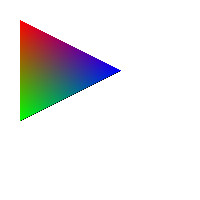スポンサーリンク
三角形の重心座標系を計算してみる
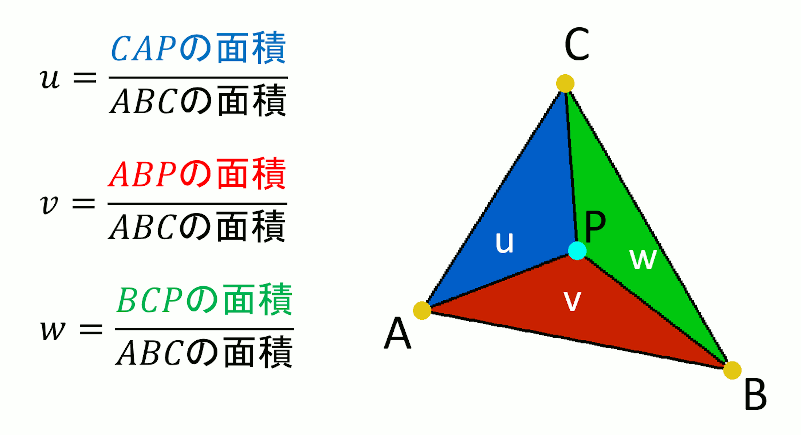
重心座標系は、ある三角形が頂点A,B,Cからなるとき、三角形上の点Pの座標を、ABCの座標とパラメータuvwを使って、P=wA+uB+vC の形で表す方法。
此の何が嬉しいかというと、例えば三角形ABCの上に点Pがあったとする。次に三角形ABCを変形して三角形A'B'C'を作る。この時、点PはA'B'C'上ではどの位置(x,y,z)に該当するかを知りたい。
こんな時、あらかじめPの重心座標系を求め、uvwを計算しておけば、ABCの座標が変わってもuvwからP'のxyzを求めることができる。
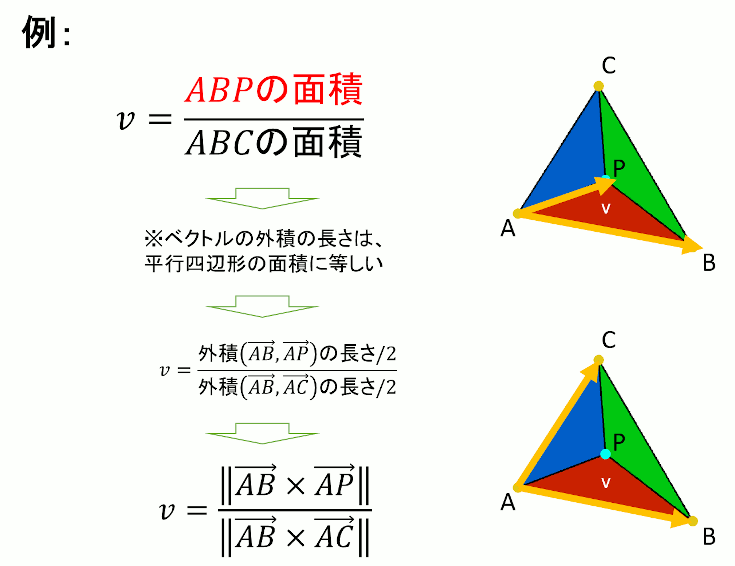
u,v,wの計算方法
BarycentricCoordinates.hpp
#pragma once
// https://www.study.suzulang.com/3dcg-functions/vmmath-hpp #include "vmmath.hpp" #include<array>
//! @brief ABCの頂点から外積で求められる平行四辺形の面積 //! @param [in] A 頂点1の三次元座標 //! @param [in] B 頂点2の三次元座標 //! @param [in] C 頂点3の三次元座標 //! @return 平行四辺形の面積 double parellogram( const std::array<double, 3>& A, const std::array<double, 3>& B, const std::array<double, 3>& C ) { // P = wA+uB+vC std::array<double, 3> AtoB; szl::mathv::vector_from_line3(AtoB, A, B); std::array<double, 3> AtoC; szl::mathv::vector_from_line3(AtoC, A, C); //外積を求める std::array<double, 3> parallelogramABC; szl::mathv::outer3(parallelogramABC, AtoB, AtoC); //△ABCの面積の二倍 return szl::mathv::length3(parallelogramABC); }
//! @brief 三角形ABC上の点Pの重心座標系での位置を求める //! @param [out] u △CAP/△ABC //! @param [out] v △ABP/△ABC //! @param [out] w △BCP/△ABC //! @param [in] A 頂点1 //! @param [in] B 頂点2 //! @param [in] C 頂点3 //! @param [in] P 三角形内部の点 //! @return なし void BarycentricCoordinates( double* u, double* v, double* w, const std::array<double, 3> A, const std::array<double, 3> B, const std::array<double, 3> C, const std::array<double, 3> P ) { double parellogramABC = parellogram(A, B, C); *u = parellogram(C, A, P) / parellogramABC; *v = parellogram(A, B, P) / parellogramABC; *w = parellogram(B, C, P) / parellogramABC; }
実験
LineCross.hpp
以前作った、線分の交差判定のプログラムで定義した頂点データに色情報を追加する。
struct RGB { int r, g, b; }; template<typename ScalarT> struct Point { ScalarT x, y; RGB color; // 色情報 Point(const ScalarT X, const ScalarT Y) :x(X), y(Y) {} template<typename T> Point(const Point<T>& src) { x = src.x; y = src.y; color.r = src.color.r; color.g = src.color.g; color.b = src.color.b; } Point() {} };
scanConversion.hpp
以前作ったscanConversion.hppの、点を打つPlot関数を以下のように変更する。これは三角形内部の色をABC山頂点に与えた色情報を使うようにし、補間を重心座標系で行うようにする。
#pragma once #include "NByteData.hpp" #include "LineCross.hpp" #include "BarycentricCoordinates.hpp" template<typename PixelType> struct imagedata { int width; int height; PixelType* img; }; //! @brief 水平な線分ともう一方の線分との交差判定を行う //! @param [out] cross 交差していた場合の座標(ピクセル単位) //! @param [in] scanL 水平な線分 //! @param [in] L 線分 bool isPixelHorizonalCross( Pointi* cross, const LineSegmenti& scanL, const LineSegmenti& L) { //三角形塗りつぶしようなので、scanLは必ずLの始点・終点よりも広い範囲をとる //そのため始点・終点のY座標が一致していたら交差しているのでtrueを返す if (scanL.s.y == L.s.y) { *cross = L.s; return true; } if (scanL.s.y == L.e.y) { *cross = L.e; return true; } return isCrossPixel(cross, scanL, L); } //! @brief 画素に色を設定 //! @param [in,out] img 画像データ //! @param [in] P 書き込み先の座標 //! @param [in] A 頂点1の座標と色 //! @param [in] B 頂点2の座標と色 //! @param [in] C 頂点3の座標と色 //! @return なし template<typename PixelType> void Plot( imagedata<PixelType> *img, Pointi P, const Pointi A, const Pointi B, const Pointi C ) { std::array<double, 3> _A{ A.x,A.y,0 }; std::array<double, 3> _B{ B.x,B.y,0 }; std::array<double, 3> _C{ C.x,C.y,0 }; std::array<double, 3> _P{ P.x,P.y,0 }; //変更 double u, v, w; BarycentricCoordinates( &u,&v,&w, _A, _B, _C, _P ); // P = wA+uB+vC unsigned char cR = w * A.color.r; unsigned char cG = u * B.color.g; unsigned char cB = v * C.color.b; PixelType Color{ cR,cG,cB }; img->img[P.y * img->width + P.x] = Color; } //! @brief 走査変換で頂点ABCからなる三角形を描画 //! @param [in,out] img 画像データ //! @param [in] A 頂点1の座標 //! @param [in] B 頂点2の座標 //! @param [in] C 頂点3の座標 template<typename PixelType> void scanConversion( imagedata<PixelType> *img, const Pointi A, const Pointi B, const Pointi C ) { //入力された頂点をY座標が小さい順にソート Pointi m[3]{ A,B,C }; std::sort( std::begin(m), std::end(m), [](const auto& s, const auto& t) { return s.y < t.y; }); //X座標の最大・最小より少し広い範囲 const int xmin = std::min_element( std::begin(m), std::end(m), [](const auto& s, const auto& t) {return s.x < t.x; } )->x - 1; const int xmax = std::max_element( std::begin(m), std::end(m), [](const auto& s, const auto& t) {return s.x < t.x; } )->x + 1; /* 0 / | / | / | 1 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | 2 ソートにより三角形の配列mはy座標順に並んでいる */ // 走査線と 01,02 for (int y = m[0].y; y < m[1].y; y++) { //上半分について処理 LineSegmenti scan( Pointi(xmin, y), Pointi(xmax, y) ); Pointi cross01; Pointi cross02; LineSegmenti L01(m[0], m[1]); LineSegmenti L02(m[0], m[2]); bool ab = isPixelHorizonalCross(&cross01, scan, L01); bool ac = isPixelHorizonalCross(&cross02, scan, L02); if (ab == true && ac == true) { int cxmin = (std::min)(cross01.x, cross02.x); int cxmax = (std::max)(cross01.x, cross02.x); for (int x = cxmin; x <= cxmax; x++) { Pointi P(x, y); Plot(img, P,A,B,C);//変更 } } } // 走査線と 12 , 01 for (int y = m[1].y; y <= m[2].y; y++) { LineSegmenti scan( Pointi(xmin, y), Pointi(xmax, y) ); Pointi cross12; Pointi cross02; LineSegmenti L12(m[1], m[2]); LineSegmenti L02(m[0], m[2]); bool bc = isPixelHorizonalCross(&cross12, scan, L12); bool ac = isPixelHorizonalCross(&cross02, scan, L02); if (bc == true && ac == true) { int cxmin = (std::min)(cross12.x, cross02.x); int cxmax = (std::max)(cross12.x, cross02.x); for (int x = cxmin; x <= cxmax; x++) { Pointi P(x, y); Plot(img, P, A, B, C);//変更 } } } }
呼び出し例
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include "Bresenham.hpp" #include "scanConversion.hpp" void ppmP3_write( const char* const fname, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p, const int vmax ); using ucrgb = NByteData<3>; ucrgb Black = ucrgb{ 0,0,0 }; ucrgb White = ucrgb{ 255,255,255 }; ucrgb Red = ucrgb{ 255,0,0 }; void test1(imagedata<ucrgb>& img,bool fill); void test2(imagedata<ucrgb>& img,bool fill); void test3(imagedata<ucrgb>& img,bool fill); void test4(imagedata<ucrgb>& img,bool fill); void test5(imagedata<ucrgb>& img,bool fill); void test6(imagedata<ucrgb>& img, bool fill);
int main() { int width = 200; int height = 200; std::vector<ucrgb> image; image.resize(width*height, White); imagedata<ucrgb> imginfo; imginfo.width = width; imginfo.height = height; imginfo.img = &image[0]; std::fill(image.begin(), image.end(), White); test1(imginfo,true); std::fill(image.begin(), image.end(), White); test2(imginfo, true); std::fill(image.begin(), image.end(), White); test3(imginfo, true); std::fill(image.begin(), image.end(), White); test4(imginfo, true); std::fill(image.begin(), image.end(), White); test5(imginfo, true); std::fill(image.begin(), image.end(), White); test6(imginfo, true); }
//! @brief PPM(RGB各1byte,カラー,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @param [in] vmax 全てのRGBの中の最大値。普通の画像なら255 //! @details RGBRGBRGB....のメモリを渡すと、RGBテキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void ppmP3_write( const char* const fname, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p, const int vmax ) { FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P3\n%d %d\n%d\n", width, height, vmax); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d ", p[k * 3 + 0], p[k * 3 + 1], p[k * 3 + 2] ); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
void test1(imagedata<ucrgb>& imginfo, bool fill) { Pointi A{ 20,20 }; Pointi B{ 20,120 }; Pointi C{ 120,70 }; //追加 A.color = RGB{ 255,0,0 }; B.color = RGB{ 0,255,0 }; C.color = RGB{ 0,0,255 }; Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, C.x, C.y, A.x, A.y, Black); if (fill) { scanConversion<ucrgb>(&imginfo, A, B, C); } ppmP3_write(R"(C:\test\t1.ppm)", imginfo.width, imginfo.height, imginfo.img->data(), 255); } void test2(imagedata<ucrgb>& imginfo, bool fill) { Pointi A{ 20,20 }; Pointi B{ 120,20 }; Pointi C{ 100,100 }; //追加 A.color = RGB{ 255,0,0 }; B.color = RGB{ 0,255,0 }; C.color = RGB{ 0,0,255 }; Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, C.x, C.y, A.x, A.y, Black); if (fill) { scanConversion<ucrgb>(&imginfo, A, B, C); } ppmP3_write(R"(C:\test\t2.ppm)", imginfo.width, imginfo.height, imginfo.img->data(), 255); } void test3(imagedata<ucrgb>& imginfo, bool fill) { Pointi A{ 100,20 }; Pointi B{ 20,50 }; Pointi C{ 130,100 }; //追加 A.color = RGB{ 255,0,0 }; B.color = RGB{ 0,255,0 }; C.color = RGB{ 0,0,255 }; Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, C.x, C.y, A.x, A.y, Black); if (fill) { scanConversion<ucrgb>(&imginfo, A, B, C); } ppmP3_write(R"(C:\test\t3.ppm)", imginfo.width, imginfo.height, imginfo.img->data(), 255); } void test4(imagedata<ucrgb>& imginfo, bool fill) { Pointi A{ 20,20 }; Pointi B{ 20,20 }; Pointi C{ 20,20 }; //追加 A.color = RGB{ 255,0,0 }; B.color = RGB{ 0,255,0 }; C.color = RGB{ 0,0,255 }; Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, C.x, C.y, A.x, A.y, Black); if (fill) { scanConversion<ucrgb>(&imginfo, A, B, C); } ppmP3_write(R"(C:\test\t4.ppm)", imginfo.width, imginfo.height, imginfo.img->data(), 255); } void test5(imagedata<ucrgb>& imginfo, bool fill) { Pointi A{ 20,20 }; Pointi B{ 100,20 }; Pointi C{ 50,20 }; //追加 A.color = RGB{ 255,0,0 }; B.color = RGB{ 0,255,0 }; C.color = RGB{ 0,0,255 }; Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, C.x, C.y, A.x, A.y, Black); if (fill) { scanConversion<ucrgb>(&imginfo, A, B, C); } ppmP3_write(R"(C:\test\t5.ppm)", imginfo.width, imginfo.height, imginfo.img->data(), 255); } void test6(imagedata<ucrgb>& imginfo, bool fill) { Pointi A{ 20,20 }; Pointi B{ 20,50 }; Pointi C{ 20,100 }; //追加 A.color = RGB{ 255,0,0 }; B.color = RGB{ 0,255,0 }; C.color = RGB{ 0,0,255 }; Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, A.x, A.y, B.x, B.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, B.x, B.y, C.x, C.y, Black); Bresenham(&imginfo.img[0], imginfo.width, imginfo.height, C.x, C.y, A.x, A.y, Black); if (fill) { scanConversion<ucrgb>(&imginfo, A, B, C); } ppmP3_write(R"(C:\test\t6.ppm)", imginfo.width, imginfo.height, imginfo.img->data(), 255); }
実行結果
この記事のトラックバックURL: