スポンサーリンク
Bezier曲線をなめらかにする(やや強引)
tを適当にstepを決めて進めてその頂点をブレゼンハムなどで結ぶと折れ線になってしまうので、なめらかな曲線にできないか検討した。
Bezierのtを求める
Bezierの式はこうなっている。
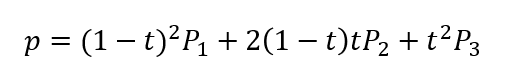
これを展開してまとめなおしてみる。
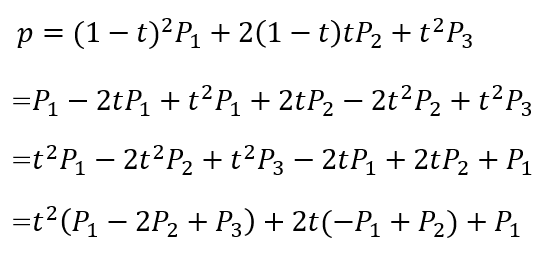
すると普通の二次方程式にできる。P1,P2,P3は定数なので、pが分かれば解の公式でtを求められる。
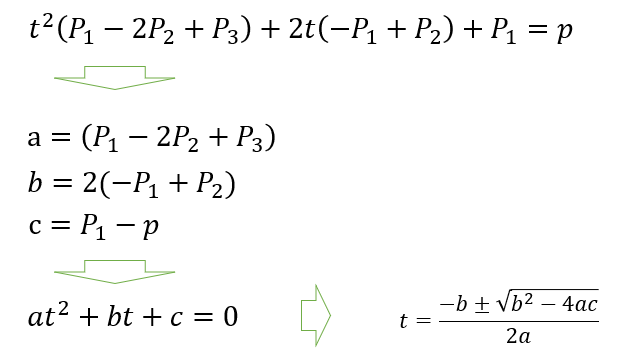
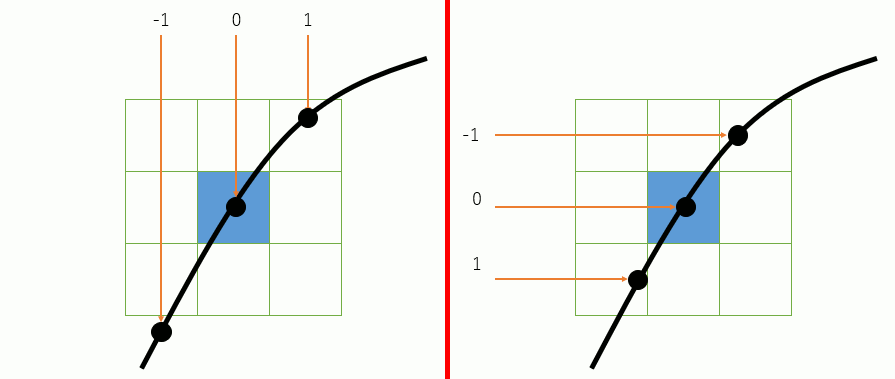
仮にある点pのピクセルが点灯したとして、その次の点は、pの周辺の8点のどれかであるから、例えばp.x-1 , p.x , p.x+1 を使って 解の公式を使えば、p.xがその値の時のtが得られる。
本当は連立方程式なりなんなりを解けばいいのかもしれないが、私にそんな知恵はないので、p.x-1,p.x,p.x+1 , p.y-1,p.y,p.y+1 のそれぞれに対応するtを求め、一番直前のピクセルに近い距離のものを選ぶ。
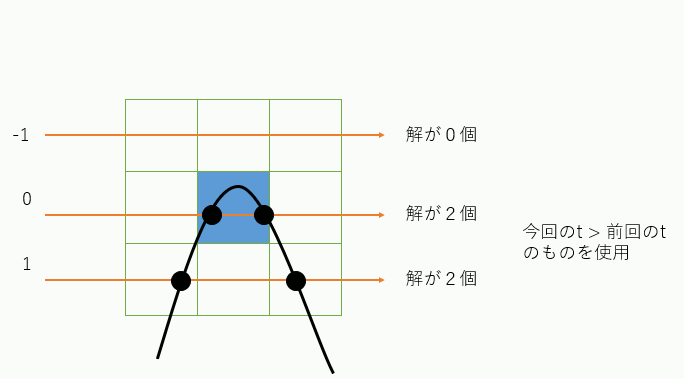
ただし二次方程式なので、解が虚数になることがある。この場合は対象外。さらに解が二つ出てきたら、どちらかが「現在のtの値」より小さい、つまりバックしてしまう点なので、そうならないほうを選ぶ。
ソースコード
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include <iostream> #include <array> #include <vector> #include <optional> using rgb_t = std::array<unsigned char, 3>; struct Image_t { int width; int height; std::vector<rgb_t> data; Image_t(int _width_, int _height_) { width = _width_; height = _height_; data = std::vector<rgb_t>(width * height); } inline int pos(const int x, const int y)const { return y * width + x; } inline bool valid(const int x, const int y)const { if (x < 0)return false; if (y < 0)return false; if (x >= width)return false; if (y >= height)return false; } }; void ppmP3_write( const char* const fname, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p ); struct coord_t { int x, y; bool operator==(const coord_t& src) { return x == src.x && y == src.y; } bool operator!=(const coord_t& src) { return x != src.x || y != src.y; } }; struct coordd_t { double x, y; }; //! @brief 画像をクリア //! @param [in,out] img クリアする画像 //! @param [in] color クリアする色 //! @return なし void fill(Image_t& img, const rgb_t color) { std::fill(img.data.begin(), img.data.end(), color); } //! @brief 大きさのある点(矩形)を書き込む //! @param [in,out] img 書き込む画像 //! @param [in] pos 書き込む位置 //! @param [in] color 書き込む色 //! @param [in] size 点の大きさ //! @return なし void plot(Image_t& img, const coord_t pos, const rgb_t color, const int size) { int bx = pos.x - size / 2; int ax = bx + size; int by = pos.y - size / 2; int ay = by + size; for (size_t x = bx; x < ax; x++) { for (size_t y = by; y < ay; y++) { if (img.valid(x, y)) { img.data[img.pos(x, y)] = color; } } } } struct QuadraticEquation { double plus; double minus; };
//! @brief Bezierのtを求める関数 //! @param [in] P1 最初の点の座標 //! @param [in] P2 ハンドルの点の座標 //! @param [in] P3 最後の点の座標 //! @param [in] p求めたい点の座標 //! @return pを得るためのtの値 値は零個~最大二個。零個の時はstd::nulloptを返す std::optional<QuadraticEquation> BezierInverse(double P1,double P2,double P3,double p) { double a = P1 - 2 * P2 + P3; double b = 2 * (-P1 + P2); double c = P1 - p; double test = pow(b, 2) - 4 * a * c; // (-b +- sqrt(test)) / (2*a) double plus,minus; if (test < 0) { //sqrtの中が負数なら虚数なので解をなしとする return std::nullopt; } else { plus = (-b + sqrt(test)) / (2 * a); minus = (-b - sqrt(test)) / (2 * a); } return QuadraticEquation{ plus,minus }; }
coordd_t BezierXY(coord_t P1, coord_t P2, coord_t P3, double t) { double ti = 1.0 - t; coordd_t dP; dP.x = pow(ti, 2) * P1.x + 2 * ti * t * P2.x + pow(t, 2) * P3.x; dP.y = pow(ti, 2) * P1.y + 2 * ti * t * P2.y + pow(t, 2) * P3.y; return dP; }
//! @brief Bézier Curve //! @param [in,out] img 書き込む画像 //! @param [in] 制御点三点 //! @param [in] color 書き込む色 //! @return なし //! @sa https://ja.javascript.info/bezier-curve void Bezier(Image_t& img, const std::array<coord_t, 3>& points, const rgb_t& color) { const int step = 30; coord_t P1 = points[0]; coord_t P2 = points[1]; coord_t P3 = points[2]; coord_t Pbefore = P1; //最初の一点をプロット if (img.valid(P1.x, P1.y)) { plot(img, P1, color, 1); } // tの候補を確認 std::vector< double > cands; double t = 0.0; while (t < 1.0 && Pbefore!=P3){ coord_t P = Pbefore; double derror = (std::numeric_limits<double>::max)(); double rett = 100; coord_t Pn; coord_t tmp; coordd_t cd; cands.clear(); // 現在の頂点の周辺 for (int x = -1; x <= 1; x++) { auto tx = BezierInverse(P1.x, P2.x, P3.x, P.x + x); if (tx != std::nullopt) { cands.push_back(tx.value().plus); cands.push_back(tx.value().minus); } } for (int y = -1; y <= 1; y++) { auto ty = BezierInverse(P1.y, P2.y, P3.y, P.y + y); if (ty != std::nullopt) { cands.push_back(ty.value().plus); cands.push_back(ty.value().minus); } } for (auto tt : cands) { // 直前の点を描いたtより大きく、 // かつ0.0~1.0に収まっている場合 if (tt > t && tt > 0.0 && tt <= 1.0 ) { cd = BezierXY(P1, P2, P3, tt); tmp.x = round(cd.x); tmp.y = round(cd.y); if (tmp != P) { double d = pow(cd.x - P.x, 2) + pow(cd.y - P.y, 2); if (d < derror) { Pn = tmp; derror = d; rett = tt; } } } } t = rett; if (img.valid(Pn.x, Pn.y)) { plot(img, Pn, color, 1); } else { printf("%d %d", Pn.x, Pn.y); } Pbefore = Pn; } }
int main() { Image_t img(400, 250); fill(img, rgb_t{ 255,255,255 }); std::array<coord_t, 3> vcd; vcd[2] = { 50,20 }; vcd[1] = { 200,200 }; vcd[0] = { 300,60 }; plot(img, vcd[0], rgb_t{ 125,0,0 }, 5);// ハンドルを描画 plot(img, vcd[1], rgb_t{ 125,0,0 }, 5); plot(img, vcd[2], rgb_t{ 125,0,0 }, 5); Bezier(img, vcd, rgb_t{ 0,0,255 });// ベジェ曲線を描く ppmP3_write("abc.ppm", img.width, img.height, (unsigned char*)img.data.data()); } //! @brief PPM(RGB各1byte,カラー,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @param [in] vmax 全てのRGBの中の最大値。普通の画像なら255 //! @details RGBRGBRGB....のメモリを渡すと、RGBテキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void ppmP3_write( const char* const fname, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p ) { FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P3\n%d %d\n%d\n", width, height, 255); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d ", p[k * 3 + 0], p[k * 3 + 1], p[k * 3 + 2] ); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
実行例
この記事のトラックバックURL: