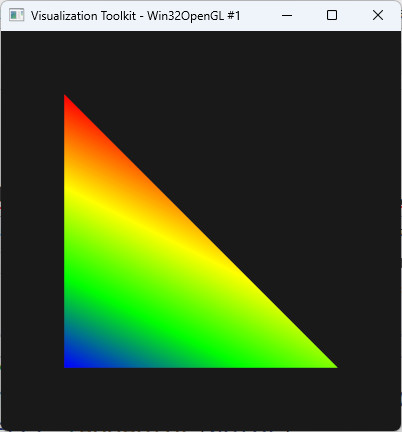
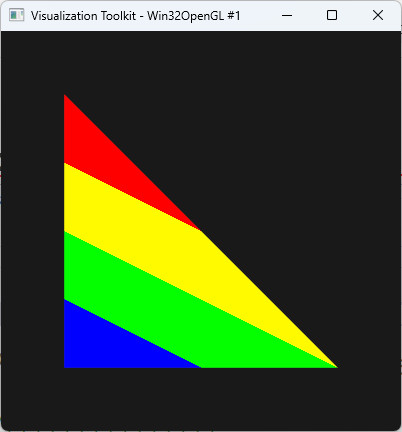
std::filesystemを使って出たときの例外テストをした
アクセスが拒否されました
以下のコードを実行して、例外が発生。
std::filesystem::directory_iterator dir_itr = std::filesystem::directory_iterator(path);
directory_iterator::directory_iterator: アクセスが拒否されました。: "C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\CrashReports"
例外はキャッチすればいいが再現できるようにしておきたい。
再現
1.コマンドプロンプトから、以下のコマンドでディレクトリのアクセス制限を設定する。
icacls C:\test\myaccess\accesstest_directory1 /deny Users:(OI)(CI)F
2.以下を実行
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <filesystem> int main() { std::string pathstr = R"(C:\test\myaccess\accesstest_directory1)"; std::filesystem::path path(pathstr); try { std::filesystem::directory_iterator dir_itr = std::filesystem::directory_iterator(path); } catch (const std::filesystem::filesystem_error& e) { std::cout << e.what() << std::endl; return 1; } }
3.アクセス制限を戻す
icacls C:\test\myaccess\accesstest_directory1 /remove:d Users
Unicode 文字のマッピングがターゲットのマルチバイト コード ページにありません。
これは文字列の変換で発生するのでstd::exceptionでキャッチする。
1.「你好」などCP932で表示できない文字列のフォルダを作成。
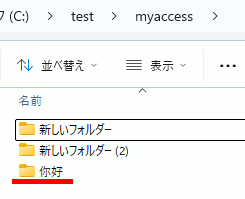
2.以下を実行
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <filesystem> int main() { std::string pathstr = R"(C:\test\myaccess\)"; std::filesystem::path path(pathstr); std::filesystem::directory_iterator dir_itr; // ディレクトリイテレータを取得 try { dir_itr = std::filesystem::directory_iterator(path); } catch (const std::filesystem::filesystem_error& e) { std::cout << e.what() << std::endl; return 1; } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
std::string fname; for (const auto& entry : dir_itr) { try { fname = entry.path().filename().string(); std::cout << fname << std::endl; } catch (const std::exception& e) { // Unicode 文字のマッピングがターゲットのマルチバイト コード ページにありません。 std::cout << e.what() << std::endl; } catch (const std::filesystem::filesystem_error& e) { std::cout << e.what() << std::endl; } }
}
zipファイル内から画像を取り出して表示
libzipでzipファイルから画像データを取り出し、skiaでデコードし、wxWidgetsで表示する。
左右カーソルで画像切り替えをする。
LoadImageZip.hpp
zipから画像を取り出す関数群。
#pragma once #include <include/core/SkBitmap.h> #include <zip.h> #include <memory> #include <string> #include <vector> struct ImageData { std::unique_ptr<SkBitmap> bitmap; std::string filename; }; std::vector<ImageData> FilesInZip(const char* pathname); std::vector<std::uint8_t> GetZipData(zip_t* zipArchive, zip_int64_t index); std::unique_ptr<SkBitmap> ImageFromBinary(const std::vector<std::uint8_t>& contents);
LoadImageZip.cpp
#include <include/core/SkStream.h> #include <include/codec/SkCodec.h> #include <iostream> #include <zip.h> #include <vector> #include "LoadImageZip.hpp"
// zipファイルから画像データを取り出す std::vector<ImageData> FilesInZip(const char* pathname) { std::vector<ImageData> files; int error = 0; // zipファイルを読み取り専用で開く zip_t* zipArchive = zip_open(pathname, ZIP_RDONLY, &error); if (zipArchive == nullptr) { return std::vector<ImageData>(); } // zipファイル内のエントリ数を取得 zip_int64_t item_count = zip_get_num_entries(zipArchive, 0); // 各エントリの名前を取得して表示 for (zip_uint64_t i = 0; i < static_cast<zip_uint64_t>(item_count); ++i) { // ファイル名を取得 const char* file_name = zip_get_name(zipArchive, i, 0); // Zipファイル内のデータを取得 std::vector<std::uint8_t> binary = GetZipData(zipArchive, i); // バイナリデータから画像を作成 std::unique_ptr<SkBitmap> bitmap = ImageFromBinary(binary); // ファイル名と画像を一覧に追加 files.emplace_back(ImageData{ std::move(bitmap),file_name }); } // zipファイルを閉じる zip_close(zipArchive); return files; }
// zipファイルからバイナリデータを取得 std::vector<std::uint8_t> GetZipData(zip_t* zipArchive, zip_int64_t index) { struct zip_stat sb; zip_stat_index(zipArchive, index, 0, &sb); // 2番目のファイルのファイルサイズと同じメモリを確保する std::vector<std::uint8_t> contents(sb.size); // ファイルの内容をメモリに読み込む zip_file* zf = zip_fopen(zipArchive, sb.name, 0); zip_fread(zf, contents.data(), sb.size); zip_fclose(zf); return contents; }
// バイナリデータをSkiaの画像に変換 std::unique_ptr<SkBitmap> ImageFromBinary(const std::vector<std::uint8_t>& contents) { sk_sp<SkData> skdata = SkData::MakeWithoutCopy(contents.data(), contents.size()); if (!skdata) { std::cerr << "SkData作成に失敗しました" << std::endl; return nullptr; } // データからSkCodecを作成 std::unique_ptr<SkCodec> codec(SkCodec::MakeFromData(skdata)); if (!codec) { return nullptr; } SkImageInfo info = codec->getInfo().makeColorType(kN32_SkColorType); std::unique_ptr<SkBitmap> bitmap = std::make_unique<SkBitmap>(); if (!bitmap->tryAllocPixels(info)) { return nullptr; // メモリ確保に失敗 } SkCodec::Result ret = codec->getPixels( info, // 画像の情報 bitmap->getPixels(), // ロード先のメモリ bitmap->rowBytes() // ロード先の1行のバイト数 ); return bitmap; }
main.cpp
// https://docs.wxwidgets.org/3.0/overview_helloworld.html // プリプロセッサに以下二つを追加 // __WXMSW__ // WXUSINGDLL // サブシステムをWindowsに設定(WinMainで呼び出すので) // Windows (/SUBSYSTEM:WINDOWS) #ifndef WX_PRECOMP #include <wx/wx.h> #endif #include <wx/gdicmn.h> // wxPointに必要 #include <wx/frame.h> // wxFrameに必要 #ifdef _DEBUG #pragma comment(lib,"wxbase32ud.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxbase32ud_net.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxbase32ud_xml.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_adv.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_aui.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_core.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_gl.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_html.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_media.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_propgrid.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_qa.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_ribbon.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_richtext.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_stc.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_webview.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32ud_xrc.lib") #else #pragma comment(lib,"wxbase32u.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxbase32u_net.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxbase32u_xml.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_adv.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_aui.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_core.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_gl.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_html.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_media.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_propgrid.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_qa.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_ribbon.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_richtext.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_stc.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_webview.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"wxmsw32u_xrc.lib") #endif #if defined(_DEBUG) #pragma comment(lib, "skia.dll.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "skshaper.dll.lib") #else #pragma comment(lib, "skia.dll.lib") #endif #pragma comment(lib, "zip.lib") ///////////////////////////////////// #include <include/core/SkCanvas.h> #include <include/core/SkBitmap.h> #include <include/core/SkSurface.h> ///////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////// #include "LoadImageZip.hpp" #include <string> // SkBitmapからRGBデータを取得 void PixelRGB(std::vector<std::uint8_t>& rgb, const SkBitmap& skbmp); // ウィンドウ作成 class MyFrame : public wxFrame { std::vector<ImageData> files; std::vector<wxBitmap> wxbitmaps; size_t index = 0; public: void ToBitmaps() { for (auto& file : files) { const SkBitmap& my_bitmap = *file.bitmap; int width = my_bitmap.width(); int height = my_bitmap.height(); std::vector<std::uint8_t> rgb; rgb.resize(width * height * 3); PixelRGB(rgb, my_bitmap); wxImage img(width, height, (unsigned char*)rgb.data(), true); wxBitmap wxbitmap(img); wxbitmaps.push_back(wxbitmap); } } void PostCreate() { files = FilesInZip("C:/temp/images.zip"); ToBitmaps(); index = 0; // OnPaintイベントを設定 Bind(wxEVT_PAINT, &MyFrame::OnPaint, this); // キーボードイベント Bind(wxEVT_KEY_DOWN, &MyFrame::OnKeyDown, this); this->Layout(); // レイアウトの更新 } // キーボードイベント void OnKeyDown(wxKeyEvent& event) { if (event.GetKeyCode() == WXK_RIGHT) { index++; if (index >= files.size()) { index = 0; } Refresh(); } else if (event.GetKeyCode() == WXK_LEFT) { if (index == 0) { index = files.size() - 1; } else { index--; } Refresh(); } } MyFrame(const wxString& title, const wxPoint& pos, const wxSize& size) : wxFrame(NULL, wxID_ANY, title, pos, size) { // CallAfter : 現在処理中のイベントが終わったらPostCreateを実行 // コンストラクタはウィンドウ生成イベント扱い CallAfter(&MyFrame::PostCreate); } // OnPaintイベント void OnPaint(wxPaintEvent& event) { if (wxbitmaps.empty()) { return; } const wxBitmap& wxbitmap = wxbitmaps[index]; // wxWidgetsのウィンドウに表示 wxPaintDC dc(this); dc.DrawBitmap(wxbitmap, 0, 0, true); } }; ///////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////// // wxWidgetsのアプリケーション作成 class MyApp : public wxApp { public: virtual bool OnInit() { MyFrame* frame = new MyFrame("Hello World", wxPoint(50, 50), wxSize(550, 550)); frame->Show(true); return true; } }; ///////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////////////////// // WinMainをマクロで定義 wxIMPLEMENT_APP(MyApp); void PixelRGB(std::vector<std::uint8_t>& rgb, const SkBitmap& skbmp) { if (!skbmp.readyToDraw()) { return; } if (skbmp.colorType() != kRGBA_8888_SkColorType && skbmp.colorType() != kBGRA_8888_SkColorType) { return; } rgb.clear(); int Width = skbmp.width(); int Height = skbmp.height(); size_t rowBytes = skbmp.rowBytes(); const SkImageInfo& info = skbmp.info(); int channels = info.bytesPerPixel(); std::uint8_t* pixels = (std::uint8_t*)skbmp.getPixels(); rgb.resize(Width * Height * 3); for (int i = 0; i < Height; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < Width; j++) { size_t pos_ppm = (i * Width + j) * 3; size_t pos_sk = (i * rowBytes + j * channels); rgb[pos_ppm + 0] = pixels[pos_sk + 2]; rgb[pos_ppm + 1] = pixels[pos_sk + 1]; rgb[pos_ppm + 2] = pixels[pos_sk + 0]; } } }
動的ライブラリをロードする機能をクロスプラットフォームで書いてみた
windowsのLoadLibrary、Linux/MacOSのdlopenをラップしたクラスを作成。
最近Mac miniを買ったので、MacOSでのビルドも確認できるようになった。
ModuleLoader.hpp
#include <functional> #include <string> #if defined(_WIN32) || defined(_WIN64)
#include <Windows.h>
#elif defined(__APPLE__) && defined(__MACH__)
#include <dlfcn.h>
#elif defined(__linux__)
#include <dlfcn.h>
#else #error "Unknown platform" #endif class ModuleLoader { #if defined(_WIN32) || defined(_WIN64)
using ModuleType = HMODULE; using FuncType = FARPROC; ModuleType _ModuleLoad(const char* filename) { return LoadLibraryA(filename); } ModuleType _ModuleLoad(const wchar_t* filename) { return LoadLibraryW(filename); } ModuleType _ModuleLoad(const char16_t* filename) { return LoadLibraryW( (const wchar_t*)filename); } FuncType _GetFunction(const char* filename) { return GetProcAddress(_module, filename); } void _FileErrorCheck() { if (_module == nullptr) { DWORD dwError = GetLastError(); LPSTR lpMsgBuf; FormatMessageA( FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS, NULL, dwError, MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), (LPSTR)&lpMsgBuf, 0, NULL ); _latest_error = lpMsgBuf; // メモリを解放 LocalFree(lpMsgBuf); _load_success = false; } else { _latest_error.clear(); _load_success = true; } } void _ModuleUnloader() { FreeLibrary(_module); }
#elif defined(__APPLE__) && defined(__MACH__)
using ModuleType = void*; using FuncType = void*; ModuleType _ModuleLoad(const char* filename) { dlerror(); return dlopen(filename, RTLD_LAZY); } void _FileErrorCheck() { if (_module == nullptr) { const char* error_msg = dlerror(); if (error_msg) { _latest_error = error_msg; } } } FuncType _GetFunction(const char* function_name) { return dlsym(_module, function_name); } void _ModuleUnloader() { dlclose(_module); }
#elif defined(__linux__)
using ModuleType = void*; using FuncType = void*; ModuleType _ModuleLoad(const char* filename) { dlerror(); return dlopen(filename, RTLD_LAZY); } void _FileErrorCheck() { if (_module == nullptr) { const char* error_msg = dlerror(); if (error_msg) { _latest_error = error_msg; } } } FuncType _GetFunction(const char* function_name) { return dlsym(_module, function_name); } void _ModuleUnloader() { dlclose(_module); }
#else #error "Unknown platform" #endif std::string _latest_error; ModuleType _module = nullptr; bool _load_success = false; public:
template<typename CharType> ModuleLoader(const CharType* module_name) { _latest_error.clear(); _module = _ModuleLoad(module_name); _FileErrorCheck(); } template<typename Function> Function* GetFunction(const char* function_name) { auto func = _GetFunction(function_name); if(func == nullptr) { _latest_error = "Function \"" + std::string(function_name) + "\" is not found"; return nullptr; } return reinterpret_cast<Function*>(func); } const std::string& GetErrorMessage() const { return _latest_error; } bool IsLoadSuccess() const { return _load_success; } ~ModuleLoader() { _ModuleUnloader(); }
};
a.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "ModuleLoader.hpp" int main() { //ModuleLoader loader("MyDLL.dll"); ModuleLoader loader("mylib.so"); if (loader.IsLoadSuccess() == false) { std::cout << loader.GetErrorMessage() << std::endl; std::function<int(int, int)> add_func = loader.GetFunction<int(int, int)>("add"); if (add_func == nullptr) { std::cout << loader.GetErrorMessage() << std::endl; } else { int result = add_func(3, 5); std::cout << "result::: " << result << std::endl; } } return 0; }
VC++でdynaloを使用しDLLを動的ロードする
Win32APIではLoadLibraryを使用してdllを動的ロードできるが、クロスプラットフォームのライブラリのdynaloを使用してみる。dynaloはヘッダオンリーなのでその点はよい。
https://github.com/maddouri/dynalo
プラグイン機能を作りたくて探していてdynaloを見つけたのだが、正直以下の理由により個人的意見としては他の手を探したい。今記事のストックが無くて困っているので書いておく。
Windowsでdynaloを使う場合
Windowsでは内部でWin32APIのLoadLibraryを使用しているが、実はLoadLibraryはマクロで、実体はLoadLibraryW,LoadLibraryAのいずれかであり、これはUNICODEマクロで切り替えられている。
プロジェクトをUNICODEでビルドすると、LoadLibraryWが有効化されるが、dynaloのコンストラクタがstd::stringをとるため、型の違いで以下のエラーが出る。
dynalo-master\include\dynalo\detail\windows\dynalo.hpp(36,24): error C2665: 'std::basic_string<char,std::char_traits<char>,std::allocator<char>>::basic_string': オーバーロードされた関数ですべての引数の型を変換できませんでした dynalo-master\include\dynalo\detail\windows\dynalo.hpp(66,35): error C2664: 'HMODULE LoadLibraryW(LPCWSTR)': 引数 1 を 'const _Elem *' から 'LPCWSTR' へ変換できません。 dynalo-master\include\dynalo\detail\windows\dynalo.hpp(66,35): error C2664: with dynalo-master\include\dynalo\detail\windows\dynalo.hpp(66,35): error C2664: [ dynalo-master\include\dynalo\detail\windows\dynalo.hpp(66,35): error C2664: _Elem=char dynalo-master\include\dynalo\detail\windows\dynalo.hpp(66,35): error C2664: ]
対処法
要は中でWindows.hを読んでいるということなので、マルチバイトでビルドすればいけるが、ライブラリを使用するために文字セットの設定を変えるのは避けたい。とりあえず動作確認だけなら以下のようにUNICODEマクロを無効化すればいい。しかしほかのWin32APIの使用箇所との不整合が起こる気がする。
結論:プロジェクトがUNICODEなら他のライブラリを使うべき
// WindowsでUnicodeでビルドすると、UNICODEマクロが定義されるので、 // LoadLibrary関数がLoadLibraryWになる。そのため、UNICODEマクロをundefする。 #undef UNICODE #include "dynalo.hpp" #define UNICODE
使用例
DLL側
特に何も考えずDLLを作成
BOOL APIENTRY DllMain( HMODULE hModule, DWORD ul_reason_for_call, LPVOID lpReserved ) { switch (ul_reason_for_call) { case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH: case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH: case DLL_THREAD_DETACH: case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH: break; } return TRUE; }
extern "C" { __declspec(dllexport) int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; }
}
使用例
get_functionで関数を取得できる。
#include <iostream> #include <functional> // マルチバイト文字セットでビルドすること #include "dynalo.hpp" int main() { try { // DLLのロード dynalo::library mydll("MyDLL.dll"); // 関数の取得 std::function<int(int,int)> add_func = mydll.get_function<int(int, int)>("add"); // 関数を実行 int result = add_func(3, 5); std::cout << "result = " << result << std::endl; } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cerr << "Error: " << e.what() << std::endl; } return 0; }
動的ライブラリのロード方法
Windows
書いたつもりだがサイト内検索しても出てこないのでまだやってないらしい。
#include <iostream> #include <functional> #include <Windows.h> int main() { HMODULE hModule = LoadLibraryA("MyDLL.dll"); FARPROC func = GetProcAddress(hModule, "add"); std::function<int(int, int)> add_func = reinterpret_cast<int(*)(int, int)>(func); int result = add_func(3, 5); std::cout << "result: " << result << std::endl; FreeLibrary(hModule); return 0; }
Linux
mylib.so
extern "C" { int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; } }
a.out
#include <iostream> #include <functional> #include <dlfcn.h> int main(){ void* handle = dlopen("./mylib.so",RTLD_LAZY); using add_func_ptr = int (*)(int,int); std::function<int(int,int)> add_func =(add_func_ptr)dlsym(handle,"add"); int result = add_func(3,5); std::cout << "result:" << result << std::endl; dlclose(handle); }
所感
さすがに記事が寂しすぎるのでWindowsとLinux版のコードを載せた。
あとMacOSでは拡張子を.dylibにすればよいらしい。
vulkanをインストール・Rust+ashで動作確認
とりあえずVulkan SDKをいれる。LunarGのサイトからVulkanSDKのインストーラをダウンロードしてインストール。
何も考えず次へを押していく。なおインストール先のデフォルトはC:\VulkanSDK\バージョン。
Rustで動作チェック
Rustのvulkanラッパーはいくつかあるがとりあえずashを使用
Cargo.toml
ash = { version = "0.38.0", features = ["linked"] }
main.rs
extern crate ash; use ash::vk; use std::ffi::{CStr, CString}; use std::ptr; fn main() { ///////////////////////////////////////////// // Vulkanライブラリのエントリポイントを作成 let entry = ash::Entry::linked(); ///////////////////////////////////////////// // アプリケーション情報を設定 let app_name = CString::new("Vulkan Sample").unwrap(); let engine_name = CString::new("No Engine").unwrap(); let app_info = vk::ApplicationInfo { s_type: vk::StructureType::APPLICATION_INFO, p_next: ptr::null(), p_application_name: app_name.as_ptr(), application_version: vk::make_version(1, 0, 0), p_engine_name: engine_name.as_ptr(), engine_version: vk::make_version(1, 0, 0), api_version: vk::API_VERSION_1_0, _marker: Default::default(), }; ///////////////////////////////////////////// // インスタンス作成情報の設定 let create_info = vk::InstanceCreateInfo { s_type: vk::StructureType::INSTANCE_CREATE_INFO, p_next: ptr::null(), flags: vk::InstanceCreateFlags::empty(), p_application_info: &app_info, enabled_layer_count: 0, pp_enabled_layer_names: ptr::null(), enabled_extension_count: 0, pp_enabled_extension_names: ptr::null(), _marker: Default::default(), }; ///////////////////////////////////////////// // Vulkanインスタンスの作成 let instance = unsafe { entry.create_instance(&create_info, None) .expect("Vulkanインスタンスの作成に失敗しました") }; ///////////////////////////////////////////// // システム上の物理デバイス(GPUなど)の列挙 let physical_devices = unsafe { instance.enumerate_physical_devices() .expect("物理デバイスの列挙に失敗しました") }; println!("検出された物理デバイス数: {}", physical_devices.len()); ///////////////////////////////////////////// // デバイスの情報を出力 for device in physical_devices { let properties = unsafe { instance.get_physical_device_properties(device) }; // device_name はnull終端 let device_name = unsafe { CStr::from_ptr(properties.device_name.as_ptr()) }; println!("デバイス名: {}", device_name.to_str().unwrap()); } ///////////////////////////////////////////// // 使用したVulkanインスタンスの破棄 unsafe { instance.destroy_instance(None); } }
結果
デバイス名: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3070 Ti
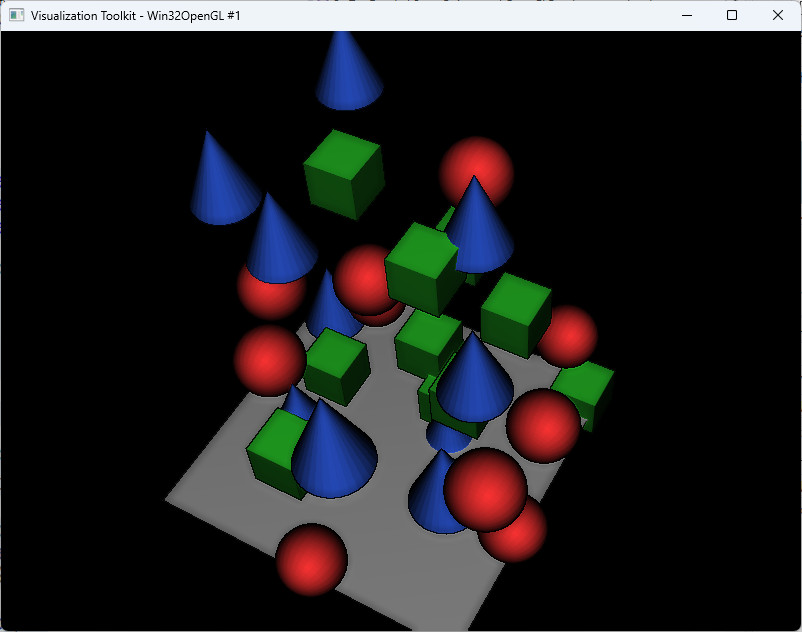
VTKでEDLシェーダを使用してみる
vtkEDLShadingを使うと簡単にEDLシェーダを使用できる。
コード
#pragma warning(disable:4996) //VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include <vtkOpenGLRenderer.h> #include <vtkOpenGLRenderWindow.h> //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include <vtkRenderStepsPass.h> #include <vtkEDLShading.h> //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include <vtkConeSource.h> #include <vtkCubeSource.h> #include <vtkPlaneSource.h> #include <vtkProperty.h> #include <vtkSphere.h> #include <vtkSphereSource.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //#include <vtkCamera.h> #pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "Psapi.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "Dbghelp.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void SetTestData(vtkSmartPointer<vtkOpenGLRenderer> renderer); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// int main() { auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkOpenGLRenderer>::New(); auto window = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); window->AddRenderer(renderer); SetTestData(renderer); // 表示データの設定 renderer->ResetCamera();
// EDL シェーダの設定 auto basicPasses = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderStepsPass>::New(); auto edl = vtkSmartPointer<vtkEDLShading>::New(); edl->SetDelegatePass(basicPasses); // renderer に EDL を適用 renderer->SetPass(edl); // マルチサンプリングオフ。EDL とは相性が悪い。深度バッファの計算が正しく行われないため。 window->SetMultiSamples(0);
// ウィンドウサイズ
window->SetSize(800, 600);
auto interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New();
window->SetInteractor(interactor);
interactor->Initialize();
window->Render();
interactor->Start();
return 0;
}
void SetTestData(vtkSmartPointer<vtkOpenGLRenderer> renderer)
{
{
auto planeSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPlaneSource>::New();
planeSource->SetOrigin(-5.0, 0.0, -5.0);
planeSource->SetPoint1(5.0, 0.0, -5.0);
planeSource->SetPoint2(-5.0, 0.0, 5.0);
planeSource->SetResolution(50, 50);
planeSource->Update();
planeSource->SetCenter(0.0, -5.0, 0.0);
auto planeMapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
planeMapper->SetInputConnection(planeSource->GetOutputPort());
auto planeActor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
planeActor->SetMapper(planeMapper);
planeActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(0.8, 0.8, 0.8); // 薄いグレー
planeActor->GetProperty()->SetSpecular(0.1);
planeActor->GetProperty()->SetDiffuse(0.9);
renderer->AddActor(planeActor);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
// x,y,zを乱数で生成
double x, y, z;
x = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
y = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
z = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
auto sphereSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource>::New();
sphereSource->SetCenter(-2.0, 1.0, 0.0); // 床から1.0上に
sphereSource->SetRadius(1.0);
sphereSource->SetThetaResolution(30);
sphereSource->SetPhiResolution(30);
sphereSource->Update();
sphereSource->SetCenter(x, y, z);
auto sphereMapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
sphereMapper->SetInputConnection(sphereSource->GetOutputPort());
auto sphereActor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
sphereActor->SetMapper(sphereMapper);
sphereActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(1.0, 0.2, 0.2); // 赤っぽい色
renderer->AddActor(sphereActor);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
// x,y,zを乱数で生成
double x, y, z;
x = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
y = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
z = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
auto coneSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkConeSource>::New();
coneSource->SetCenter(2.0, 0.0, 0.0);
coneSource->SetRadius(1.0);
coneSource->SetHeight(2.5);
coneSource->SetDirection(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); // Y軸方向に伸ばす
coneSource->SetResolution(30);
coneSource->Update();
coneSource->SetCenter(x, y, z);
auto coneMapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
coneMapper->SetInputConnection(coneSource->GetOutputPort());
auto coneActor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
coneActor->SetMapper(coneMapper);
coneActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(0.2, 0.4, 1.0); // 青系
renderer->AddActor(coneActor);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
// x,y,zを乱数で生成
double x, y, z;
x = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
y = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
z = (-0.5 + rand() / double(RAND_MAX)) * 10;
auto cubeSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCubeSource>::New();
cubeSource->SetCenter(0.0, 1.0, 2.0);
cubeSource->SetXLength(1.5);
cubeSource->SetYLength(1.5);
cubeSource->SetZLength(1.5);
cubeSource->Update();
cubeSource->SetCenter(x, y, z);
auto cubeMapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
cubeMapper->SetInputConnection(cubeSource->GetOutputPort());
auto cubeActor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
cubeActor->SetMapper(cubeMapper);
cubeActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(0.2, 1.0, 0.2); // 緑系
renderer->AddActor(cubeActor);
}
}
VTKで頂点距離を可視化
メッシュ1の頂点からメッシュ2の頂点を探索し、最も近い頂点への距離をスカラー値としてVTKに登録して、カラーテーブルを指定して着色する。

#include <iostream> //VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> //円筒とその表示に必要 #include <vtkPointData.h> #include <vtkCellData.h> #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #include <vtkLookupTable.h> #include <vtkFloatArray.h> #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"psapi.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"dbghelp.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"ws2_32.lib") #include <vtkCellArray.h> #include <vtkTriangle.h> #include <open3d/Open3D.h> #include <open3d/geometry/PointCloud.h> #include <open3d/geometry/TriangleMesh.h> // kdtree #include <open3d/geometry/KDTreeFlann.h> #pragma comment(lib,"Open3D.lib") //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
// baseの各頂点に対して、targetの最も近い頂点までの距離を計算する std::vector<double> calcNearestPoint(std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> base, std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> target) { std::vector<double> ret; // mymeshの頂点のkd-treeを作成 open3d::geometry::KDTreeFlann kdtree; kdtree.SetGeometry(*target); // 頂点Pに最も近い頂点を探す std::vector<double> distances; std::vector<int> indices; for (auto& p : base->vertices_) { int count = kdtree.SearchKNN(p,1,indices,distances); double distance = sqrt(distances[0]); ret.push_back(distance); } return ret; }
// テストデータを作成 void CreateMeshData_o3d_1(std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> mymesh, int xcount, int ycount, float width, float height,float offsetz, float depth, float density) { // 頂点の登録 for (int i = 0; i < xcount; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < ycount; ++j) { double x = -0.5 + 1.0 * i / (xcount - 1); double y = -0.5 + 1.0 * j / (ycount - 1); double z = sin(x * density) * depth + sin(y * density) * depth + offsetz; mymesh->vertices_.push_back(Eigen::Vector3d(x * width, y * height, z)); } } // メッシュ(三角形)の作成 for (int i = 0; i < xcount - 1; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < ycount - 1; ++j) { // 四角形を2つの三角形に分割 const int p1 = i * ycount + j; // 左下 const int p2 = (i + 1) * ycount + j; // 右下 const int p3 = i * ycount + (j + 1); // 左上 const int p4 = (i + 1) * ycount + (j + 1); // 右上 // 三角形1 (p1, p2, p3) mymesh->triangles_.push_back(Eigen::Vector3i(p1, p2, p3)); // 三角形2 (p2, p4, p3) mymesh->triangles_.push_back(Eigen::Vector3i(p2, p4, p3)); } } }
struct MeshData { std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> curve; std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> flat; }; MeshData createData(int xcount,int ycount) { std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> mymesh1 = std::make_shared<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh>(); std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> mymesh2 = std::make_shared<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh>(); CreateMeshData_o3d_1(mymesh1, xcount, ycount, 2, 2, 0.0, 0.1, 10); CreateMeshData_o3d_1(mymesh2, xcount, ycount, 2, 2,-0.3, 0.05, 17); return MeshData{ mymesh1,mymesh2 }; }
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> CreateVTKMeshData(std::shared_ptr<open3d::geometry::TriangleMesh> tri,int xcount,int ycount) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> triangles = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> vertices = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); for(auto& p : tri->vertices_) { vtkIdType pid = points->InsertNextPoint(p.x(), p.y(), p.z()); vertices->InsertNextCell(1, &pid); } // メッシュ(三角形)の作成 for (int i = 0; i < xcount - 1; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < ycount - 1; ++j) { // 四角形を2つの三角形に分割 vtkIdType p1 = i * ycount + j; // 左下 vtkIdType p2 = (i + 1) * ycount + j; // 右下 vtkIdType p3 = i * ycount + (j + 1); // 左上 vtkIdType p4 = (i + 1) * ycount + (j + 1); // 右上 // 三角形1 (p1, p2, p3) vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle> triangle1 = vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle>::New(); triangle1->GetPointIds()->SetId(0, p1); triangle1->GetPointIds()->SetId(1, p2); triangle1->GetPointIds()->SetId(2, p3); triangles->InsertNextCell(triangle1); // 三角形2 (p2, p4, p3) vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle> triangle2 = vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle>::New(); triangle2->GetPointIds()->SetId(0, p2); triangle2->GetPointIds()->SetId(1, p4); triangle2->GetPointIds()->SetId(2, p3); triangles->InsertNextCell(triangle2); } } // vtkPolyData の作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(points); polyData->SetPolys(triangles); // 三角形セルを設定 return polyData; }
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> createActor(vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData, vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> table,double min_,double max_ ) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputData(polyData); if( table != nullptr) { mapper->SetLookupTable(table); mapper->SetScalarRange(min_, max_); mapper->SetInterpolateScalarsBeforeMapping(true); } vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); return actor; }
//! @brief サーモグラフィー風のカラールックアップテーブルを生成する //! @param [in] scalar_min スカラー値の最小値 //! @param [in] scalar_max スカラー値の最大値 //! @param [in] division スカラー値の範囲を何分割するか //! @return カラールックアップテーブル vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> ThermographyColorTable(const double scalar_min, const double scalar_max, const int division) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> lut = vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable>::New(); lut->SetNumberOfTableValues(division); // テーブルの要素数を設定 lut->SetTableRange(scalar_min, scalar_max); // スカラー値の範囲を設定 lut->Build(); // テーブルの i 番目の要素に対応する色を設定 for (int i = 0; i < division; i++) { double t = static_cast<double>(i) / float(division - 1); double r, g, b; if (t < 0.33) { // 青から緑への補間 double factor = t / 0.33; r = 0.0; g = factor; b = 1.0 - factor; } else if (t < 0.66) { // 緑から黄への補間 double factor = (t - 0.33) / 0.33; r = factor; g = 1.0; b = 0.0; } else { // 黄から赤への補間 double factor = (t - 0.66) / 0.34; r = 1.0; g = 1.0 - factor; b = 0.0; } // テーブルの i 番目の要素に色を設定 lut->SetTableValue( i // テーブルの要素番号 , r, g, b, 1.0 ); } return lut; }
int main(int /*argc*/, char** /*argv*/) { auto meshes = createData(100, 100); std::vector<double> scalar = calcNearestPoint(meshes.curve, meshes.flat); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> curve = CreateVTKMeshData(meshes.curve, 100, 100); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> flat = CreateVTKMeshData(meshes.flat, 100, 100); // scalarをvtkFloatArrayに変換 vtkSmartPointer<vtkFloatArray> scalars = vtkSmartPointer<vtkFloatArray>::New(); scalars->SetName("MyScalarValues"); double _min = *std::min_element(scalar.begin(), scalar.end()); double _max = *std::max_element(scalar.begin(), scalar.end()); for (auto& s : scalar) { scalars->InsertNextValue(s); } curve->GetPointData()->AddArray(scalars); curve->GetPointData()->SetActiveScalars("MyScalarValues"); vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> colortable = ThermographyColorTable(_min, _max, 100); vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor1 = createActor(curve, colortable,_min,_max); vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor2 = createActor(flat,nullptr,0,0); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(actor1); renderer->AddActor(actor2); renderer->ResetCamera(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); renderWindow->SetInteractor(interactor); renderWindow->Render(); interactor->Start(); //イベントループへ入る return 0; }
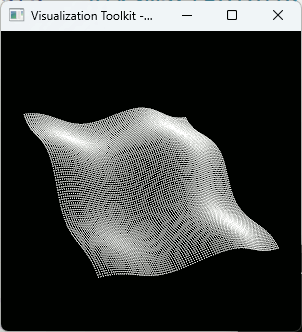
VTKでテスト用の簡単な曲面を描画

#include <iostream> //VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> #include <vtkPointData.h> #include <vtkCellData.h> #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"psapi.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"dbghelp.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"ws2_32.lib") #include <vtkCellArray.h> #include <vtkTriangle.h> //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> CreateMeshData(bool cloudonly,int xcount, int ycount,float width,float height,float depth,float density) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> triangles = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> vertices = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); // 頂点の登録 for (int i = 0; i < xcount; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < ycount; ++j) { double x = -0.5 + 1.0 * i / (xcount - 1); double y = -0.5 + 1.0 * j / (ycount - 1); double z = sin(x * density)*depth + sin(y * density) * depth; vtkIdType pid = points->InsertNextPoint(x*width, y*height, z); if (cloudonly == true) { vertices->InsertNextCell(1, &pid); } } } if (cloudonly == true) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(points); polyData->SetVerts(vertices); return polyData; } // メッシュ(三角形)の作成 for (int i = 0; i < xcount - 1; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < ycount - 1; ++j) { // 四角形を2つの三角形に分割 vtkIdType p1 = i * ycount + j; // 左下 vtkIdType p2 = (i + 1) * ycount + j; // 右下 vtkIdType p3 = i * ycount + (j + 1); // 左上 vtkIdType p4 = (i + 1) * ycount + (j + 1); // 右上 // 三角形1 (p1, p2, p3) vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle> triangle1 = vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle>::New(); triangle1->GetPointIds()->SetId(0, p1); triangle1->GetPointIds()->SetId(1, p2); triangle1->GetPointIds()->SetId(2, p3); triangles->InsertNextCell(triangle1); // 三角形2 (p2, p4, p3) vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle> triangle2 = vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangle>::New(); triangle2->GetPointIds()->SetId(0, p2); triangle2->GetPointIds()->SetId(1, p4); triangle2->GetPointIds()->SetId(2, p3); triangles->InsertNextCell(triangle2); } } // vtkPolyData の作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(points); polyData->SetPolys(triangles); // 三角形セルを設定 return polyData; }
int main(int /*argc*/, char** /*argv*/) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = CreateMeshData(false,500, 500,2,2,0.1,10); vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputData(polyData); actor->SetMapper(mapper); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(actor); renderer->ResetCamera(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); ////////////////////////////////////// auto renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); renderWindow->SetInteractor(interactor); renderWindow->Render(); interactor->Start(); //イベントループへ入る return 0; }
vtkLookupTableで頂点に設定したスカラー値を元にサーモグラフィー着色
#include <iostream> //VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> #include <vtkSmartPointer.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> //円筒とその表示に必要 #include <vtkPointData.h> #include <vtkCellData.h> #include <vtkPolyData.h> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> #include <vtkLookupTable.h> #include <vtkFloatArray.h> #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"psapi.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"dbghelp.lib") #pragma comment(lib,"ws2_32.lib") #include <vtkCellArray.h> #include <vtkTriangle.h> //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
//! @brief サーモグラフィー風のカラールックアップテーブルを生成する //! @param [in] scalar_min スカラー値の最小値 //! @param [in] scalar_max スカラー値の最大値 //! @param [in] division スカラー値の範囲を何分割するか //! @return カラールックアップテーブル vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> ThermographyColorTable(const double scalar_min, const double scalar_max, const int division) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> lut = vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable>::New(); lut->SetNumberOfTableValues(division); // テーブルの要素数を設定 lut->SetTableRange(scalar_min, scalar_max); // スカラー値の範囲を設定 lut->Build(); // テーブルの i 番目の要素に対応する色を設定 for (int i = 0; i < division; i++) { double t = static_cast<double>(i) / float(division - 1); double r, g, b; if (t < 0.33) { // 青から緑への補間 double factor = t / 0.33; r = 0.0; g = factor; b = 1.0 - factor; } else if (t < 0.66) { // 緑から黄への補間 double factor = (t - 0.33) / 0.33; r = factor; g = 1.0; b = 0.0; } else { // 黄から赤への補間 double factor = (t - 0.66) / 0.34; r = 1.0; g = 1.0 - factor; b = 0.0; } // テーブルの i 番目の要素に色を設定 lut->SetTableValue( i // テーブルの要素番号 ,r,g,b,1.0 ); } return lut; }
int main(int, char* []) { ///////////////////////////// // 三頂点を定義 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); points->InsertNextPoint(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); points->InsertNextPoint(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); points->InsertNextPoint(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); // 三角形を定義 vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> triangles = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); vtkIdType pts[3] = { 0, 1, 2 }; triangles->InsertNextCell(3, pts); // ポリゴンデータを作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(points); polyData->SetPolys(triangles); ///////////////////////////// // 各頂点にスカラー値を設定 vtkSmartPointer<vtkFloatArray> scalars = vtkSmartPointer<vtkFloatArray>::New(); scalars->SetName("MyScalarValues"); scalars->InsertNextValue(0.0); // 頂点0 に 0.0 を設定 scalars->InsertNextValue(50.0); // 頂点1 に 50.0 を設定 scalars->InsertNextValue(100.0); // 頂点2 に 100.0 を設定 polyData->GetPointData()->SetScalars(scalars); vtkSmartPointer<vtkFloatArray> scalars2 = vtkSmartPointer<vtkFloatArray>::New(); scalars2->SetName("MyScalarValues2"); scalars2->InsertNextValue(0.0); // 頂点0 に 0.0 を設定 scalars2->InsertNextValue(90.0); // 頂点1 に 50.0 を設定 scalars2->InsertNextValue(0.0); // 頂点2 に 100.0 を設定 polyData->GetPointData()->AddArray(scalars2); polyData->GetPointData()->SetActiveScalars("MyScalarValues"); ///////////////////////////// // ルックアップテーブルの設定 // scalar_min から scalar_max までのスカラー値を 100 段階に分け、それぞれの範囲に対応する色を設定 float scalar_min = 0.0; float scalar_max = 100.0; // スカラー値の最小値と最大値 int division = 200; // スカラー値の範囲を何分割するか vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> thermocolor = ThermographyColorTable(scalar_min, scalar_max,division); ///////////////////////////// // マッパーとアクターの設定 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputData(polyData); mapper->SetLookupTable(thermocolor); mapper->SetScalarRange(scalar_min, scalar_max); // スカラー値の補間を先に行い、その後ルックアップテーブルで色を決定 mapper->SetInterpolateScalarsBeforeMapping(true); vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); ///////////////////////////// // レンダラー等の設定 vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer> renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); renderer->AddActor(actor); renderer->SetBackground(0.1, 0.1, 0.1); vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow> renderWindow = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); renderWindow->SetSize(800, 600); vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor> interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); interactor->SetRenderWindow(renderWindow); renderWindow->Render(); interactor->Start(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }