スポンサーリンク
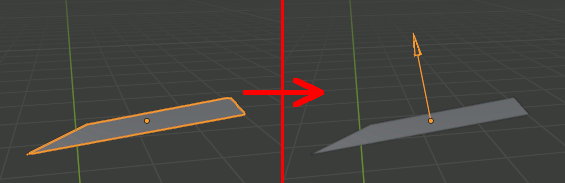
Blender Pythonでポリゴンの法線をグローバル座標系で取得して表示する
import bpy import bmesh import mathutils import numpy import math
# @brief オブジェクトの指定したpolygonの法線を取得 # @param [in] obj オブジェクト # @param [in] polyIndex ポリゴン番号 # @return 法線(グローバル座標系) def got_polygon_normal(obj,polyIndex): # オブジェクトの行列を取得 local44 = obj.matrix_world ll_inv = local44.inverted() ll_inv_norm = ll_inv.transposed().to_3x3() vn = obj.data.polygons[polyIndex].normal return ll_inv_norm @ vn
# @brief 任意軸回転 # @sa https://www.study.suzulang.com/bpy/bpy-arbitrary-axis-rotation # @param [in,out] obj 回転するオブジェクト # @param [in] axis 回転軸 # @param [in] radian 回転角をラジアンで指定 # @return なし def rotate_object(obj,axis,radian): rot_mat= mathutils.Matrix.Rotation( radian, 4, axis ) # decompose world_matrix's components, and from them assemble 4x4 matrices orig_loc, orig_rot, orig_scale = obj.matrix_world.decompose() # orig_loc_mat = mathutils.Matrix.Translation(orig_loc) orig_rot_mat = orig_rot.to_matrix().to_4x4() orig_scale_mat = (mathutils.Matrix.Scale(orig_scale[0],4,(1,0,0)) @ mathutils.Matrix.Scale(orig_scale[1],4,(0,1,0)) @ mathutils.Matrix.Scale(orig_scale[2],4,(0,0,1))) # # assemble the new matrix obj.matrix_world = orig_loc_mat @ rot_mat @ orig_rot_mat @ orig_scale_mat
# @brief (0,0,1)のベクトルを法線方向に回転するための回転軸と回転角度を求める # @param [in] the_normal 今回使用する法線 # @return 回転軸,回転角(ラジアン) def calc_to_normal(the_normal): Zvec = mathutils.Vector((0,0,1)) vn = the_normal onorm = mathutils.Vector(vn) onorm.normalize() # 外積 axis = mathutils.Vector.cross(Zvec,onorm) axis.normalize() # 内積 th = mathutils.Vector.dot(Zvec,onorm) # 角度算出 rad = math.acos( numpy.clip(th,-1.0,1.0) ) return axis , rad
# @brief オブジェクトの0番目のポリゴンの法線を計算し、empty arrowで表示する # @param [in] target 目的のオブジェクト def disp_polygon_normal(target): tnormal = got_polygon_normal(target,0) axis , rad = calc_to_normal(tnormal) bpy.ops.object.empty_add(type="SINGLE_ARROW") arrow = bpy.context.active_object rotate_object(arrow,axis,rad) arrow.location = target.location
# 実行例 target = bpy.context.active_object disp_polygon_normal(target)
参考
この記事のトラックバックURL: