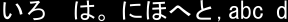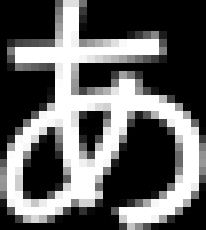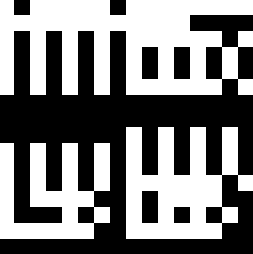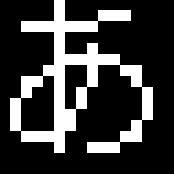FreeType2を試す-5- 一行のテキストを出力
文字列を画像として出力する。
仕組みとしては、画像と高さ、幅情報、移動量情報を全て配列にし、一行分描画してから高さ計算を行う。
#pragma once #include <ft2build.h> #include FT_FREETYPE_H #include <freetype/ftbitmap.h> #include <vector>
// 人文字の画像とサイズ・位置の情報 struct charpict { std::vector<char> m_pic; int width; int height; int left; int top; int advancex; int advancey; };
// 文字列をラスタライズするクラス class SingleLineText { std::vector<charpict> m_pict; int imageWidth; //!< 結果画像の幅 int imageHeight;//!< 結果画像の高さ std::vector<unsigned char> m_image;//!< 結果画像 FT_Library* m_plib; FT_Face face; // handle to face object
//! @brief m_imageに書き込むための座標計算関数 //! @param [in] x 二次元座標のx //! @param [in] y 二次元座標のy //! @return 一次元配列のindex int pixel_pos(const int x, const int y) { return y * imageWidth + x; }
//! @brief 作成済みの一文字の画像を全体画像に書き込む //! @param [in] index m_pictのindex。何文字目をレンダリングするか //! @param [in] pen_x この文字のm_image上の描画開始位置 //! @param [in] maxtop 全ての文字の中の高さの最大値 //! @return なし void draw_single_character(const int index, const int pen_x, const int maxtop) { char* buffer = &m_pict[index].m_pic[0]; int Width = m_pict[index].width; int Height = m_pict[index].height; int startx = pen_x + m_pict[index].left; int starty = -m_pict[index].top + maxtop; for (size_t y = 0; y < Height; y++) { for (size_t x = 0; x < Width; x++) { int xx = startx + x; int yy = starty + y; if (xx < 0)continue; if (yy < 0)continue; if (xx >= imageWidth)continue; if (yy >= imageHeight)continue; if (buffer[y * Width + x]) { m_image[pixel_pos(xx, yy)] = buffer[y * Width + x]; } } } }
//! @brief 全ての文字を結果に書き込む //! @param [in] maxtop 全ての文字の中の高さの最大値 //! @return なし void characters_to_image(const int maxtop) { int pen_x = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < m_pict.size(); i++) { if (m_pict[i].m_pic.size()) { // 画像書き込み draw_single_character(i, pen_x,maxtop); } // 描画位置を更新 pen_x += m_pict[i].advancex; } }
public:
//! @brief コンストラクタ //! @param [in] ftLib FreeTypeライブラリオブジェクトへのポインタ //! @param [in] fontfilename フォントファイル名 SingleLineText(FT_Library* ftLib,const char* fontfilename) { m_plib = ftLib; FT_Error error; // フォントファイル読み込み error = FT_New_Face( *m_plib, fontfilename, 0, &face ); //文字コード指定 error = FT_Select_Charmap( face, // target face object FT_ENCODING_UNICODE // エンコード指定 ); if (error == FT_Err_Unknown_File_Format) { throw "FT_Err_Unknown_File_Format"; } else if (error) { throw "FT_Err"; } }
//! @brief ラスタライズ
//! @param [in] text 元のテキスト
//! @param [in] pixel_size_y 文字サイズ
//! @return なし
void rasterize(std::wstring text,const int pixel_size_y) {
FT_Error error;
error = FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes(
face, // handle to face object
0, // pixel_width
pixel_size_y); // pixel_height
int maxtop = INT_MIN;
imageHeight = INT_MIN;
imageWidth = 0;
m_pict.clear();
//textの各文字について画像を作成
for (size_t k = 0; k < text.size(); k++) {
// 文字の取得
FT_ULong character = text[k];
FT_UInt char_index = FT_Get_Char_Index(face, character);
// グリフ(字の形状)読込
//FT_LOAD_COLOR
error = FT_Load_Glyph(face, char_index, FT_LOAD_RENDER | FT_LOAD_COLOR);
if (error)
return; // ignore errors
// 文字を画像化
//FT_RENDER_MODE_MONO
//FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL
FT_Render_Glyph(face->glyph, FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL);
//データを8bit画像にする
FT_Bitmap tmpbmp;
FT_Bitmap_Init(&tmpbmp);
FT_Bitmap_Convert(*m_plib, &face->glyph->bitmap, &tmpbmp, 1);
m_pict.emplace_back();
////////////////////////////////////////
//画像を配列に保存
const int Width = tmpbmp.width;
const int Height = tmpbmp.rows;
for (size_t y = 0; y < Height; y++) {
for (size_t x = 0; x < Width; x++) {
m_pict.back().m_pic.push_back(tmpbmp.buffer[y * Width + x]);
}
}
FT_Bitmap_Done(*m_plib, &tmpbmp);
m_pict.back().width = Width;
m_pict.back().height = Height;
m_pict.back().left = face->glyph->bitmap_left;
m_pict.back().top = face->glyph->bitmap_top;
m_pict.back().advancex = face->glyph->advance.x >> 6;
m_pict.back().advancey = face->glyph->advance.y >> 6;
////////////////////////////////////////
maxtop = (std::max)(maxtop, m_pict.back().top);
imageHeight = (std::max)(
imageHeight,
-m_pict[k].top + maxtop + m_pict[k].height
);
imageWidth += m_pict.back().advancex;
}
//結果画像のメモリ確保
m_image.resize(imageWidth * imageHeight, 0);
//画像に全ての文字を書き込む
characters_to_image(maxtop);
}
void done_face() { FT_Done_Face(face); }
int ImageWidth() { return imageWidth; } int ImageHeight() { return imageHeight; } const unsigned char* image()const { return &m_image[0]; } };
呼び出し
#include <string> #include <array> #include "SingleLineText.hpp" #include "pnm_rw.hpp" #pragma warning(disable:4996) #pragma comment(lib,"freetyped.lib") int main() { FT_Library library; // handle to library FT_Error error; error = FT_Init_FreeType(&library); if (error) return -1; ////msgothic.ttc //meiryo SingleLineText slt(&library, "C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\msgothic.ttc"); int pixel_size_y = 24; std::wstring chars = L"いろ は。にほへと,abc d"; slt.rasterize(chars, pixel_size_y);//画像の作成 //ファイル出力 write_pnm( "C:\\test\\text.pgm", slt.image(), slt.ImageWidth(), slt.ImageHeight(), PNM_TYPE::P2 ); slt.done_face(); // FreeType2の解放 FT_Done_FreeType(library); }
FreeType2を試す-4 – アンチエイリアス
#include <ft2build.h> #include FT_FREETYPE_H //FT_Bitmap_Convert #include <freetype/ftbitmap.h> #pragma warning(disable:4996) #pragma comment(lib,"freetype.lib")
//! @brief PGM(1byte,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details 1画素1Byteのメモリを渡すと、テキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pgmP2_Write(const char* const fname, const int width, const int height,const int vmax, const unsigned char* const p) { // PPM ASCII FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P2\n%d %d\n%d\n", width, height,vmax); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d ", p[k]); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
int main() { FT_Library library; // handle to library FT_Error error; error = FT_Init_FreeType(&library); if (error) return -1; FT_Face face; // handle to face object //msgothic.ttc //meiryo.ttc // フォントファイル読み込み error = FT_New_Face( library, "C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\msgothic.ttc", 0, &face ); //文字コード指定 error = FT_Select_Charmap( face, // target face object FT_ENCODING_UNICODE // エンコード指定 ); if (error == FT_Err_Unknown_File_Format) return -1; else if (error) return -1; int pixel_heigth = 32; //この二つの値でフォントサイズ調整 FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes( face, // handle to face object 0, // pixel_width pixel_heigth // pixel_height ); // 文字の取得 FT_ULong character = wchar_t(L'あ'); FT_UInt char_index = FT_Get_Char_Index(face, character);
// グリフ(字の形状)読込 error = FT_Load_Glyph(face, char_index, FT_LOAD_RENDER | FT_LOAD_COLOR); if (error) return -1; // ignore errors
// 文字を画像化 FT_Render_Glyph(face->glyph, FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL); FT_Bitmap glyphbitmap; FT_Bitmap_Convert(library, &face->glyph->bitmap, &glyphbitmap, 1); int Width = glyphbitmap.width; int Height = glyphbitmap.rows; pgmP2_Write(// ファイル保存 "C:\\test\\freetypetest.pbm", Width, Height, 255, glyphbitmap.buffer ); // FreeType2の解放 FT_Done_Face(face); FT_Done_FreeType(library); }
FreeType2を試す-3-小さいサイズで描画
出力用関数
//! @brief PBM(1byte,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details 1画素1Byteのメモリを渡すと、0,1テキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pbmP1_Write(const char* const fname, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p) { // PPM ASCII FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P1\n%d\n%d\n", width, height); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d ", p[k] ? 0 : 1); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
この時、以下のコードで、以下のpixel_heightで出力すると、正常に出力されない。文字サイズが小さすぎると結果が壊れる。
失敗例
#include <ft2build.h> #include FT_FREETYPE_H #pragma warning(disable:4996) #pragma comment(lib,"freetype.lib") int main() { FT_Library library; // handle to library FT_Error error; error = FT_Init_FreeType(&library); if (error) return -1; FT_Face face; // handle to face object //msgothic.ttc //meiryo.ttc // フォントファイル読み込み error = FT_New_Face( library, "C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\msgothic.ttc", 0, &face ); //文字コード指定 error = FT_Select_Charmap( face, // target face object FT_ENCODING_UNICODE // エンコード指定 ); if (error == FT_Err_Unknown_File_Format) return -1; else if (error) return -1;
int pixel_heigth =16;
//この二つの値でフォントサイズ調整 FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes( face, // handle to face object 0, // pixel_width pixel_heigth // pixel_height ); // 文字の取得 FT_ULong character = wchar_t(L'あ'); FT_UInt char_index = FT_Get_Char_Index(face, character); // グリフ(字の形状)読込 error = FT_Load_Glyph(face, char_index, FT_LOAD_RENDER); if (error) return -1; // ignore errors // 文字を画像化 FT_Render_Glyph(face->glyph, FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL); FT_Bitmap& glyphbitmap = face->glyph->bitmap; int Width = glyphbitmap.width; int Height = glyphbitmap.rows; pbmP1_Write(// ファイル保存 "C:\\test\\freetypetest.pbm", Width, Height, glyphbitmap.buffer ); // FreeType2の解放 FT_Done_Face(face); FT_Done_FreeType(library); }
これは(多分)、フォントサイズが小さいときはビットマップフォントが使われ、pixel_typeが変わってしまっているから。
FT_Bitmap_Convertで画像データを変換すれば、取り出したフォントの形式にかかわらず、8bppにできる。
FT_Bitmap glyphbitmap;// 新しい画像データ FT_Bitmap_Init(&glyphbitmap);// 新しい画像データの初期化 FT_Bitmap_Convert(library, &face->glyph->bitmap, &glyphbitmap, 1);// 文字画像を8bppに変換 int Width = glyphbitmap.width; int Height = glyphbitmap.rows; pgmP2_Write(// ファイル保存 "C:\\test\\freetypetest.pbm", Width, Height, 255, glyphbitmap.buffer ); FT_Bitmap_Done(library, &glyphbitmap);// 文字画像を解放
成功例
int main() { FT_Library library; // handle to library FT_Error error; error = FT_Init_FreeType(&library); if (error) return -1; FT_Face face; // handle to face object //msgothic.ttc //meiryo.ttc // フォントファイル読み込み error = FT_New_Face( library, "C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\msgothic.ttc", 0, &face ); //文字コード指定 error = FT_Select_Charmap( face, // target face object FT_ENCODING_UNICODE // エンコード指定 ); if (error == FT_Err_Unknown_File_Format) return -1; else if (error) return -1; int pixel_heigth = 16; //この二つの値でフォントサイズ調整 FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes( face, // handle to face object 0, // pixel_width pixel_heigth // pixel_height ); // 文字の取得 FT_ULong character = wchar_t(L'あ'); FT_UInt char_index = FT_Get_Char_Index(face, character); // グリフ(字の形状)読込 error = FT_Load_Glyph(face, char_index, FT_LOAD_RENDER | FT_LOAD_COLOR); if (error) return -1; // ignore errors // 文字を画像化 FT_Render_Glyph(face->glyph, FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL);
FT_Bitmap glyphbitmap; FT_Bitmap_Init(&glyphbitmap); FT_Bitmap_Convert(library, &face->glyph->bitmap, &glyphbitmap, 1); int Width = glyphbitmap.width; int Height = glyphbitmap.rows; pgmP2_Write(// ファイル保存 "C:\\test\\freetypetest.pbm", Width, Height, 255, glyphbitmap.buffer ); FT_Bitmap_Done(library, &glyphbitmap);
// FreeType2の解放 FT_Done_Face(face); FT_Done_FreeType(library); }
pixel_mode
フォントサイズによってpixel_modeが違うことがある。以下のコードで確認する。
switch (face->glyph->bitmap.pixel_mode) { case FT_PIXEL_MODE_NONE: printf("FT_PIXEL_MODE_NONE"); break; case FT_PIXEL_MODE_MONO: printf("FT_PIXEL_MODE_MONO"); break; case FT_PIXEL_MODE_GRAY: printf("FT_PIXEL_MODE_GRAY"); break; case FT_PIXEL_MODE_GRAY2: printf("FT_PIXEL_MODE_GRAY2"); break; case FT_PIXEL_MODE_GRAY4: printf("FT_PIXEL_MODE_GRAY4"); break; case FT_PIXEL_MODE_LCD: printf("FT_PIXEL_MODE_LCD"); break; case FT_PIXEL_MODE_LCD_V: printf("FT_PIXEL_MODE_LCD_V"); break; case FT_PIXEL_MODE_BGRA: printf("FT_PIXEL_MODE_BGRA"); break; } getchar();
| pixel height | pixel_mode |
|---|---|
| 16 | FT_PIXEL_MODE_MONO |
| 32 | FT_PIXEL_MODE_GRAY |
FreeType2を試す-2 文字列を描画してみる
#include <string> #include <array> #include <ft2build.h> #include FT_FREETYPE_H #pragma warning(disable:4996) #pragma comment(lib,"freetyped.lib")
const int imageWidth = 1000; const int imageHeight = 300; std::array<unsigned char, imageWidth* imageHeight> image; int pixel_pos(const int x, const int y) { return y * imageWidth + x; }
void draw(const FT_Bitmap& bmp,int startx, int starty) { int Width = bmp.width; int Height = bmp.rows; for (size_t y = 0; y < Height; y++) { for (size_t x = 0; x < Width; x++) { int xx = startx + x; int yy = starty + y; if (xx < 0)continue; if (yy < 0)continue; if (bmp.buffer[y*Width+x]) { image[pixel_pos(xx, yy)] = 1; } } } }
//! @brief PBM(1byte,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details 1画素1Byteのメモリを渡すと、0,1テキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pbmP1_Write(const char* const fname, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p) { // PPM ASCII FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P1\n%d\n%d\n", width, height); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d ", p[k]?0:1); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
int main() { FT_Library library; // handle to library FT_Error error; error = FT_Init_FreeType(&library); if (error) return -1; FT_Face face; // handle to face object // フォントファイル読み込み error = FT_New_Face( library, "C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\meiryo.ttc", 0, &face ); //文字コード指定 error = FT_Select_Charmap( face, // target face object FT_ENCODING_UNICODE // エンコード指定 ); if (error == FT_Err_Unknown_File_Format) return -1; else if (error) return -1; //この二つの値でフォントサイズ調整 FT_F26Dot6 fontsize=16*64; FT_UInt CHAR_RESOLUTION = 300; error = FT_Set_Char_Size( face, // handle to face object 0, // char_width in 1/64th of points fontsize, // char_height in 1/64th of points CHAR_RESOLUTION, // horizontal device resolution CHAR_RESOLUTION); // vertical device resolution int pen_x=0; int pen_y=0;
std::wstring chars = L"いろ は。にほへと,abc d"; for (size_t k = 0; k < chars.size(); k++) { // 文字の取得 FT_ULong character = chars[k]; FT_UInt char_index = FT_Get_Char_Index(face, character); // グリフ(字の形状)読込 error = FT_Load_Glyph(face, char_index, FT_LOAD_RENDER); if (error) return -1; // ignore errors // 文字を画像化 FT_Render_Glyph(face->glyph, FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL);
// 画像書き込み draw( face->glyph->bitmap, pen_x + face->glyph->bitmap_left, pen_y - face->glyph->bitmap_top + 100 );
// 描画位置を更新 pen_x += face->glyph->advance.x >> 6; pen_y += face->glyph->advance.y >> 6; // not useful for now }
// ファイル書き込み pbmP1_Write( "C:\\test\\freetypetest.pbm", imageWidth, imageHeight, &image[0] ); // FreeType2の解放 FT_Done_Face(face); FT_Done_FreeType(library); }
出力結果
ピクセル数で指定
/* //この二つの値でフォントサイズ調整 FT_F26Dot6 fontsize = 16 * 64; FT_UInt CHAR_RESOLUTION = 300; error = FT_Set_Char_Size( face, // handle to face object 0, // char_width in 1/64th of points fontsize, // char_height in 1/64th of points CHAR_RESOLUTION, // horizontal device resolution CHAR_RESOLUTION); // vertical device resolution */ FT_Set_Pixel_Sizes( face, // handle to face object 0, // pixel_width 64 // pixel_height );
FreeType2を試す-1-一文字だけ出力
まず一文字だけpbmファイル出力するプログラムが以下。
#include <ft2build.h> #include FT_FREETYPE_H #pragma warning(disable:4996) #pragma comment(lib,"freetype.lib")
//! @brief PBM(1byte,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details 1画素1Byteのメモリを渡すと、0,1テキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pbmP1_Write(const char* const fname, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p) { // PPM ASCII FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P1\n%d\n%d\n", width, height); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d ", p[k]?0:1); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
int main() { FT_Library library; // handle to library FT_Error error; error = FT_Init_FreeType(&library); if (error) return -1; FT_Face face; // handle to face object // フォントファイル読み込み error = FT_New_Face( library, "C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\meiryo.ttc", 0, &face ); //文字コード指定 error = FT_Select_Charmap( face, // target face object FT_ENCODING_UNICODE // エンコード指定 ); if (error == FT_Err_Unknown_File_Format) return -1; else if (error) return -1; //この二つの値でフォントサイズ調整 FT_F26Dot6 fontsize=16*64; FT_UInt CHAR_RESOLUTION = 300; error = FT_Set_Char_Size( face, // handle to face object 0, // char_width in 1/64th of points fontsize, // char_height in 1/64th of points CHAR_RESOLUTION, // horizontal device resolution CHAR_RESOLUTION); // vertical device resolution // 文字の取得 FT_ULong character = wchar_t(L'あ'); FT_UInt char_index = FT_Get_Char_Index(face, character); // グリフ(字の形状)読込 error = FT_Load_Glyph(face, char_index, FT_LOAD_RENDER); if (error) return -1; // ignore errors // 文字を画像化 FT_Render_Glyph(face->glyph, FT_RENDER_MODE_NORMAL); int Width = face->glyph->bitmap.width; int Height = face->glyph->bitmap.rows; pbmP1_Write(// ファイル保存 "C:\\test\\freetypetest.pbm", Width, Height, face->glyph->bitmap.buffer ); // FreeType2の解放 FT_Done_Face(face); FT_Done_FreeType(library); }
出力結果

PNM Writer(改)
PNMの書き込み関数を書いた。
ただし前回のPNM Readerで書いたPNM_TYPE列挙体が共通のため、前回のPNM Readerと同じファイルに書くことが望ましい。
プログラム本体(含 PNM Reader)
#pragma once #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm>
//! @brief PNMファイルの種類 enum class PNM_TYPE { P1 = 1, //Portable bitmap ASCII P2 = 2, //Portable graymap ASCII P3 = 3, //Portable pixmap ASCII P4 = 4, //Portable bitmap Binary P5 = 5, //Portable graymap Binary P6 = 6, //Portable pixmap Binary PError = 7, PBitmap = 8, PGraymap = 9, PPixmap = 10 };
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // PNM Reader
//! @class CGetGrayBits //! @brief 配列上のx番目の画素値を取得するクラス //! @sa https://suzulang.com/bit-depth-1-2-4-getpixelvalue/ class CGetGrayBits { unsigned char* m_p; //!< 画素へのポインタ const int m_depth = 1; //!< ビット深度 unsigned char m_mask = 1; //!< depth8未満の時のビットマスク public: //! @brief コンストラクタ //! @param [in] p 画素配列へのポインタ CGetGrayBits( const void* const p) : m_p(static_cast<unsigned char*>(const_cast<void*>(p))) { } //! @brief 指定した番号の画素を取得 //! @param [in] x 画素番号 //! @return 画素値 int operator[](const std::size_t x) { // x ドットが何バイト目かを算出 (0開始) std::size_t byte = x / (8 / m_depth); unsigned char c = m_p[byte]; std::size_t pos = x % (8 / m_depth); int shift = 8 - m_depth - pos * m_depth; unsigned char mask1 = m_mask << shift; unsigned int val = (c & mask1) >> shift; return val; } }; //! @brief ストリームから入力 bitmap ASCII //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] s 入力ストリーム void read_P1(std::vector<unsigned char>& img, std::ifstream& s) { while (s.eof() == false) { char c; s.read(&c, 1); if (isdigit(c) != false) { img.push_back(c - '0'); } } } //! @brief ストリームから入力 graymap,pixmap ASCII //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] s 入力ストリーム void read_P23(std::vector<unsigned char> & img, std::ifstream & s) { while (s.eof() == false) { std::string val; s >> val; int value; try { value = std::stoi(val); } catch (std::invalid_argument) { continue; } img.push_back(value); } } //! @brief ストリームから入力 bitmap Binary //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] s 入力ストリーム //! @return なし //! @details P4は1ビット=1画素なので全部読み込んでから1ビットずつとりだしている void read_P4(std::vector<unsigned char> & img, std::ifstream & s, int count) { std::vector<unsigned char> tmp; unsigned char tc; while (!s.eof()) { s.read((char*)& tc, sizeof(char)); tmp.push_back(tc); } CGetGrayBits bits(&tmp[0]); for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) { img.push_back(bits[i]); } } //! @brief ストリームから入力 graymap,pixmap Binary //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] s 入力ストリーム //! @return なし void read_P56(std::vector<unsigned char> & img, std::ifstream & s) { while (s.eof() == false) { unsigned char c; s.read((char*)& c, 1); img.push_back(c); } } //! @brief pnmファイルを読み込む //! @param [in] fpathname pnmファイルへのパス //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] width 横方向の画素数 //! @param [out] height 縦方向の画素数 //! @param [out] maxvalue 画素の最大値 //! @param [out] datatype 形式を識別する定数 //! @retval true 読込成功 //! @retval false 読込失敗 bool read_pnm(const char* fpathname, std::vector<unsigned char> * img, int* width, int* height, int* maxvalue, PNM_TYPE * datatype) { std::ifstream ifs(fpathname, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary); if (!ifs) return false; std::string text; *width = -1; *height = -1; *maxvalue = -1; //タイプの読み取り PNM_TYPE type; { int _type = (int)PNM_TYPE::PError; while (std::getline(ifs, text).eof() == false) { if (text[0] == 'P') { _type = ((int)text[1] - (int)'0'); break; } } switch (_type) { case (int)PNM_TYPE::P1:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PBitmap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P2:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PGraymap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P3:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PPixmap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P4:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PBitmap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P5:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PGraymap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P6:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PPixmap; break; default: *datatype = PNM_TYPE::PError; return false; } type = (PNM_TYPE)_type; } while (std::getline(ifs, text).eof() == false) { //コメントスキップ if (text[0] == '#') continue; //コメントでないなら各種値の入力 std::stringstream ss(text); //幅入力 if (*width < 0) { ss >> *width; if (*width < 0) continue; } //高さ入力 if (*height < 0) { ss >> *height; if (*height < 0) continue; } //最大値入力 if (*datatype != PNM_TYPE::PBitmap) { if (*maxvalue < 0) { ss >> *maxvalue; if (*maxvalue < 0) continue; } } break; } int count = *width * *height; switch (type) { case PNM_TYPE::P1: img->reserve(count); read_P1(*img, ifs); break; case PNM_TYPE::P2: img->reserve(count); read_P23(*img, ifs); break; case PNM_TYPE::P3: img->reserve(count * 3); read_P23(*img, ifs); break; case PNM_TYPE::P4: read_P4(*img, ifs, count); break; case PNM_TYPE::P5: read_P56(*img, ifs); break; case PNM_TYPE::P6: read_P56(*img, ifs); break; } }
// ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // PNM Writer
//! @brief 1byteの各ビットに配列のようにアクセスするためのクラス class bititerator_t { unsigned char* m_c; int m_index; public: bititerator_t(unsigned char* c, const int index) { m_c = c; m_index = 7 - index; } void operator=(const int value) { unsigned char mask = (1 << m_index); if (value) { *m_c |= mask; } else { *m_c &= ~mask; } } operator unsigned char() { unsigned char mask = (1 << m_index); return (*m_c & mask) ? 1 : 0; } }; //! @brief 1byteの各ビットに配列のようにアクセスするためのクラス class BitArray { unsigned char c; public: BitArray() :c(0) {} bititerator_t operator[](const int i) { return bititerator_t(&c, i); } operator unsigned char() { return c; } unsigned char operator=(const unsigned char value) { c = value; return c; } };
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//! @brief データタイプを文字列に変換 std::string to_string(const PNM_TYPE type) { switch (type) { case PNM_TYPE::P1:return "P1"; break; case PNM_TYPE::P2:return "P2"; break; case PNM_TYPE::P3:return "P3"; break; case PNM_TYPE::P4:return "P4"; break; case PNM_TYPE::P5:return "P5"; break; case PNM_TYPE::P6:return "P6"; break; } return ""; } //! @brief 各データタイプにおける1ピクセルのビット数を求める int pixel_bit_count(const PNM_TYPE type) { switch (type) { case PNM_TYPE::P1:return 1; break; case PNM_TYPE::P2:return 8; break; case PNM_TYPE::P3:return 8 * 3; break; case PNM_TYPE::P4:return 1; break; case PNM_TYPE::P5:return 8; break; case PNM_TYPE::P6:return 8 * 3; break; } return -1; }
//! @brief Portable bitmap ASCII //! @param [in,out] s 出力先 //! @param [in] img 1byte1画素の画像データ //! @param [in] width 幅画素数 //! @param [in] height 高さ画素数 //! @return なし void write_P1(std::ofstream& s, const unsigned char* img, const int width, const int height) { int count = width * height; for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) { s << std::to_string(img[i] ? 1 : 0); } }
//! @brief ストリームへ出力 Portable graymap ASCII //! @param [in,out] 出力先 //! @param [in] img 画像データ //! @param [in] width 画素数幅 //! @param [in] height 画素数高さ //! @return なし void write_P2(std::ofstream & s, const unsigned char* img, const int width, const int height) { int count = width * height; int i = 0; for (size_t h = 0; h < height; h++) { for (size_t w = 0; w < width; w++) { s << std::to_string(img[i]) << " "; i++; } s << std::endl; } }
//! @brief ストリームへ出力 Portable pixmap ASCII //! @param [in,out] 出力先 //! @param [in] img 画像データ //! @param [in] width 画素数幅 //! @param [in] height 画素数高さ //! @return なし void write_P3(std::ofstream & s, const unsigned char* img, const int width, const int height) { int count = width * height; int i = 0; for (size_t h = 0; h < height; h++) { for (size_t w = 0; w < width; w++) { s << std::to_string(img[i * 3 + 0]) << " "; s << std::to_string(img[i * 3 + 1]) << " "; s << std::to_string(img[i * 3 + 2]) << " "; i++; } s << std::endl; } }
//! @brief ストリームへ出力 Portable bitmap Binary //@details 入力が1byte 1pixel なので、 8要素を1byteにまとめる //! @param [in,out] 出力先 //! @param [in] img 画像データ //! @param [in] count 画素数 //! @return なし void write_P4(std::ofstream & s, const unsigned char* img, const int count) { int bitindex = 0; BitArray bits; for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (bitindex == 0) { bits = 0; } bits[bitindex] = img[i]; bitindex++; bitindex %= 8; if (bitindex == 0) { unsigned char c = bits; s.write((const char*)& c, 1); } } }
//! @brief ストリームへ出力 Portable graymap Binary , Portable pixmap Binary //@details 入力が1byte 1pixel なので、 8要素を1byteにまとめる //! @param [in,out] 出力先 //! @param [in] img 画像データ //! @param [in] bytes 画像データのバイト数 //! @return なし void write_P56(std::ofstream & s, const unsigned char* img, const int bytes) { s.write((char*)img, bytes); }
//! @brief pnmファイルを書き込む //! @param [in] fpathname pnmファイルへのパス //! @param [in] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [int] width 横方向の画素数 //! @param [in] height 縦方向の画素数 //! @param [in] datatype 形式を識別、指定する定数 //! @retval true 書き込み成功 //! @retval false 書き込み失敗 bool write_pnm(const char* fpathname, const unsigned char* img, const int width, const int height, const PNM_TYPE datatype) { if (datatype >= PNM_TYPE::PError) return false; int count = width * height; if (count <= 0) return false; std::ofstream ofs(fpathname, std::ios::out | std::ios::binary); if (!ofs) return false; int pixelbit = pixel_bit_count(datatype); ofs << to_string(datatype) << std::endl; ofs << width << " " << height << std::endl; int maxvalue = -1; if ((datatype != PNM_TYPE::P1) && (datatype != PNM_TYPE::P4)) { maxvalue = *std::max_element( img, img + count * pixel_bit_count(datatype) / 8); ofs << maxvalue << std::endl; } switch (datatype) { case PNM_TYPE::P1: write_P1(ofs, img, width, height); break; case PNM_TYPE::P2: write_P2(ofs, img, width, height); break; case PNM_TYPE::P3: write_P3(ofs, img, width, height); break; case PNM_TYPE::P4: write_P4(ofs, img, width * height); break; case PNM_TYPE::P5: write_P56(ofs, img, width * height); break; case PNM_TYPE::P6: write_P56(ofs, img, width * height * 3); break; } }
テストプログラム
#include <iostream> #include "pnm_rw.hpp" int main() { const char* fpathname = "C:\\test\\butterfly-5546907_640-ascii.pbm"; std::vector<unsigned char> img; int width, height, maxvalue; PNM_TYPE type; read_pnm( fpathname, &img, &width, &height, &maxvalue, &type );
switch (type) { case PNM_TYPE::PBitmap: write_pnm("C:\\test\\out-ascii.pbm", img.data(), width, height, PNM_TYPE::P1); write_pnm("C:\\test\\out-binary.pbm", img.data(), width, height, PNM_TYPE::P4); break; case PNM_TYPE::PGraymap: write_pnm("C:\\test\\out-ascii.pgm", img.data(), width, height, PNM_TYPE::P2); write_pnm("C:\\test\\out-binary.pgm", img.data(), width, height, PNM_TYPE::P5); break; case PNM_TYPE::PPixmap: write_pnm("C:\\test\\out-ascii.ppm", img.data(), width, height, PNM_TYPE::P3); write_pnm("C:\\test\\out-binary.ppm", img.data(), width, height, PNM_TYPE::P6); break; }
}
PNM Reader(改)
プログラム本体(pnm_reader.hpp)
#pragma once #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #pragma warning(disable:4996)
//! @class CGetGrayBits //! @brief 配列上のx番目の画素値を取得するクラス //! @sa https://suzulang.com/bit-depth-1-2-4-getpixelvalue/ class CGetGrayBits { unsigned char* m_p; //!< 画素へのポインタ const int m_depth = 1; //!< ビット深度 unsigned char m_mask = 1; //!< depth8未満の時のビットマスク public: //! @brief コンストラクタ //! @param [in] p 画素配列へのポインタ CGetGrayBits( const void* const p) : m_p(static_cast<unsigned char*>(const_cast<void*>(p))) { } //! @brief 指定した番号の画素を取得 //! @param [in] x 画素番号 //! @return 画素値 int operator[](const std::size_t x) { // x ドットが何バイト目かを算出 (0開始) std::size_t byte = x / (8 / m_depth); unsigned char c = m_p[byte]; std::size_t pos = x % (8 / m_depth); int shift = 8 - m_depth - pos * m_depth; unsigned char mask1 = m_mask << shift; unsigned int val = (c & mask1) >> shift; return val; } };
//! @brief PNMファイルの種類 enum class PNM_TYPE { P1 = 1, //Portable bitmap ASCII P2 = 2, //Portable graymap ASCII P3 = 3, //Portable pixmap ASCII P4 = 4, //Portable bitmap Binary P5 = 5, //Portable graymap Binary P6 = 6, //Portable pixmap Binary PError = 7, PBitmap = 8, PGraymap = 9, PPixmap = 10 };
//! @brief ストリームから入力 bitmap ASCII //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] s 入力ストリーム void read_P1(std::vector<unsigned char>& img, std::ifstream& s) { while (s.eof() == false) { char c; s.read(&c, 1); if (isdigit(c) != false) { img.push_back(c - '0'); } } }
//! @brief ストリームから入力 graymap,pixmap ASCII //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] s 入力ストリーム void read_P23(std::vector<unsigned char> & img, std::ifstream & s) { while (s.eof() == false) { std::string val; s >> val; int value; try { value = std::stoi(val); } catch (std::invalid_argument) { continue; } img.push_back(value); } }
//! @brief ストリームから入力 bitmap Binary //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] s 入力ストリーム //! @return なし //! @details P4は1ビット=1画素なので全部読み込んでから1ビットずつとりだしている void read_P4(std::vector<unsigned char> & img, std::ifstream & s, int count) { std::vector<unsigned char> tmp; unsigned char tc; while (!s.eof()) { s.read((char*)& tc, sizeof(char)); tmp.push_back(tc); } CGetGrayBits bits(&tmp[0]); for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) { img.push_back(bits[i]); } }
//! @brief ストリームから入力 graymap,pixmap Binary //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] s 入力ストリーム //! @return なし void read_P56(std::vector<unsigned char> & img, std::ifstream & s) { while (s.eof() == false) { unsigned char c; s.read((char*)& c, 1); img.push_back(c); } }
//! @brief pnmファイルを読み込む //! @param [in] fpathname pnmファイルへのパス //! @param [out] img 画像の格納先 //! @param [out] width 横方向の画素数 //! @param [out] height 縦方向の画素数 //! @param [out] maxvalue 画素の最大値 //! @param [out] datatype 形式を識別する定数 //! @retval true 読込成功 //! @retval false 読込失敗 bool read_pnm(const char* fpathname, std::vector<unsigned char> * img, int* width, int* height, int* maxvalue, PNM_TYPE * datatype) { std::ifstream ifs(fpathname, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary); if (!ifs) return false; std::string text; *width = -1; *height = -1; *maxvalue = -1; //タイプの読み取り PNM_TYPE type; { int _type = (int)PNM_TYPE::PError; while (std::getline(ifs, text).eof() == false) { if (text[0] == 'P') { _type = ((int)text[1] - (int)'0'); break; } } switch (_type) { case (int)PNM_TYPE::P1:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PBitmap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P2:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PGraymap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P3:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PPixmap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P4:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PBitmap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P5:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PGraymap; break; case (int)PNM_TYPE::P6:*datatype = PNM_TYPE::PPixmap; break; default: *datatype = PNM_TYPE::PError; return false; } type = (PNM_TYPE)_type; } while (std::getline(ifs, text).eof() == false) { //コメントスキップ if (text[0] == '#') continue; //コメントでないなら各種値の入力 std::stringstream ss(text); //幅入力 if (*width < 0) { ss >> *width; if (*width < 0) continue; } //高さ入力 if (*height < 0) { ss >> *height; if (*height < 0) continue; } //最大値入力 if (*datatype != PNM_TYPE::PBitmap) { if (*maxvalue < 0) { ss >> *maxvalue; if (*maxvalue < 0) continue; } } break; } int count = *width * *height; switch (type) { case PNM_TYPE::P1: img->reserve(count); read_P1(*img, ifs); break; case PNM_TYPE::P2: img->reserve(count); read_P23(*img, ifs); break; case PNM_TYPE::P3: img->reserve(count * 3); read_P23(*img, ifs); break; case PNM_TYPE::P4: read_P4(*img, ifs, count); break; case PNM_TYPE::P5: read_P56(*img, ifs); break; case PNM_TYPE::P6: read_P56(*img, ifs); break; } }
テスト用コード
#include <iostream> #include "pnm_reader.hpp"
//! @brief pnmの各型式のデータをppm形式の格納方法に変更する //! @param [out] dst 結果画像データ //! @param [in] src 元画像データ //! @param [in] pixelcount 画素数 //! @param [in] type P1~P6のいずれか //! @return なし void pnm_to_ppm( std::vector<unsigned char>& dst, unsigned char* src, int pixelcount, PNM_TYPE type ) { switch (type) { case PNM_TYPE::P1: case PNM_TYPE::P4: case PNM_TYPE::PBitmap: for (size_t i = 0; i < pixelcount; i++) { dst.push_back(src[i] ? 0 : 255); dst.push_back(src[i] ? 0 : 255); dst.push_back(src[i] ? 0 : 255); } break; case PNM_TYPE::P2: case PNM_TYPE::P5: case PNM_TYPE::PGraymap: for (size_t i = 0; i < pixelcount; i++) { dst.push_back(src[i]); dst.push_back(src[i]); dst.push_back(src[i]); } break; case PNM_TYPE::P3: case PNM_TYPE::P6: case PNM_TYPE::PPixmap: for (size_t i = 0; i < pixelcount; i++) { dst.push_back(src[i * 3 + 0]); dst.push_back(src[i * 3 + 1]); dst.push_back(src[i * 3 + 2]); } break; } }
//! @brief PPM(RGB各1byte,カラー,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] vmax 全てのRGBの中の最大値 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details RGBRGBRGB....のメモリを渡すと、RGBテキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pnmP3_Write( const char* const fname, const int vmax, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p) { FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P3\n%d %d\n%d\n", width, height, vmax); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d ", p[k * 3 + 0], p[k * 3 + 1], p[k * 3 + 2]); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
int main() { const char* fpathname = "C:\\test\\butterfly-5546907_640-binary.ppm"; std::vector<unsigned char> img; int width, height, maxvalue; PNM_TYPE type; read_pnm( fpathname, &img, &width, &height, &maxvalue, &type ); std::vector<unsigned char> tmp; pnm_to_ppm(tmp, &img[0], width * height,type); ////////////////////////////// const char* fname = "C:\\test\\out.ppm"; pnmP3_Write(fname, 255, width, height, &tmp[0]); }
C++ templateで条件を複数並べるif/elifみたいなものを作る
多分まだ上げてなかったと思う。タイトルはif-elifとしてあるけれど個人的な好みでSwitch / Caseにしてある。
以下のように、Switch< /* .... */ >::type とし、typeを決定する。
そのtypeは、Case<条件 , 型 > とし、条件がtrueの時の型とする。
条件は再起で上から順番に評価していて、trueが見つかった時点で探索をやめるので、複数あると先に書いた方が採用される。
#include "pch.h" #include <iostream>
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Switch / Case
template<bool BOOL, typename Second> struct Case { static constexpr bool TBOOL = BOOL; using TSecond = Second; }; template<class Head, class... Tail> struct Switch { using type = typename std::conditional< Head::TBOOL, typename Head::TSecond, // trueの時 typename Switch<Tail...>::type //falseの時 >::type; }; //再起終端用特殊化 template<class Head> struct Switch<Head> { using type = typename std::conditional< Head::TBOOL, typename Head::TSecond, // trueの時 void >::type; };
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 動作テスト用クラスstruct forInt {void disp() {std::cout << "int" << std::endl;}}; struct forFloat {void disp() {std::cout << "float" << std::endl;}}; struct forChar {void disp() {std::cout << "char" << std::endl;}};//動作テスト用関数 template<typename T> void disp_type(T val) { // 型 T によってDispTypeが変わる using DispType = typename Switch< Case<std::is_same<int, T>::value, forInt>, Case<std::is_same<float, T>::value, forFloat>, Case<std::is_same<char, T>::value, forChar> >::type; DispType tmp; tmp.disp(); }int main() { char value = 10; disp_type(value); }
C++ templateで配列の種類を特定する
C++には T[N] 形式の他に、
・std::array
・std::vector
・std::valarray
等の配列の形式がある。このうちstdの<type_traits>で判別できるのはT[N]型か否かを判別するstd::is_arrayしか用意されていないようなので、その他を判別するテンプレートを用意する。
#include <iostream> #include<vector> #include<array> #include<valarray> int primarray[10]; std::array<int, 10> stdarray; std::vector<int> vectordata; std::valarray<int> valarraydata; namespace CheckPrimitiveArray { // type_traits内に同様のものがある
template<class> struct is_array :std::false_type {}; template<class T> struct is_array<T[]> : std::true_type {}; template<class T, std::size_t N> struct is_array<T[N]> : std::true_type {};
void example() { std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << "--- is_array" << std::endl; std::cout << "primitive:" << is_array<decltype(primarray)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "stdarray :" << is_array<decltype(stdarray)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "vector :" << is_array<decltype(vectordata)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "valarray :" << is_array<decltype(valarraydata)>::value << std::endl; } } namespace CheckVectorArray {
template<class> struct is_vector : std::false_type {};
template<class T, class ALLOCATOR> struct is_vector<std::vector<T, ALLOCATOR>> : std::true_type {};
void example() { std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << "--- is_vector" << std::endl; std::cout << "primitive:" << is_vector<decltype(primarray)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "stdarray :" << is_vector<decltype(stdarray)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "vector :" << is_vector<decltype(vectordata)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "valarray :" << is_vector<decltype(valarraydata)>::value << std::endl; } } namespace CheckStdArray {
template<class> struct is_stdarray :std::false_type {}; template<class T, std::size_t N> struct is_stdarray<std::array<T, N>> :std::true_type {};
void example() { std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << "--- is_stdarray" << std::endl; std::cout << "primitive:" << is_stdarray<decltype(primarray)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "stdarray :" << is_stdarray<decltype(stdarray)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "vector :" << is_stdarray<decltype(vectordata)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "valarray :" << is_stdarray<decltype(valarraydata)>::value << std::endl; } } namespace CheckValArray {
template<class> struct is_valarray : std::false_type {};
template<class T> struct is_valarray<std::valarray<T>> : std::true_type {};
void example() { std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << "--- is_valarray" << std::endl; std::cout << "primitive:" << is_valarray<decltype(primarray)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "stdarray :" << is_valarray<decltype(stdarray)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "vector :" << is_valarray<decltype(vectordata)>::value << std::endl; std::cout << "valarray :" << is_valarray<decltype(valarraydata)>::value << std::endl; } } int main() { CheckPrimitiveArray::example(); CheckStdArray::example(); CheckVectorArray::example(); CheckValArray::example(); getchar(); }
判別結果
--- is_array
primitive:1
stdarray :0
vector :0
valarray :0
--- is_stdarray
primitive:0
stdarray :1
vector :0
valarray :0
--- is_vector
primitive:0
stdarray :0
vector :1
valarray :0
--- is_valarray
primitive:0
stdarray :0
vector :0
valarray :1