スポンサーリンク
レイキャストを実装してみる(2) レイと球の交差
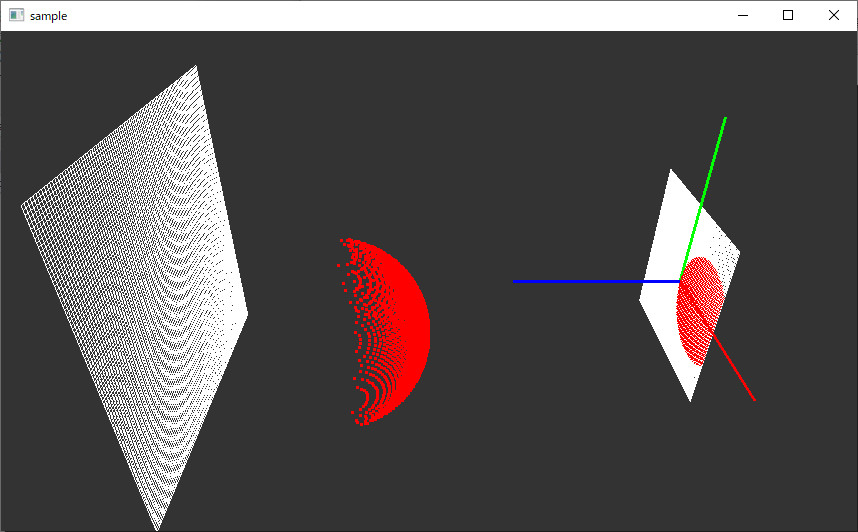
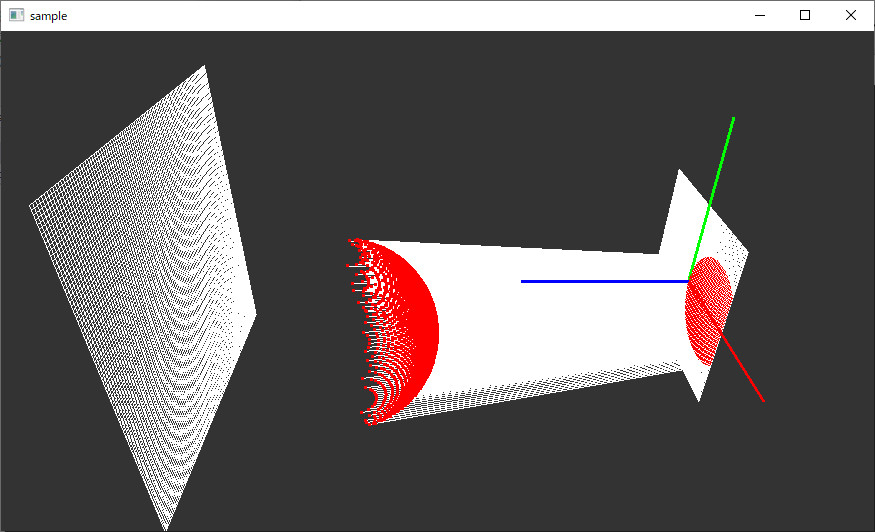
前回作成したレイと球を交差させて、その状態を可視化する。
raycast.hpp
#pragma once #include "Grid.hpp" #include <array>
////////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////////////// // 球オブジェクト class object_sphere { glm::vec3 _center; glm::vec3 _color; float _r; public: object_sphere(glm::vec3 center_, glm::vec3 color_, float radius_) : _center(center_), _color(color_), _r(radius_) {} object_sphere() {} bool intersect(glm::vec3* pos_, glm::vec3* color_, const std::array<glm::vec3, 2>& ray_)const; };
////////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////////////// // 画像として塗りつぶすピクセル struct hit_pixel_t { glm::vec3 _position; // 交点の座標 glm::vec3 _color; // 交点の色 hit_pixel_t(const glm::vec3& position_, const glm::vec3& color_) : _position(position_), _color(color_) {} };
// レイキャスト用のクラス class my_raycast { grid g[2]; float _startZ; float _endZ; int _pxwidth; int _pxheight; public: my_raycast() {} int width()const { return _pxwidth; } int height()const { return _pxheight; } // レイの開始点となるグリッド、終点となるグリッドを作成する void set(const float startZ_, const float endZ_, const int pxwidth_, const int pxheight_); //グリッド取得 const grid& get_grid(const size_t index)const { return g[index]; } //グリッドから作成するレイの数を取得 int ray_count() { return g[0].cellCount(); } //グリッドから作成するレイを取得 std::array<glm::vec3, 2> get_ray(const size_t index)const; //始点グリッド、終点グリッドの中間の位置を取得(表示用) float lookatZ()const { return (_startZ + _endZ) / 2.f; }
////////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////////////// private: object_sphere _obj;//球オブジェクト std::vector< hit_pixel_t > _hits;//レイキャストの結果 public: void raycast();//レイキャスト std::vector< hit_pixel_t >& get_intersects() {return _hits;} void set_object(const object_sphere& obj_);
};
raycast.cpp
レイキャストの部分はglm::intersectRaySphereを使う。
#include "raycast.hpp" #include <glm/gtx/intersect.hpp>
bool object_sphere::intersect(glm::vec3* pos_, glm::vec3* color_, const std::array<glm::vec3, 2>& ray_) const { glm::vec3 nray = glm::normalize(ray_[1] - ray_[0]); float distance; bool valid = glm::intersectRaySphere(ray_[0], nray, _center, _r * _r, distance); *pos_ = ray_[0] + nray * distance; *color_ = _color; return valid; }
void my_raycast::set(const float startZ_, const float endZ_, const int pxwidth_, const int pxheight_) { _startZ = startZ_; _endZ = endZ_; _pxwidth = pxwidth_; _pxheight = pxheight_; glm::vec3 vecx(1, 0, 0); glm::vec3 vecy(0, 1, 0); g[0] = grid( vecx, vecy, glm::vec3(0, 0, _startZ), 1.f, 1.f, pxwidth_, pxheight_ ); g[1] = grid( vecx, vecy, glm::vec3(0, 0, _endZ), 2.f, 2.f, pxwidth_, pxheight_ ); } std::array<glm::vec3, 2> my_raycast::get_ray(const size_t index)const { return std::array<glm::vec3, 2>{ g[0][index].center(), g[1][index].center() }; } void my_raycast::set_object(const object_sphere& obj_) { _obj = obj_; }
void my_raycast::raycast() {
//結果の初期化
float inf = std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity(); _hits.resize(_pxheight * _pxwidth, hit_pixel_t( glm::vec3(inf, inf, inf),//球とレイの交点を無効な値に設定 glm::vec3(0, 0, 0)//色を黒に ) ); for (size_t y = 0; y < _pxheight; y++) { for (size_t x = 0; x < _pxwidth; x++) { size_t index = y * _pxwidth + x; auto ray = get_ray(index);//レイ取得 glm::vec3 p; glm::vec3 c; if (_obj.intersect(&p,&c, ray) == true) {//球との交点を算出 _hits[index]._position = p;//交差していたらその座標を保存 _hits[index]._color = c; } } } }
main.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <array> #include<GL/freeglut.h> #include<gl/GL.h> #include "raycast.hpp" #include<glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp> #include<glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp> my_raycast mydata; //! @brief グリッドを表示 //! @param [in] g グリッドオブジェクト //! @param [in] dispcenter セルの中央を表示するか void drawGrid(const grid& g, const bool dispcenter) { glLineWidth(1); glColor3d(1, 1, 1); for (size_t i = 0; i < g.cellCount(); i++) { glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP); glVertex3fv(glm::value_ptr(g.p0(i))); glVertex3fv(glm::value_ptr(g.p1(i))); glVertex3fv(glm::value_ptr(g.p2(i))); glVertex3fv(glm::value_ptr(g.p3(i))); glEnd(); } if (dispcenter) { glPointSize(1); glColor3d(1, 1, 1); glBegin(GL_POINTS); for (size_t i = 0; i < g.cellCount(); i++) { glVertex3fv( glm::value_ptr(g[i].center())); } glEnd(); } } void drawXYZ() { glLineWidth(3); glBegin(GL_LINES); glColor3f(1, 0, 0); glVertex3f(0, 0, 0); glVertex3f(1, 0, 0); glColor3f(0, 1, 0); glVertex3f(0, 0, 0); glVertex3f(0, 1, 0); glColor3f(0, 0, 1); glVertex3f(0, 0, 0); glVertex3f(0, 0, 1); glEnd(); glLineWidth(1); } void drawRays() { glBegin(GL_LINES); for (size_t i = 0; i < mydata.ray_count(); i++) { auto ray = mydata.get_ray(i); glColor3f(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); glVertex3fv(glm::value_ptr(ray[0])); glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glVertex3fv(glm::value_ptr(ray[1])); } glEnd(); } //ウィンドウの幅と高さ int width, height; //描画関数 void disp(void) { glViewport(0, 0, width, height); glClearColor(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); glm::mat4 proj = glm::perspectiveFov(glm::radians(45.f), (float)width, (float)height, 0.1f, 50.f); glLoadMatrixf(glm::value_ptr(proj)); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); glLoadIdentity(); ////////////////////////////////////////// ////////////////////////////////////////// // カメラの設定 float z = mydata.lookatZ(); glm::mat4 look = glm::lookAt( glm::vec3(3, 2, z ),// eye glm::vec3(0, 0, z ), // lookat glm::vec3(0,1, 0) // up ); glLoadMatrixf(glm::value_ptr(look)); ////////////////////////////////////////// // グリッドを表示 drawGrid(mydata.get_grid(0), false);//from drawGrid(mydata.get_grid(1), false);//to ////////////////////////////////////////// // 作成したレイを表示 //drawRays(); ////////////////////////////////////////// // 始点から衝突した点までの線分を表示 #if 0 glLineWidth(1); glBegin(GL_LINES); for (size_t i = 0; i < mydata.get_intersects().size(); i++) { //for (size_t x = 0; x < mydata.get_intersects()[y].size(); x++) { glVertex3fv( glm::value_ptr( mydata.get_grid(0)[i].center() ) ); glVertex3fv( glm::value_ptr( mydata.get_intersects()[i]._position ) ); //} } glEnd(); #endif
///////////////////////////////////////////// // 三次元上にレイと球の交差点表示 glPointSize(3); glBegin(GL_POINTS); for (size_t i = 0; i < mydata.get_intersects().size(); i++) { glColor3fv( glm::value_ptr( mydata.get_intersects()[i]._color ) ); glVertex3fv( glm::value_ptr( mydata.get_intersects()[i]._position ) ); } glEnd(); glPointSize(1);
drawXYZ();
// グリッドの上にレイと球の交差点表示 glColor3d(1, 1, 1); glBegin(GL_POINTS); for (size_t i = 0; i < mydata.get_intersects().size(); i++) { if (isinf(mydata.get_intersects()[i]._position.x) == false) { glColor3fv( glm::value_ptr( mydata.get_intersects()[i]._color ) ); glVertex3fv( glm::value_ptr( mydata.get_grid(0)[i].center() ) ); } } glEnd();
glFlush(); } //ウィンドウサイズの変化時に呼び出される void reshape(int w, int h) { width = w; height = h; disp(); } //エントリポイント int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitWindowPosition(100, 50); glutInitWindowSize(500, 500); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGBA); mydata.set(
0.f,//始点のZ座標
3.f,//終点のZ座標
100,//X方向の解像度
100 //Y方向の解像度
); /////////////////////////////////// mydata.set_object(
object_sphere(
glm::vec3(0.5, 0, 2),//球の中心座標
glm::vec3(1, 0, 0),//球の色
0.5//球の半径
)
); mydata.raycast();//レイキャスト glutCreateWindow("sample"); glutDisplayFunc(disp); glutReshapeFunc(reshape); glutMainLoop(); return 0; }
この記事のトラックバックURL: