3area(arr, nlow, nhigh, cond); nlow = ret[0]; // 左側開始位置 size_t newpivot = ret[1]; // 処理後のpivotの位置 nhigh = ret[2]; // 右側終了位置 // [nlow~newpivot-1][newpivot][newpivot+1~nhigh] に分割される // このとき、 if (newpivot == target_index) { // [nlow~newpivot-1][target_index][newpivot+1~nhigh] であれば、 // target_indexの要素番号のデータはtarget_index番目の要素になっている return ; } else if (target_index < newpivot) { // [target_indexを含む][newpivot][newpivot+1~nhigh] であれば、 // 左側を処理 quick_select(arr, nlow, newpivot, target_index); } else { // [nlow~newpivot-1][newpivot][target_indexを含む] であれば、 // 右側を処理 quick_select(arr, newpivot+1, nhigh, target_index); } }
int main() { std::vector<PairTypeFloat> arr; arr.push_back(std::make_pair(3.7, "a")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(2.3, "b")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(7.5, "c")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(1.2, "d")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(6.8, "e")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.6, "f")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(2.4, "g")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(0.9, "h")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(6.1, "i")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.8, "j"));// arr.push_back(std::make_pair(4.5, "k")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(8.2, "l")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(9.1, "m")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(1.7, "n")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.3, "o")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(7.7, "p")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(3.8, "q")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(4.2, "r")); std::cout << "処理前の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } size_t target_index = arr.size() / 2; std::cout << target_index << "番目の要素: " << arr[target_index].first << " " << arr[target_index].second << std::endl; quick_select(arr, 0, arr.size(), target_index);// 中央値を求める std::cout << "--------------------------------------------" << std::endl; std::cout << "処理後の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } std::cout << target_index << "番目の要素: " << arr[target_index].first << " " << arr[target_index].second << std::endl; std::cout << "--------------------------------------------" << std::endl; std::cout << "ソート結果: " << std::endl; arr.clear(); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(3.7, "a")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(2.3, "b")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(7.5, "c")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(1.2, "d")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(6.8, "e")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.6, "f")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(2.4, "g")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(0.9, "h")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(6.1, "i")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.8, "j")); // arr.push_back(std::make_pair(4.5, "k")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(8.2, "l")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(9.1, "m")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(1.7, "n")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.3, "o")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(7.7, "p")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(3.8, "q")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(4.2, "r")); std::sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), [](const PairTypeFloat& a, const PairTypeFloat& b) {return a.first < b.first; }); for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } }
処理結果
[0] 3.7 a
[1] 2.3 b
[2] 7.5 c
[3] 1.2 d
[4] 6.8 e
[5] 5.6 f
[6] 2.4 g
[7] 0.9 h
[8] 6.1 i
[9] 5.8 j
[10] 4.5 k
[11] 8.2 l
[12] 9.1 m
[13] 1.7 n
[14] 5.3 o
[15] 7.7 p
[16] 3.8 q
[17] 4.2 r
9番目の要素: 5.8 j
--------------------------------------------
処理後の配列:
[0] 3.7 a
[1] 2.3 b
[2] 4.2 r
[3] 1.2 d
[4] 3.8 q
[5] 1.7 n
[6] 2.4 g
[7] 0.9 h
[8] 4.5 k
[9] 5.3 o
[10] 5.6 f
[11] 5.8 j
[12] 9.1 m
[13] 8.2 l
[14] 6.1 i
[15] 7.7 p
[16] 6.8 e
[17] 7.5 c
9番目の要素: 5.3 o
--------------------------------------------
ソート結果:
[0] 0.9 h
[1] 1.2 d
[2] 1.7 n
[3] 2.3 b
[4] 2.4 g
[5] 3.7 a
[6] 3.8 q
[7] 4.2 r
[8] 4.5 k
[9] 5.3 o
[10] 5.6 f
[11] 5.8 j
[12] 6.1 i
[13] 6.8 e
[14] 7.5 c
[15] 7.7 p
[16] 8.2 l
[17] 9.1 m
C++でpartitionするプログラムを変更して[pivot未満][pivot][pivotより大きい]の領域に分割する
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <array>
// 配列の分割を行う関数 template<typename Container, class PCond> int64_t partition(Container& arr, int64_t low, int64_t high, PCond& pivot) { int64_t i = low; int64_t j = high-1; int64_t bound; while (true) { // 条件に合致するものを探す while ( (pivot.IsTrue(i) == true) ) { i++; if (i >= high) break; } // 条件に合致しないものを探す while ( (pivot.IsFalse(j) == true) ) { j--; if (j == -1) break; } // 左右の走査が交差した場合に分割終了 if (i >= j) { bound = i; break; } // 条件に合致しない要素とする要素を交換 pivot.Swap(i, j); // 走査を進める i++; j--; } return bound; }
enum BoolType { True = 1, False = 0 }; using PairTypeBool = std::pair<BoolType, std::string>; using PairTypeFloat = std::pair<float, std::string>;
// データを分割する時に必要な関数をまとめたもの struct PartitionFuncBool { std::vector<PairTypeBool>& _array; int64_t _pivot; float _value; PartitionFuncBool(std::vector<PairTypeBool>& arr,int64_t pivot_index):_array(arr) { _pivot = pivot_index; _value = _array[_pivot].first; } // 要素の交換関数 void Swap(size_t i, size_t j) { // pivotが移動したので最新のindexを保存 if(i==_pivot) _pivot = j; else if(j==_pivot) _pivot = i; std::swap(_array[i], _array[j]); } // 条件判定関数 bool IsTrue(size_t i) { return _array[i].first == _value; } bool IsFalse(size_t i) { return !IsTrue(i); } };
// データを分割する時に必要な関数をまとめたもの struct PartitionFuncFloat { std::vector<PairTypeFloat>& _array; int64_t _pivot; float _value; PartitionFuncFloat(std::vector<PairTypeFloat>& arr, int64_t pivot_index) :_array(arr) { _pivot = pivot_index; _value = _array[_pivot].first; } // 要素の交換関数 void Swap(size_t i, size_t j) { // pivotが移動したので最新のindexを保存 if (i == _pivot) _pivot = j; else if (j == _pivot) _pivot = i; std::swap(_array[i], _array[j]); } // 条件判定関数 bool IsTrue(size_t i) { return _array[i].first <= _value; } bool IsFalse(size_t i) { return !IsTrue(i); } };
template<typename Container, class PCond> std::array<int64_t, 3> partition_3area(Container& arr, int64_t low, int64_t high, PCond& cond) { int64_t bound_idx = partition< Container, PCond>(arr, low, high, cond); // cond._pivot ... 移動後のpivotのindex 前半にあるはず // bound_idx ... 条件に合致しない要素の最初のindex 後半にあるはず // pivotが前半の末尾以外にある場合は、前半末尾へ移動 if(cond._pivot != bound_idx-1) cond.Swap(cond._pivot, bound_idx-1); return { low, bound_idx-1,// 移動後のpivot high }; }
void testbool() { std::vector<PairTypeBool> arr; arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True, "a")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "b")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "c")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True, "d")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True, "e")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True, "f")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "g")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True, "h")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "i")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True, "j")); std::cout << "分割前の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } PartitionFuncBool cond(arr, arr.size() / 2); // ピボットの値を取得 // ピボット表示 std::cout << "ピボット: " << "[" << cond._pivot << "]" << arr[cond._pivot].first << " " << arr[cond._pivot].second << std::endl; auto ret = partition_3area(arr, (size_t)0, arr.size(), cond); std::cout << "分割後の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = ret[0]; i < ret[1]; i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << "[" << ret[1] << "] " << arr[ret[1]].first << " " << arr[ret[1]].second << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; for (size_t i = ret[1] + 1; i < ret[2]; i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } }
void testfloat() { std::vector<PairTypeFloat> arr; arr.push_back(std::make_pair(3.7 , "a")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(2.3 , "b")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(7.5 , "c")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(1.2 , "d")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(6.8 , "e")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.6 , "f")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(2.4 , "g")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(0.9 , "h")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(6.1 , "i")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.3 , "j")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(4.5 , "k")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(8.2 , "l")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(9.1 , "m")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(1.7 , "n")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(5.3 , "o")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(7.7 , "p")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(3.8 , "q")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(4.2 , "r")); std::cout << "分割前の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } PartitionFuncFloat cond(arr, arr.size()/2); // ピボットの値を取得 // ピボット表示 std::cout << "ピボット: " << "[" << cond._pivot << "]" << arr[cond._pivot].first << " " << arr[cond._pivot].second << std::endl; auto ret = partition_3area(arr, (size_t)0, arr.size(), cond); std::cout << "分割後の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = ret[0]; i < ret[1]; i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << "[" << ret[1] << "] " << arr[ret[1]].first << " " << arr[ret[1]].second << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; for (size_t i = ret[1] + 1; i < ret[2]; i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } }
int main() { testfloat(); std::cout << "-----------------------------------\n"; testbool(); return 0; }
floatの場合
分割前の配列:
[0] 3.7 a
[1] 2.3 b
[2] 7.5 c
[3] 1.2 d
[4] 6.8 e
[5] 5.6 f
[6] 2.4 g
[7] 0.9 h
[8] 6.1 i
[9] 5.3 j
[10] 4.5 k
[11] 8.2 l
[12] 9.1 m
[13] 1.7 n
[14] 5.3 o
[15] 7.7 p
[16] 3.8 q
[17] 4.2 r
ピボット: [9]5.3 j
分割後の配列:
[0] 3.7 a
[1] 2.3 b
[2] 4.2 r
[3] 1.2 d
[4] 3.8 q
[5] 5.3 o
[6] 2.4 g
[7] 0.9 h
[8] 1.7 n
[9] 4.5 k
[10] 5.3 j
[11] 8.2 l
[12] 9.1 m
[13] 6.1 i
[14] 5.6 f
[15] 7.7 p
[16] 6.8 e
[17] 7.5 c
Boolの例
分割前の配列:
[0] 1 a
[1] 0 b
[2] 0 c
[3] 1 d
[4] 1 e
[5] 1 f
[6] 0 g
[7] 1 h
[8] 0 i
[9] 1 j
ピボット: [5]1 f
分割後の配列:
[0] 1 a
[1] 1 j
[2] 1 h
[3] 1 d
[4] 1 e
[5] 1 f
[6] 0 g
[7] 0 c
[8] 0 i
[9] 0 b
KdTreeを自作してみる(1)ツリー作成
KdTreeを愚直に作成してみる。
mykdtree.hpp
#include<eigen/Dense> #include <vector>
struct node{ node(size_t index, int axis) : index(index), axis(axis){} size_t index; // 頂点ID int axis; // 0:x, 1:y, 2:z node* left; // ツリー1 node* right; // ツリー2 };
// pがpivotの左側にあるかどうかを判定 bool isLeft(const Eigen::Vector3d& pivot, const Eigen::Vector3d& p, int axis) { return p[axis] < pivot[axis]; }
// 再帰的にツリー作成
node* buildnode(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& points, std::vector<size_t>& indices,int axis) { if(indices.size()==0) return nullptr; if(indices.size()==1){ // 最後のノードに頂点idを与えて返る node* mynode = new node(indices[0],axis); mynode->left = nullptr; mynode->right = nullptr; return mynode; } // pivot を決定 size_t pivotIndex = indices.size() / 2; // indexの配列の中央をpivotとする Eigen::Vector3d Pivot = points[indices[pivotIndex]]; std::vector<size_t> left_indices; // ツリーの左側にセットするindexリスト std::vector<size_t> right_indices; // ツリーの右側にセットするindexリスト // pivot で分割 for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); i++) { if (i == pivotIndex) { continue; } if (isLeft(Pivot, points[indices[i]], axis)) { // ツリーの左側にセットするindexリスト更新 left_indices.push_back(indices[i]); } else { // ツリーの右側にセットするindexリスト更新 right_indices.push_back(indices[i]); } } // 新たなノード作成 node* mynode = new node(indices[pivotIndex],axis); mynode->left = buildnode(points, left_indices, (axis+1) % 3); // 左側を構築 mynode->right = buildnode(points, right_indices, (axis+1) % 3); // 右側を構築 return mynode; }
class mykdtree { std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& _points; node* node_root; public: mykdtree(std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& points) : _points(points) {} // ツリーの構築 void build() { // 最初のindexリストを作成 std::vector<size_t> indices(_points.size()); for (size_t i = 0; i < _points.size(); i++) { indices[i] = i; } // 再帰的にツリー作成 node_root = buildnode(_points, indices, 0/*X軸*/); } node* getRoot() { return node_root; } };
// デバッグ用 ツリー内のすべてのindexを取得する関数 void getAllIndices(node* root, std::vector<size_t>& indices) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } // 現在のノードのindexを追加 indices.push_back(root->index); // 左部分木のindexを取得 getAllIndices(root->left, indices); // 右部分木のindexを取得 getAllIndices(root->right, indices); }
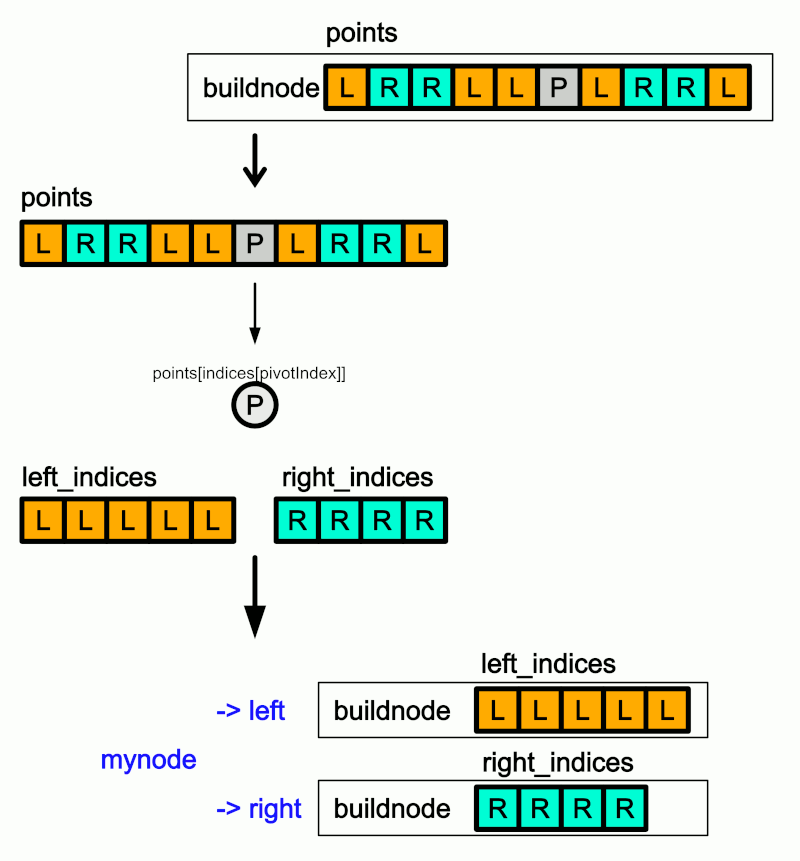
テストコード
点群を分割できていることを確認するために、ツリーで分割した領域を着色してみる。
#include <iostream> //VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"psapi.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"dbghelp.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"ws2_32.lib") #include <Eigen/Core> #include <array> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <vtkPoints.h> #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkUnsignedCharArray.h> #include <vtkPointData.h> #include <vtkVertexGlyphFilter.h> #include <vtkProperty.h> #include "mykdtree.hpp" //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle); // VTK表示用 struct MyVtkCloud { std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> points; std::array<unsigned char, 3> color; std::vector<std::array<unsigned char, 3> > color_array; vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor; void makeActor() { // VTKのデータ構造に変換 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> vtk_points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkUnsignedCharArray> vtk_colors = vtkSmartPointer<vtkUnsignedCharArray>::New(); vtk_colors->SetNumberOfComponents(3); // RGB vtk_colors->SetName("Colors"); for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) { // 点を追加 vtk_points->InsertNextPoint(points[i].x(), points[i].y(), points[i].z()); if (color_array.size() == 0) { vtk_colors->InsertNextTypedTuple(color.data()); } else { vtk_colors->InsertNextTypedTuple(color_array[i].data()); } } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(vtk_points); polyData->GetPointData()->SetScalars(vtk_colors); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// vtkSmartPointer<vtkVertexGlyphFilter> vertexFilter = vtkSmartPointer<vtkVertexGlyphFilter>::New(); vertexFilter->SetInputData(polyData); vertexFilter->Update(); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputConnection(vertexFilter->GetOutputPort()); vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); // 頂点サイズを指定 actor->GetProperty()->SetPointSize(5); // ここで頂点サイズを指定します this->actor = actor; } }; int main(int /*argc*/, char** /*argv*/) { MyVtkCloud cloud1; srand((unsigned int)7); // ランダムな点群を作成 for (size_t i = 0; i < 50000; ++i) { cloud1.points.push_back(Eigen::Vector3d::Random()); } cloud1.color = std::array<unsigned char, 3>{ 0, 255, 0 }; cloud1.makeActor(); // ツリー作成 mykdtree kdtree(cloud1.points); kdtree.build(); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 各領域を着色して表示 std::vector<size_t> indices_left; std::vector<size_t> indices_right_right; std::vector<size_t> indices_right_left_right; std::vector<size_t> indices_right_left_left; node* root = kdtree.getRoot(); // X軸の分割、左側のノードを取得 (赤) getAllIndices(root->left, indices_left); // X軸の分割、右側のノードの右を取得 (緑) getAllIndices(root->right->right, indices_right_right); // X軸の分割、右側のノードの左の右を取得 (青) getAllIndices(root->right->left->right, indices_right_left_right); // X軸の分割、右側のノードの左の左を取得 (紫) getAllIndices(root->right->left->left, indices_right_left_left); MyVtkCloud cloud_L; for (auto i : indices_left)cloud_L.points.push_back(cloud1.points[i]); cloud_L.color = std::array<unsigned char, 3>{ 255, 0, 0 }; cloud_L.makeActor(); MyVtkCloud cloud_RR; for (auto i : indices_right_right)cloud_RR.points.push_back(cloud1.points[i]); cloud_RR.color = std::array<unsigned char, 3>{ 0, 255, 0 }; cloud_RR.makeActor(); MyVtkCloud cloud_RLR; for (auto i : indices_right_left_right)cloud_RLR.points.push_back(cloud1.points[i]); cloud_RLR.color = std::array<unsigned char, 3>{ 0, 0, 255 }; cloud_RLR.makeActor(); MyVtkCloud cloud_RLL; for (auto i : indices_right_left_left)cloud_RLL.points.push_back(cloud1.points[i]); cloud_RLL.color = std::array<unsigned char, 3>{ 255, 0, 255 }; cloud_RLL.makeActor(); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////// // 表示 auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(cloud_L.actor); renderer->AddActor(cloud_RR.actor); renderer->AddActor(cloud_RLR.actor); renderer->AddActor(cloud_RLL.actor); renderer->ResetCamera(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); renderWindow->SetInteractor(interactor); renderWindow->Render(); interactor->Start(); //イベントループへ入る return 0; }

C++でpartitionするプログラムを書く
partitionは配列を[条件を満たす領域][満たさない領域]に分割する。C++の標準ライブラリにはstd::partitionという関数が用意されているので、用途によってはこれを使ってもよい。
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> // 偶数かどうかを判定する関数 bool is_even(int n) { return n % 2 == 0; } int main() { std::vector<int> numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }; // 偶数の要素を表示 std::cout << "全データ: "; for (int i = 0; i < numbers.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << numbers[i] << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; // std::partitionで偶数と奇数に分ける auto it = std::partition(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), is_even); size_t bound = std::distance(numbers.begin(), it); // 偶数の要素を表示 std::cout << "偶数: " << 0 << " ... " << bound-1 << std::endl; for(int i=0;i< bound;i++){ std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << numbers[i] << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; // 奇数の要素を表示 std::cout << "奇数: " << bound << " ... " << numbers.size() << std::endl; for (int i = bound; i < numbers.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << numbers[i] << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }
自前で実装
クイックソートと同じ原理で、配列の先頭と末尾から探索し、条件に合うものと合わないものを交換していけばできる。というかパーティションを再帰的に繰り返したのがクイックソートだといえる。
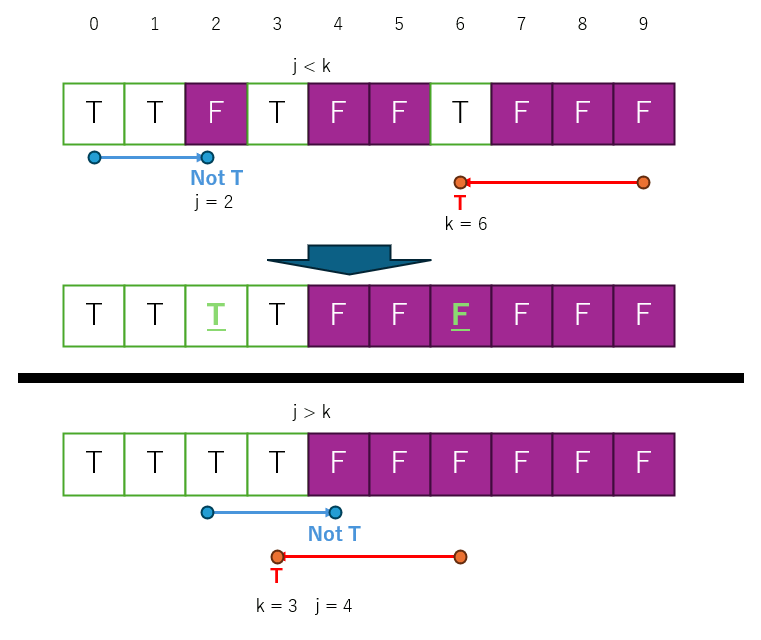
コード
#include <iostream> #include <vector>
// 配列の分割を行う関数 template<typename Container, class PCond> int64_t partition(Container& arr, int64_t low, int64_t high, PCond pivot) { int64_t i = low; int64_t j = high-1; int64_t bound; while (true) { // 条件に合致するものを探す while ( (pivot.IsTrue(i) == true) ) { i++; if (i >= high) break; } // 条件に合致しないものを探す while ( (pivot.IsFalse(j) == true) ) { j--; if (j == -1) break; } // 左右の走査が交差した場合に分割終了 if (i >= j) { bound = i; break; } // 条件に合致しない要素とする要素を交換 pivot.Swap(i, j); // 走査を進める i++; j--; } return bound; }
enum MyBOOL { True, False }; using PairType = std::pair<MyBOOL, std::string>;
// データを分割する時に必要な関数をまとめたもの struct PartitionFunc { std::vector<PairType>& _array; PartitionFunc(std::vector<PairType>& arr):_array(arr) {} // 要素の交換関数 void Swap(size_t i, size_t j) { std::swap(_array[i], _array[j]); } // 条件判定関数 bool IsTrue(size_t i) { return _array[i].first == True; } bool IsFalse(size_t i) { return !IsTrue(i); } };
int main() { std::vector<PairType> arr; arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "a")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "b")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "c")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "d")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "e")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "f")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "g")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "h")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "i")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "j")); std::cout << "分割前の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } PartitionFunc cond(arr); size_t bound_idx = partition< std::vector<PairType>, PartitionFunc>(arr, (size_t)0, arr.size(), cond); std::cout << "分割後の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < bound_idx; i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; for (size_t i = bound_idx; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } return 0; }
分割前の配列:
[0] 0 a
[1] 1 b
[2] 1 c
[3] 0 d
[4] 0 e
[5] 0 f
[6] 1 g
[7] 0 h
[8] 1 i
[9] 0 j
分割後の配列:
[0] 0 a
[1] 0 j
[2] 0 h
[3] 0 d
[4] 0 e
[5] 0 f
[6] 1 g
[7] 1 c
[8] 1 i
[9] 1 b
再帰関数の呼び出しをGraphvizで可視化する
再帰関数のバグが治らないので再帰を可視化するコードを書いた。
.dotフォーマットで出力し、Graphvizで画像化する。
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <fstream> #include <optional> struct TraceNode { std::string name; std::string retval; std::optional<std::string> text; std::vector<TraceNode> children; };
class RecursiveTrace { TraceNode root; std::vector<TraceNode*> stack; public: void setText(std::string text) { stack.back()->text = text; } void addText(std::string text) { stack.back()->text = stack.back()->text.value() + text; } RecursiveTrace() { stack.push_back(&root); } TraceNode* getRoot() { return &root; } void push(std::string name="") { stack.back()->children.emplace_back(); stack.push_back(&stack.back()->children.back()); stack.back()->name = name; } void pop() { stack.pop_back(); } void setReturn(std::string retval) { stack.back()->retval = retval; } };
RecursiveTrace ftrace;
int fibonacci(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; // 基底条件 ftrace.setText( std::string("in=") + std::to_string(n)+"\\n"); ftrace.push(std::string("a:")+std::to_string(n) + "-1"); int a = fibonacci(n - 1);// 再帰呼び出し ftrace.pop(); ftrace.push(std::string("b:") + std::to_string(n) + "-2"); int b = fibonacci(n - 2);// 再帰呼び出し ftrace.pop(); ftrace.addText("a:"+std::to_string(a)+", b:"+std::to_string(b)); ftrace.setReturn(std::to_string(a+b)); return a + b; }
//////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////////////////
// ノードを再帰的に出力する void writeNodes(std::ofstream& file, const TraceNode& node, int& nodeId) { if (!node.text) return; // 無効なノードで出力を終了 // ノードの名前を出力 std::string name = (node.name.length()==0)?"":node.name + "\\n"; std::string text = (node.text.value().length()==0)?"":node.text.value() + "\\n"; std::string retval = (node.retval.length()==0)?"":"("+node.retval + ")"; // ノードのテキストを出力 int currentId = nodeId++; file << " " << currentId << " [label=\"" << name << text << retval << "\"];\n"; // 子ノードの出力 for (const auto& child : node.children) { if (child.text) { // 子ノードが有効か確認 int childId = nodeId; file << " " << currentId << " -> " << childId << ";\n"; writeNodes(file, child, nodeId); } } }
// Graphviz用のDOTファイルを生成する void generateDotFile(const TraceNode& root, const std::string& filename) { std::ofstream file(filename); file << "digraph TraceTree {\n"; file << " node [shape=circle];\n"; int nodeId = 0; // ノードIDのカウンタ writeNodes(file, root, nodeId); file << "}\n"; file.close(); }
//////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////// int main() { int ret = fibonacci(7); auto rr = ftrace.getRoot(); // dotコマンドで画像を生成できる // 例 // dot -Tpng RecursiveTrace.dot -o RecursiveTrace.png generateDotFile(*rr, "RecursiveTrace.dot"); }
結果
以下のコマンドで出力された.dotを画像化すると呼び出し履歴が見られる
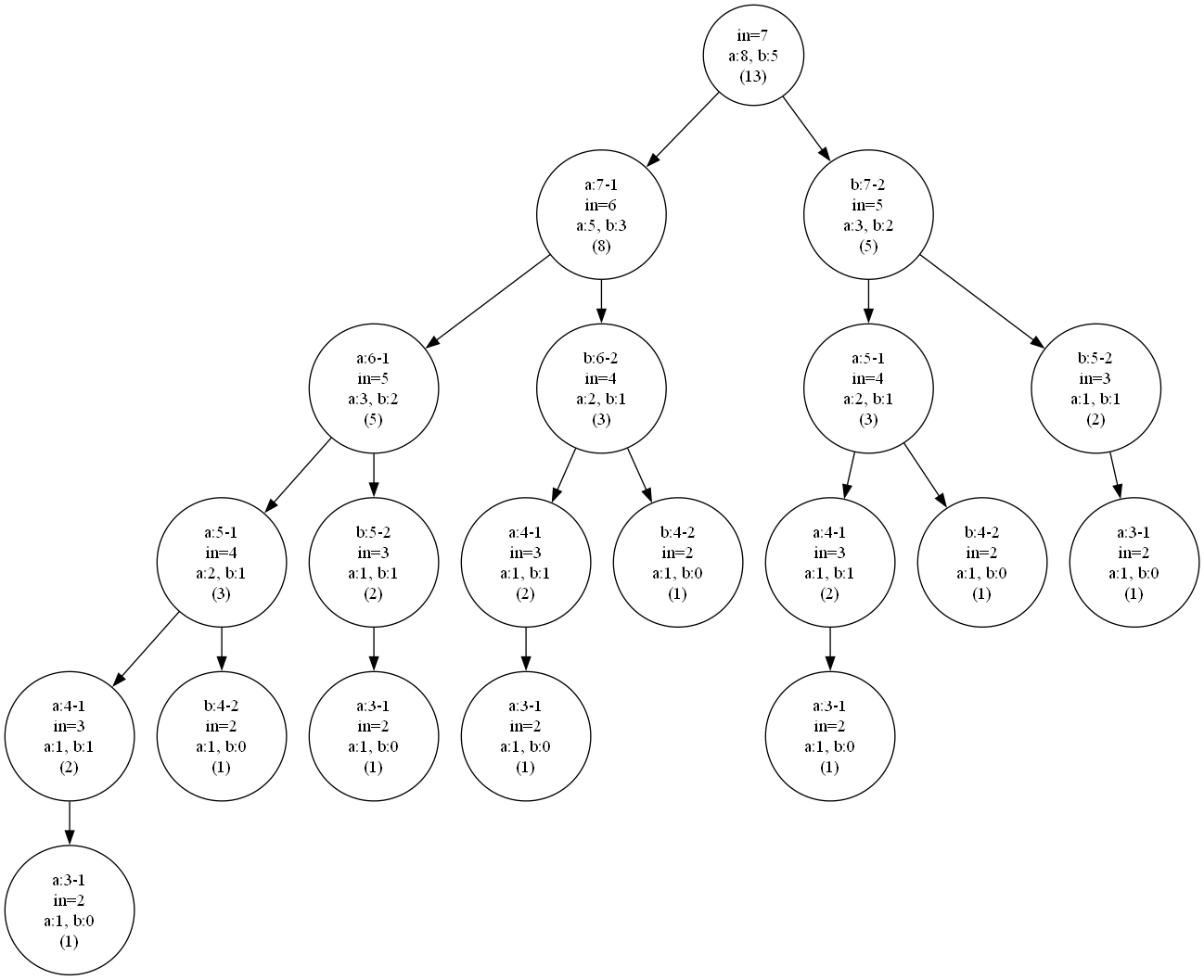
nanoflannでKdTreeを使う
nanoflannというヘッダオンリーのライブラリがあり、KdTreeを実装している。
flannとついているがFLANN(Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors)とは別物らしい。
https://github.com/jlblancoc/nanoflann
ヘッダオンリーで、nanoflann.hppをプロジェクトにインクルードするだけで使える。
さらに、点群型をテンプレートで指定するのでOpen3D等の他のライブラリと併用するときも便利。
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <array> #include "nanoflann.hpp"
// 点群データを表現するクラス struct MyPointCloud { // 点群データ std::vector< std::array<float,3> > points; // nanoflannで必要となるインタフェース関数 inline size_t kdtree_get_point_count() const { return points.size(); } // nanoflannが呼び出す、点群の座標を返す関数 // dim [0] [1] [2] は、それぞれ x, y, z inline float kdtree_get_pt(const size_t idx, const size_t dim) const { return points[idx][dim]; } // BBOXは使わなくても定義は必要 template <class BBOX> bool kdtree_get_bbox(BBOX&) const { return false; } };
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // KdTreeの定義(L2ノルム L2_Simple_Adaptor を使う3次元の点群) // L2ノルムは、ユークリッド距離の2乗 // L1ノルムは、マンハッタン距離 using KdTree = nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor< nanoflann::L2_Simple_Adaptor<float, MyPointCloud>, MyPointCloud, 3 /* 次元数 */>; ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void createCloud(MyPointCloud& cloud) { // サンプル点群を作成 for (size_t i = 0; i < 30000; i++) { cloud.points.push_back(std::array<float, 3>{ static_cast<float>(rand()) / RAND_MAX, static_cast<float>(rand()) / RAND_MAX, static_cast<float>(rand()) / RAND_MAX } ); } }
int main() { MyPointCloud cloud; createCloud(cloud); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // leaf max size は1にしているので、最後まで分割される // leaf max size を2以上にすると、ツリーの末端では配列になり、総当たりでの探索になる KdTree tree( 3 /* 次元数 */, cloud, nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptorParams(1 /* leaf max size */) ); tree.buildIndex(); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// float P[3] = { 0.5, 0.5, 0.5 }; float radius = 0.2; float search_radius = radius * radius; // 半径の二乗 // 結果の格納先 std::vector<nanoflann::ResultItem<unsigned int, float>> ret_matches; nanoflann::SearchParameters params; // 探索 const size_t nMatches = tree.radiusSearch( P, search_radius, ret_matches, params ); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// std::cout << "found " << nMatches << " points\n"; for (size_t i = 0; i < nMatches; i++) { std::cout << i << " point index: " << ret_matches[i].first << " distance: " << sqrt(ret_matches[i].second) << std::endl; } }
icuでテキストの方向を特定
ubidiでテキストが左から右か、右から左か判定する。
#include <iostream> #include <unicode/ubidi.h> #include <unicode/unistr.h> #include <unicode/utypes.h> #if defined(_DEBUG) #pragma comment(lib, "icuucd.lib") #else #pragma comment(lib, "icuuc.lib") #endif // SetConsoleOutputCP #include <windows.h> #include <codecvt>
bool isRTL(const std::u16string& text) { UErrorCode errorCode = U_ZERO_ERROR; const char16_t* buffer16 = reinterpret_cast<const char16_t*>(text.c_str()); size_t buffer_length = text.length(); // UBiDi オブジェクトを作成 UBiDi* bidi = ubidi_openSized(buffer_length, 0, &errorCode); // テキストの方向性を解析 ubidi_setPara(bidi, buffer16, buffer_length, UBIDI_DEFAULT_LTR, nullptr, &errorCode); if (U_FAILURE(errorCode)) { ubidi_close(bidi); return false; } // 方向を取得 UBiDiDirection direction = ubidi_getDirection(bidi); // UBiDi オブジェクトを解放 ubidi_close(bidi); // RTL なら true, LTR なら false return direction == UBIDI_RTL; }
int main() { SetConsoleOutputCP(CP_UTF8); // コンソール出力にUTF8を指定 std::u16string text[] = { u"Hello, how are you?", // 英語(左から右) u"こんにちは、お元気ですか?", // 日本語(左から右) u"안녕하세요, 어떻게 지내세요?", // 韓国語(左から右) u"مرحباً، كيف حالك؟", // アラビア語(右から左) u"שלום, מה שלומך", // ヘブライ語(右から左) u"ܫܠܡܐ ܐܝܟ ܐܢܬܐ", // シリア語(右から左) u"ހެޔޮން، ކިހިންދީ؟" // ディベヒ語(右から左) }; for(auto& t : text) { if (isRTL(t)) { std::cout << " RTL "; // u16string を UTF-8 に変換 std::wstring_convert<std::codecvt_utf8_utf16<char16_t>, char16_t> converter; std::string utf8str = converter.to_bytes(t); std::cout << utf8str << std::endl; } else { std::cout << " LTR "; // u16string を UTF-8 に変換 std::wstring_convert<std::codecvt_utf8_utf16<char16_t>, char16_t> converter; std::string utf8str = converter.to_bytes(t); std::cout << utf8str << std::endl; } } return 0; }
| 方向 | 例文 | 言語 |
|---|---|---|
| LTR | Hello, how are you? | 英語 |
| LTR | こんにちは、お元気ですか? | 日本語 |
| LTR | 안녕하세요, 어떻게 지내세요? | 韓国語 |
| RTL | مرحباً، كيف حالك؟ | アラビア語 |
| RTL | שלום, מה שלומך | ヘブライ語 |
| RTL | ܫܠܡܐ ܐܝܟ ܐܢܬܐ | シリア語 |
| RTL | ހެޔޮން، ކިހިންދީ؟ | ディベヒ語 |
Google Compact Language Detector (CLD3)
CLD3はGoogleが提供する、文字列から言語を推測するためのライブラリ。Apache License 2.0。
推測するものなので、例えば「漢字」は中国語として判断される。
サンスクリット語とヒンディー語、ロシア語とウクライナ語など、同じ文字や単語を使っている言語の識別制度は低くなる。
今回はvcpkgでインストールする。
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #ifdef _DEBUG #pragma comment(lib,"libprotobufd.lib") //#pragma comment(lib, "abseil_dll.lib") #else #pragma comment(lib,"libprotobuf.lib") #endif #include <cld3/nnet_language_identifier.h> #pragma comment(lib,"cld3.lib") // SetConsoleOutputCP #include <windows.h> int main() { SetConsoleOutputCP(CP_UTF8); // コンソール出力にUTF8を指定 // 検出器を初期化(最小/最大テキスト長を指定) chrome_lang_id::NNetLanguageIdentifier lang_id(0, 512); std::string text8[] = { u8"日本", u8"你好", u8"汉字", u8"榊峠", // 榊も峠も和製漢字なので、日本語として判断されてほしい。が。。。 u8"中国語では你好", u8"英語ではHello", u8"Hello", u8"Bonjour", // フランス語 u8"안녕하세요", u8"こんにちは", u8"Здравствуйте", // ロシア語 u8"Це моя книга", // ウクライナ語 u8"Это моя книга", // ロシア語 u8"مرحبا", // アラビア語 u8"नमस्ते, आप कैसे हैं?", // ヒンディー語 u8"नमस्ते", // ナマステ(サンスクリット語) u8"नमः सर्वेभ्यः।",// サンスクリット語 u8"Olá" // ポルトガル語 }; std::cout << u8"文,言語,精度" << std::endl; for( const auto& text : text8 ) { // 言語を検出 auto result = lang_id.FindLanguage(text); std::cout << text << ","; std::cout << result.language << ","; std::cout << result.probability << std::endl; } }
| 文 | 言語 | 精度 |
|---|---|---|
| 日本 | zh | 0.976997 |
| 你好 | zh | 0.999996 |
| 汉字 | zh | 0.998365 |
| 榊峠 | zh | 0.998102 |
| 中国語では你好 | ja | 0.999899 |
| 英語ではHello | ja | 0.999996 |
| Hello | sr | 0.830728 |
| Bonjour | no | 0.933856 |
| 안녕하세요 | ko | 0.999985 |
| こんにちは | ja | 1 |
| Здравствуйте | ru | 0.314022 |
| Це моя книга | uk | 0.902219 |
| Это моя книга | ru | 0.996748 |
| مرحبا | fa | 0.996155 |
| नमस्ते, आप कैसे हैं? | hi | 0.999293 |
| नमस्ते | mr | 0.999077 |
| नमः सर्वेभ्यः। | mr | 0.722388 |
| Olá | ga | 0.997063 |
Win32APIでIMEを使用(3)入力中の文字列(コンポジションウィンドウ)の枠を取得
変換中の文字列が表示されている領域(コンポジションウィンドウ)を直接取得する方法は見つからなかったが、IMEが使用中のフォントを指定してGetTextExtentPoint32を使えば、編集中の文字列の縦・横のサイズと同じものをピクセルで取得できる。
ただ、コンポジションウィンドウのフォントを取得する方法がない。
取得する方法はないが設定はImmSetCompositionFontでできるので、設定した後であれば使用中のフォントがわかるのでそれを使う。
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include <windows.h> #include <imm.h> #pragma comment(lib, "imm32.lib") #include <string>
// IMEで使用するフォントを設定 void SetFont(HIMC hIMC,HFONT hFont) { // フォントの情報を取得 LOGFONT logFont = {}; GetObject(hFont, sizeof(LOGFONT), &logFont); // IMEのコンポジションウィンドウにフォントを設定 ImmSetCompositionFont(hIMC, &logFont); }
// 変換中の文字列を取得 std::wstring GetCompositionString(HIMC hIMC) { std::wstring str; if (hIMC) { DWORD dwSize = ImmGetCompositionString(hIMC, GCS_COMPSTR, NULL, 0); if (dwSize > 0) { wchar_t* compStr = new wchar_t[dwSize / sizeof(wchar_t) + 1]; ImmGetCompositionString(hIMC, GCS_COMPSTR, compStr, dwSize); compStr[dwSize / sizeof(wchar_t)] = L'\0'; str = compStr; delete[] compStr; } } return str; }
// 文字列を描画するサイズを取得
SIZE GetTextDrawSize(const std::wstring& str, HWND hWnd, HDC hdc) { // フォントの情報を取得 HFONT hFont = (HFONT)SendMessage(hWnd, WM_GETFONT, 0, 0); // HDCにフォントを選択 HFONT old = (HFONT)SelectObject(hdc, hFont); // 変換中の文字列のサイズを計算 SIZE textSize; GetTextExtentPoint32(hdc, str.data(), str.length(), &textSize); SelectObject(hdc,old); return textSize; }
// 変換中の文字列の描画領域を計算 SIZE CalculateCompositionStringSIZE(HWND hWnd, HIMC hIMC,HDC hdc) { SIZE size = { 0, 0 }; if (hIMC) { std::wstring test = GetCompositionString(hIMC); size = GetTextDrawSize(test,hWnd,hdc); OutputDebugStringW(test.c_str()); } return size; }
// 変換中の文字列 void test_GCS_COMPSTR(HWND hWnd,HIMC hIMC, HDC hdc) { DWORD inputBytes = ImmGetCompositionStringW(hIMC, GCS_COMPSTR, NULL, 0); int inx = 100; int iny = 100; if (inputBytes) { SIZE size = CalculateCompositionStringSIZE(hWnd, hIMC, hdc); int iny2 = iny - 50; // inx ,iny-50 にsizeの矩形を描画 RECT rect; rect.left = inx; rect.top = iny2; rect.right = inx + size.cx; rect.bottom = iny2 + size.cy; Rectangle(hdc, rect.left, rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom); } if (inputBytes) { std::wstring text = GetCompositionString(hIMC); SetBkMode(hdc, TRANSPARENT); // 確定した文字列を描画 TextOutW(hdc, inx, iny, text.data(), text.length()); SetBkMode(hdc, OPAQUE); } }
// GCS_RESULTSTR void test_GCS_RESULTSTR(HIMC hIMC,HDC hdc) { // GCS_RESULTSTR ... IMEの入力が確定されたフラグ // 確定した文字列のバイト数を取得(NULLは含まない) DWORD inputBytes = ImmGetCompositionStringW(hIMC, GCS_RESULTSTR, NULL, 0); if (inputBytes) { size_t U16Count = inputBytes / sizeof(wchar_t) + 1;// wchar_tでの、NULLを含んだ文字数 wchar_t* buffer = new wchar_t[U16Count]; // 確定した文字列を取得 ImmGetCompositionStringW(hIMC, GCS_RESULTSTR, buffer, inputBytes); buffer[U16Count - 1] = L'\0'; // 確定した文字列を描画 int inx = 100; int iny = 100; TextOutW(hdc, inx, iny, buffer, wcslen(buffer)); delete[] buffer; } }
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) { HIMC hIMC; int inx = 100; int iny = 100; switch (message) { case WM_CREATE: // IMEを使用可能にする hIMC = ImmAssociateContext(hWnd, ImmCreateContext()); SetFont(hIMC, (HFONT)GetStockObject(DEFAULT_GUI_FONT)); break; case WM_IME_STARTCOMPOSITION: OutputDebugString(L"IME 入力開始\n"); hIMC = ImmGetContext(hWnd); // IMEコンテキストを取得 if (hIMC) { // IMEのウィンドウ位置を設定 COMPOSITIONFORM cf2; cf2.dwStyle = CFS_POINT; cf2.ptCurrentPos.x = inx; cf2.ptCurrentPos.y = iny; ImmSetCompositionWindow(hIMC, &cf2); // IMEのウィンドウ位置を設定 ImmReleaseContext(hWnd, hIMC); } break; case WM_IME_COMPOSITION: // IMEの入力中の処理 hIMC = ImmGetContext(hWnd); if (hIMC) { HDC hdc = GetDC(hWnd); RECT rc{ 0,0,640,480 };// 画面クリア FillRect(hdc, &rc, (HBRUSH)(WHITE_BRUSH)); if (lParam & GCS_COMPSTR) { test_GCS_COMPSTR(hWnd,hIMC, hdc); // 編集中の処理 } if (lParam & GCS_RESULTSTR) { test_GCS_RESULTSTR(hIMC, hdc); // 確定時の処理 } ReleaseDC(hWnd, hdc); ImmReleaseContext(hWnd, hIMC); } break; case WM_IME_ENDCOMPOSITION: OutputDebugString(L"IME 入力終了\n"); break; case WM_DESTROY: PostQuitMessage(0); break; default: return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam); } return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);; } int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, PWSTR pCmdLine, int nCmdShow) { WNDCLASS wc; wc.style = CS_HREDRAW | CS_VREDRAW; wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc; wc.cbClsExtra = 0; wc.cbWndExtra = 0; wc.hInstance = hInstance; wc.hIcon = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION); wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW); wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW + 1); wc.lpszMenuName = NULL; wc.lpszClassName = L"SZL-IME-TEST"; RegisterClass(&wc); HWND hWnd = CreateWindowW(L"SZL-IME-TEST", L"title", WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, 640, 480, NULL, NULL, hInstance, NULL); ShowWindow(hWnd, nCmdShow); UpdateWindow(hWnd); MSG msg = {}; while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0)) { TranslateMessage(&msg); DispatchMessage(&msg); } return (int)msg.wParam; }
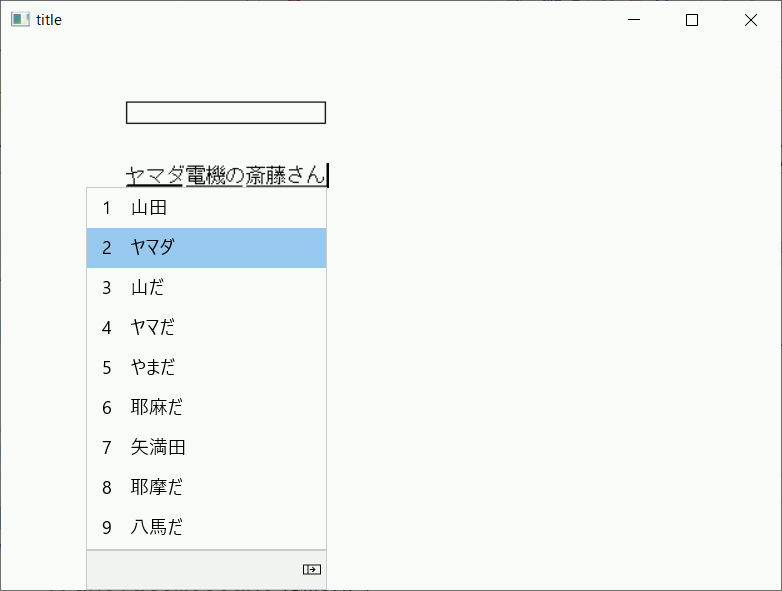
Win32APIでIMEを使用(2)
WM_IME_COMPOSITIONはlParamによって取得できる情報を区別している。特にGCS_COMPATTRは変換中の文字列の一文字ずつの情報を扱うのでATTR_*でさらに分岐が必要。
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include <windows.h> #include <imm.h> #pragma comment(lib, "imm32.lib") #include <string> // https://learn.microsoft.com/ja-jp/windows/win32/intl/ime-composition-string-values
// 変換中の文字列 GCS_COMPSTR void test_GCS_COMPSTR(HIMC hIMC, HDC hdc) { DWORD inputBytes = ImmGetCompositionStringW(hIMC, GCS_COMPSTR, NULL, 0); if (inputBytes) { size_t U16Count = inputBytes / sizeof(wchar_t) + 1;// wchar_tでの、NULLを含んだ文字数 wchar_t* buffer = new wchar_t[U16Count]; // 確定した文字列を取得 ImmGetCompositionStringW(hIMC, GCS_COMPSTR, buffer, inputBytes); buffer[U16Count - 1] = L'\0'; // 確定した文字列を描画 int inx = 0; int iny = 0; TextOutW(hdc, inx, iny, buffer, wcslen(buffer)); delete[] buffer; } }
// 変換中の文字列の属性情報 GCS_COMPATTR void test_GCS_COMPATTR(HIMC hIMC, HDC hdc) { DWORD attr = ImmGetCompositionString(hIMC, GCS_COMPATTR, NULL, 0); BYTE* buffer = new BYTE[attr];// 変換中の文字数と同じ個数の要素を確保 ImmGetCompositionString(hIMC, GCS_COMPATTR, buffer, attr);// 変換中の各文字ごとに状態情報が格納される char str[256] = {}; for (size_t i = 0; i < 256; i++) str[i] = ' '; str[255] = '\0'; TextOutA(hdc, 0, 30, str, strlen(str)); size_t i; for (i = 0; i < attr; i++) { switch (buffer[i]) { case ATTR_INPUT: str[i] = 'I'; break; case ATTR_TARGET_CONVERTED: str[i] = 'T'; break; case ATTR_CONVERTED: str[i] = 'C'; break; case ATTR_FIXEDCONVERTED: str[i] = 'F'; break; case ATTR_TARGET_NOTCONVERTED: str[i] = 'N'; break; case ATTR_INPUT_ERROR: str[i] = 'E'; break; } } str[i] = '*'; TextOutA(hdc, 0, 30, str, strlen(str)); delete[] buffer; }
// 変換中の文字列内のカーソル位置 void test_GCS_CURSORPOS(HIMC hIMC, HDC hdc) { LONG cursorPos = ImmGetCompositionString(hIMC, GCS_CURSORPOS, NULL, 0); char str[256] = {}; sprintf(str, "cursorPos:%d", cursorPos); TextOutA(hdc, 0, 50, str, strlen(str)); }
// 変換開始位置 GCS_DELTASTART void test_GCS_DELTASTART(HIMC hIMC, HDC hdc) { LONG deltaStart = ImmGetCompositionString(hIMC, GCS_DELTASTART, NULL, 0); char str[256] = {}; sprintf(str, "deltaStart:%d", deltaStart); TextOutA(hdc, 0, 90, str, strlen(str)); }
// GCS_RESULTSTR void test_GCS_RESULTSTR(HIMC hIMC,HDC hdc) { // GCS_RESULTSTR ... IMEの入力が確定されたフラグ // 確定した文字列のバイト数を取得(NULLは含まない) DWORD inputBytes = ImmGetCompositionStringW(hIMC, GCS_RESULTSTR, NULL, 0); if (inputBytes) { size_t U16Count = inputBytes / sizeof(wchar_t) + 1;// wchar_tでの、NULLを含んだ文字数 wchar_t* buffer = new wchar_t[U16Count]; // 確定した文字列を取得 ImmGetCompositionStringW(hIMC, GCS_RESULTSTR, buffer, inputBytes); buffer[U16Count - 1] = L'\0'; // 確定した文字列を描画 int inx = 100; int iny = 100; TextOutW(hdc, inx, iny, buffer, wcslen(buffer)); delete[] buffer; } }
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) { HIMC hIMC; int inx = 100; int iny = 100; switch (message) { case WM_CREATE: // IMEを使用可能にする ImmAssociateContext(hWnd, ImmCreateContext()); break; case WM_IME_STARTCOMPOSITION: OutputDebugString(L"IME 入力開始\n"); hIMC = ImmGetContext(hWnd); // IMEコンテキストを取得 if (hIMC) { // IMEのウィンドウ位置を設定 COMPOSITIONFORM cf2; cf2.dwStyle = CFS_POINT; cf2.ptCurrentPos.x = inx; cf2.ptCurrentPos.y = iny; ImmSetCompositionWindow(hIMC, &cf2); // IMEのウィンドウ位置を設定 ImmReleaseContext(hWnd, hIMC); } break; case WM_IME_COMPOSITION: // IMEの入力中の処理 hIMC = ImmGetContext(hWnd); if (hIMC) { HDC hdc = GetDC(hWnd); if (lParam & GCS_RESULTSTR) { test_GCS_RESULTSTR(hIMC,hdc); } if (lParam & GCS_COMPSTR) { test_GCS_COMPSTR(hIMC, hdc); } if (lParam & GCS_COMPATTR) { test_GCS_COMPATTR(hIMC, hdc); } if (lParam & GCS_CURSORPOS) { test_GCS_CURSORPOS(hIMC, hdc); } if (lParam & GCS_DELTASTART) { test_GCS_DELTASTART(hIMC, hdc); } ReleaseDC(hWnd, hdc); ImmReleaseContext(hWnd, hIMC); } break; case WM_IME_ENDCOMPOSITION: OutputDebugString(L"IME 入力終了\n"); break; case WM_DESTROY: PostQuitMessage(0); break; default: return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam); } return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);; }
