スポンサーリンク
OpenGLで簡易的な矢印を描く
本格的な矢印はポリゴン数も計算も大変なので簡易的な矢印を実装する。
なおそろそろ拡張子.hppを割と意識して使うことにする
ソースコード
矢印描画(drawarrow.hpp)
#pragma once #include <Windows.h> #include <gl/GL.h> namespace numath { typedef double real_t; //! @brief ラジアンを度に変換 //! @param [in] radian ラジアンの値 //! @return 度の値 inline real_t toDegree(const real_t radian) { return radian * 180 / 3.1415926535897932384626; } //! @brief 三次元のベクトルを正規化する //! @param [in,out] pV 三次元ベクトル1 要素数3 //! @retval true 成功 //! @retval false 失敗 inline bool normalize(real_t* const pV) { const int X = 0; const int Y = 1; const int Z = 2; real_t len; real_t& x = pV[X]; real_t& y = pV[Y]; real_t& z = pV[Z]; len = static_cast<real_t>(sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z)); if (len < static_cast<real_t>(1e-6)) return false; len = static_cast<real_t>(1.0) / len; x *= len; y *= len; z *= len; return true; } //! @brief ベクトルの長さを求める //! @param [in] vec 三次元ベクトル1 要素数3 //! @return vecの長さを表すスカラー値 inline real_t length(real_t const* const vec) { const int X = 0; const int Y = 1; const int Z = 2; return sqrt(vec[X] * vec[X] + vec[Y] * vec[Y] + vec[Z] * vec[Z]); } //! @brief 二つの三次元ベクトルの内積を求める //! @param [in] vec1 三次元ベクトル1 要素数3 //! @param [in] vec1 三次元ベクトル2 要素数3 //! @return ベクトルの内積 inline real_t inner(real_t const* const vec1, real_t const* const vec2) { const int X = 0; const int Y = 1; const int Z = 2; return ((vec1[X]) * (vec2[X]) + (vec1[Y]) * (vec2[Y]) + (vec1[Z]) * (vec2[Z])); } //! @brief 二つの三次元ベクトルの角度を求める //! @param [in] vec1 三次元ベクトル1 要素数3 //! @param [in] vec1 三次元ベクトル2 要素数3 //! @return ベクトルの角度(ラジアン) inline real_t vectorAngle(real_t const* const vec1, real_t const* const vec2) { real_t x = inner(vec1, vec2) / (length(vec1) * length(vec2)); if (x <= -1) x = -0.9999999; if (x >= 1) x = 0.99999999; return acos(x); } //! @brief ベクトルにスカラー値をかける //! @param [in,out] 対象の三次元ベクトル1 要素数3 //! @param scalar スカラー値 //! @return なし inline void vectorMult3(real_t * dst, const real_t scalar) { dst[0] *= scalar; dst[1] *= scalar; dst[2] *= scalar; } //! @brief 始点終点の線分をベクトルに変換 //! @param [out] vec3 結果を格納する三次元ベクトル 要素数3 //! @param [out] from 始点を表す三次元ベクトル 要素数3 //! @param [out] to 終点三次元ベクトル 要素数3 //! @return vec3のポインタ inline real_t* lineToVector3(real_t * const vec3, const real_t * const from, const real_t * const to) { vec3[0] = to[0] - from[0]; vec3[1] = to[1] - from[1]; vec3[2] = to[2] - from[2]; return vec3; } //! @brief 与えられた二つのベクトルの外積を求める //! @param [out] dvec 結果を格納する三次元ベクトル 要素数3 //! @param [in] svec 三次元ベクトル1 要素数3 //! @param [in] svec 三次元ベクトル2 要素数3 //! @return なし inline void outer(real_t * const dvec, real_t const* const svec1, real_t const* const svec2) { const int X = 0; const int Y = 1; const int Z = 2; const real_t& x1 = svec1[X]; const real_t& y1 = svec1[Y]; const real_t& z1 = svec1[Z]; const real_t& x2 = svec2[X]; const real_t& y2 = svec2[Y]; const real_t& z2 = svec2[Z]; dvec[X] = static_cast<real_t>(y1 * z2 - z1 * y2); dvec[Y] = static_cast<real_t>(z1 * x2 - x1 * z2); dvec[Z] = static_cast<real_t>(x1 * y2 - y1 * x2); } //! @brief 与えられたベクトルと垂直なベクトルを計算する //! @param dst13 結果を表す三次元ベクトル 要素数3(一つ目 必須) //! @param dst23 結果を表す三次元ベクトル 要素数3(二つ目 いらないならnullptrを指定) //! @param src3 入力する三次元ベクトル 要素数3 //! @return なし inline void rightAngleVector(real_t * const dst13, real_t * const dst23, const real_t * const src3) { real_t tmp[3] = { 1,0,0 }; //tmpとsrc3の角度0またはそれに限りなく近いなら、別なベクトルを用意 if (toDegree(vectorAngle(tmp, src3)) < 0.1) { tmp[0] = 0; tmp[1] = 1; tmp[2] = 0; } //外積を求める outer(dst13, tmp, src3); if (dst23 != nullptr) { outer(dst23, src3, dst13); } } } //! @brief 矢印を描画 //! @param [in] 矢印の始点 //! @param [out] 矢印の終点 //! @return なし inline void drawArrow(const double* from3, const double* to3) { glBegin(GL_LINES); glVertex3dv(from3); glVertex3dv(to3); glEnd(); numath::real_t v[3]; numath::lineToVector3(v, from3, to3); double len = numath::length(v); numath::real_t p3[3] = { from3[0], from3[1], from3[2] }; numath::vectorMult3(v, 0.8); numath::real_t v1[3], v2[3]; numath::rightAngleVector(v1, v2, v); numath::normalize(v1); numath::normalize(v2); numath::vectorMult3(v1, len * 0.03); numath::vectorMult3(v2, len * 0.03); const double* f = from3; const double* t = to3; glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP); glVertex3d(f[0] + v[0], f[1] + v[1], f[2] + v[2]); glVertex3d(f[0] + v[0] + v1[0], f[1] + v[1] + v1[1], f[2] + v[2] + v1[2]); glVertex3d(t[0], t[1], t[2]); glEnd(); glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP); glVertex3d(f[0] + v[0], f[1] + v[1], f[2] + v[2]); glVertex3d(f[0] + v[0] + v2[0], f[1] + v[1] + v2[1], f[2] + v[2] + v2[2]); glVertex3d(t[0], t[1], t[2]); glEnd(); glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP); glVertex3d(f[0] + v[0], f[1] + v[1], f[2] + v[2]); glVertex3d(f[0] + v[0] - v1[0], f[1] + v[1] - v1[1], f[2] + v[2] - v1[2]); glVertex3d(t[0], t[1], t[2]); glEnd(); glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP); glVertex3d(f[0] + v[0], f[1] + v[1], f[2] + v[2]); glVertex3d(f[0] + v[0] - v2[0], f[1] + v[1] - v2[1], f[2] + v[2] - v2[2]); glVertex3d(t[0], t[1], t[2]); glEnd(); }
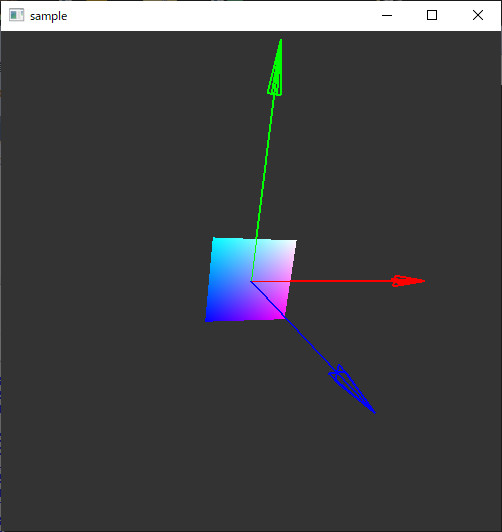
使用例
#include <iostream> #include <Windows.h> #include <gl/GL.h> #include <gl/GLU.h> #include <gl/freeglut.h> // freeglut: // http://freeglut.sourceforge.net/ //矢印描画関数 #include "drawarrow.hpp" //ウィンドウの幅と高さ int width, height; double rotate_angle=0; //描画関数 void disp(void) { glClearColor(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); glViewport(0, 0, width, height); //カメラの設定 glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); gluPerspective(60, width / (double)height, 0.1, 3); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); glLoadIdentity(); glTranslated(0, 0, -2); //表示用の回転 glRotated(rotate_angle, 0, 1, 0); glRotated(rotate_angle, 1, 0, 0); //矢印を三つ描画 glLineWidth(2); double from[3] = { 0,0,0 }; double tox[3] = { 1,0,0 }; double toy[3] = { 0,1,0 }; double toz[3] = { 0,0,1 }; glColor3d(1, 0, 0); drawArrow(from, tox); glColor3d(0, 1, 0); drawArrow(from, toy); glColor3d(0, 0, 1); drawArrow(from, toz); glLineWidth(1); double v = 0.2; glBegin(GL_QUADS); glColor3d(0, 0, 1); glVertex2d(-v, -v); glColor3d(1, 0, 1); glVertex2d(v, -v); glColor3d(1, 1, 1); glVertex2d(v, v); glColor3d(0, 1, 1); glVertex2d(-v, v); glEnd(); glFlush(); } //ウィンドウサイズの変化時に呼び出される void reshape(int w, int h) { width = w; height = h; disp(); } void timer(int value) { rotate_angle += 5; disp(); glutTimerFunc(100, timer, 0); } //エントリポイント int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitWindowPosition(100, 50); glutInitWindowSize(500, 500); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGBA); glutCreateWindow("sample"); glutDisplayFunc(disp); glutReshapeFunc(reshape); glutTimerFunc(1000, timer, 0);//タイマー glutMainLoop(); return 0; }
この記事のトラックバックURL: