スポンサーリンク
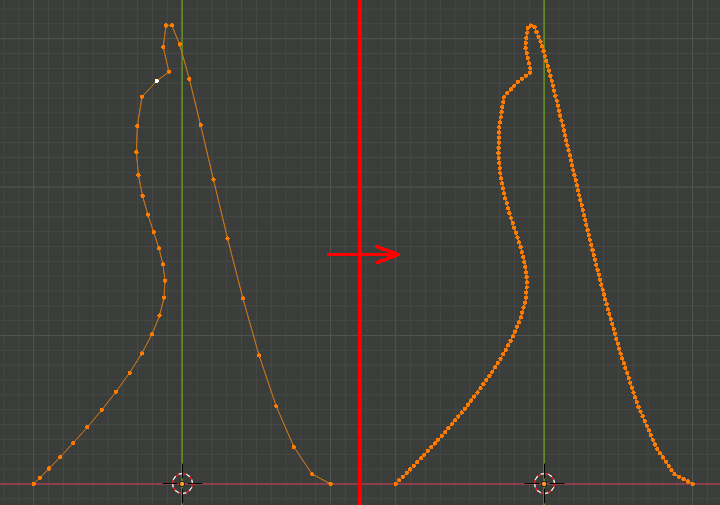
Blender Pythonでエッジからなる曲線を再分割して等間隔の頂点リストにする
なんと表現していいか正直わからないがやりたいのは以下。
・分割する個数を指定できる
・頂点を等間隔に設置
ソースコード
コードの多くは、前に作った頂点をソートするプログラムになっている。ソートしないと点を補完する位置がわからない。補間の処理は後半部分になる。
import bpy import numpy as np ###################################################### # 現在選択中のオブジェクトを取得 def select_object(): ob = bpy.context.active_object if ob.type != 'MESH': raise TypeError("Active object is not a Mesh") mesh = ob.data #print( len(mesh.edges) ) #print( len(mesh.vertices) ) return mesh.vertices, mesh.edges ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief 端点を取得 # @param [in] verts 頂点リスト # @param [in] edges エッジリスト # @param [in] target 端点は二つあるので0,1のどちらか # @return 頂点番号 def get_end_points(verts,edges,target): dic = {} for v in range(len(verts)): dic[v] = 0 for e in edges: dic[e.vertices[0]] += 1 dic[e.vertices[1]] += 1 ends = [] for i in range(len(dic)): if dic[ i ] == 1: ends.append( i ) return ends[target] ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief vtxを持つエッジのリストを取得 # @param [in] edges エッジリスト # @param [in] vtx 頂点index # @return エッジindexの配列 def get_edge_by_point(edges,vtx): edgelist = [] for e in edges: if e.vertices[0] == vtx or e.vertices[1] ==vtx: edgelist.append(e.index) return edgelist ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief V1を持ち、V2を持たないエッジ # @param [in] V1 頂点index(持つ頂点) # @param [in] v2 頂点index(持たない頂点) # @return 見つかったエッジindex # @retval None そのようなエッジはなかった def get_edge_V1_but_V2(edges,V1,V2): for e in edges: if e.vertices[0] == V1 and e.vertices[1] != V2: return e.index if e.vertices[1] == V1 and e.vertices[0] != V2: return e.index return None ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief edgeを構成する2頂点のうち、vertexでないほうの頂点を返す # @param [in] edge エッジリスト # @param [in] vertex 基準となる頂点のIndex # @return 頂点番号 def get_another_point_on_edge(edge,vertex): if edge.vertices[0] == vertex: return edge.vertices[1] if edge.vertices[1] == vertex: return edge.vertices[0] ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief 一直線に連続した順番の頂点一覧を取得 # @param [in] verts 頂点リスト # @param [in] edges エッジリスト # @param [in] order 端点のどちら側から探索するか(0 or 1) # @return 頂点一覧 def get_connected_vertex_list(verts,edges,order): # 結果の格納先 vlist = [] # 最初の頂点を取得。「端点」は二つだけ存在するので # 結果は二つ求まる(0,1)。そのうちのorder番を取得 EP = get_end_points(verts,edges,order) vlist.append(EP) #その要素が結果の一番目 edgeidxlist = get_edge_by_point(edges,EP)# EPを持つエッジの一覧。要素数1の配列になるはず # エッジ最初の頂点を持つエッジ endpointedge = edges[edgeidxlist[0]] #EP(最初の端点)でない方の頂点を取得 another = get_another_point_on_edge( endpointedge , EP ) # 端点を持つエッジの、端点でないほうの頂点は、二番目の頂点 vlist.append(another) # 無限ループを使うのでループ上限を設けておく looplimit = 100 while True: # 前回の前回見つけた頂点 before = vlist[len(vlist)-2] # 前回見つけた頂点。この頂点の次の頂点を探したい now = vlist[len(vlist)-1] #nowを持ち、beforeを持たないエッジを検索 nextedge = get_edge_V1_but_V2(edges,now,before) # 端点には「nowを持ち、beforeを持たないエッジ」がないので、Noneが入っている if nextedge is None: break #nextedgeの、nowでない方の頂点を取得 next = get_another_point_on_edge( edges[nextedge] , now ) vlist.append(next) looplimit -= 1 if looplimit == 0: break return vlist ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief 頂点のソート機能のエントリポイント # @param [in] obj 対象のオブジェクト def points_sort(obj): # 頂点群を取得 _verts = obj[0] _edges = obj[1] # 頂点番号のテキストオブジェクトを追加 #add_text_numbers(_verts) vtx_c_list = get_connected_vertex_list(_verts,_edges,0) print(vtx_c_list) points = [] for v in vtx_c_list: points.append( obj[0][v].co ) # 頂点一覧 return points
###################################################### ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief 結果の頂点+エッジのオブジェクトを作成する
# @param [in] points 頂点座標群
# @return なし
def new_interpo_curve(points): # make mesh vertices = points edges = [] for i in range(0,len(vertices)-1): edges.append([i,i+1]) faces = [] new_mesh = bpy.data.meshes.new('new_mesh') new_mesh.from_pydata(vertices, edges, faces) new_mesh.update() # make object from mesh new_object = bpy.data.objects.new('new_object', new_mesh) # make collection new_collection = bpy.data.collections.new('new_collection') bpy.context.scene.collection.children.link(new_collection) # add object to scene collection new_collection.objects.link(new_object)
###################################################### ###################################################### ###################################################### # @brief オブジェクトの頂点を補間する # @param obj 選択したオブジェクト # @param N 補間する頂点数 # @return 補間した頂点座標群 def p_subd(obj,N): # オブジェクトの頂点をソート points = points_sort(obj) distances = [] distances.append(0.0) lensum = 0.0 for pid in range(0,len(points)-1): lensum += np.linalg.norm(points[pid] - points[pid+1]) distances.append(lensum) for pd in distances: print(pd) ####################################### # 移動量の決定 a = lensum / (N-1) # 結果の保存先 interpo = [] # distancesのindex dista = 0
breakfor=False
# i の範囲は 0...N-1 for i in range(0,N): pos = i * a while distances[dista+1] < pos : if i==N-1: interpo.append(points[len(points)-1])
breakfor=True
break dista+=1 if breakfor==True:
break
# 移動方向の決定 _from = points[dista] _to = points[dista+1] vec = _to - _from veclen = np.linalg.norm(vec) vec = vec / veclen dlen = pos - distances[dista] pnew = _from + vec * dlen interpo.append(pnew) return interpo
# 選択したオブジェクト obj = select_object() # objを細分化した頂点群を作成 points = p_subd(obj,50) # pointsからオブジェクトを作成 new_interpo_curve(points)
C++で実装した場合
vmmath.hpp:
https://www.study.suzulang.com/3dcg-functions/vmmath-hpp
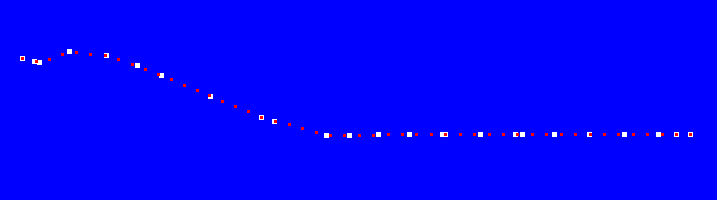
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include <GL/glut.h> #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") #include "vmmath.hpp" #include <array> #include <vector> #include <cassert> std::vector<std::array<double, 3> > points; std::vector<std::array<double, 3> > interpo; void display(void) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); glOrtho(-4, 4, -4, 4, 1, -1); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); glLoadIdentity(); glPushMatrix(); glTranslated(0, 0, -0.5); glColor3d(1, 1, 1); glPointSize(5); glBegin(GL_POINTS); for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { glVertex3dv(points[i].data()); } glEnd(); glColor3d(1, 0, 0); glPointSize(3); glBegin(GL_POINTS); for (size_t i = 0; i < interpo.size(); i++) { glVertex3dv(interpo[i].data()); } glEnd(); glPopMatrix(); glFlush(); }
//! @brief 再分割 //! @param [in] N 再分割後の頂点数 //! @param [in] points 再分割対象の頂点群 //! @return 再分割結果 std::vector<std::array<double, 3> > interporate(const size_t N, std::vector<std::array<double, 3> >& points) { std::vector<std::array<double, 3> > _interpo_; std::vector<double> distances; distances.push_back(0.0); double len = 0; // 全体の長さ計算 for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size() - 1; i++) { size_t j = i + 1; len += szl::mathv::distance3(points[i], points[j]); distances.push_back(len); } assert(N >= 2); // N-1分割するときの 点から次の点までの距離 double a = len / (N - 1); size_t dista = 0; bool breakfor=false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++) { double pos = i * a; while (distances[dista + 1] < pos) { if (i == N - 1) { _interpo_.push_back(points.back());
breakfor=true;
break; } dista++; }
if (breakfor==true)
break;
std::array<double, 3> from = points[dista];//移動の始点 std::array<double, 3> to = points[dista + 1]; std::array<double, 3> vec;//移動方向 szl::mathv::vector_from_line3(vec, from, to); szl::mathv::normalize3(vec); //移動量 double dlen = pos - distances[dista]; std::array<double, 3> pnew; pnew[0] = from[0] + vec[0] * dlen; pnew[1] = from[1] + vec[1] * dlen; pnew[2] = from[2] + vec[2] * dlen; _interpo_.push_back(pnew); } return _interpo_; }
void init(void) { points.push_back({ -3.517056703567505 , 0.8161399364471436 , -6.102355065706888e-09 }); points.push_back({ -3.4123122692108154 , 0.7847403883934021 , -5.867581087670715e-09 }); points.push_back({ -3.3656115531921387 , 0.7668724656105042 , -5.733980401601002e-09 }); points.push_back({ -3.0980424880981445 , 0.8815682530403137 , -6.591572176972704e-09 }); points.push_back({ -2.770911931991577 , 0.8392514586448669 , -6.275163944025053e-09 }); points.push_back({ -2.4997775554656982 , 0.732718288898468 , -5.478603348763045e-09 }); points.push_back({ -2.2808961868286133 , 0.6278470754623413 , -4.694470145949481e-09 }); points.push_back({ -1.8470044136047363 , 0.41193005442619324 , -3.0800362260663405e-09 }); points.push_back({ -1.3970714807510376 , 0.1896354854106903 , -1.4179162288741054e-09 }); points.push_back({ -1.2790554761886597 , 0.14838068187236786 , -1.1094490881546903e-09 }); points.push_back({ -0.8242318630218506 , -0.001560855540446937 , 1.1680695473359481e-11 }); points.push_back({ -0.6166437864303589 , -0.0058229416608810425 , 4.3537274480032195e-11 }); points.push_back({ -0.3599426746368408 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ -0.08002424240112305 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 0.2106800079345703 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 0.23912858963012695 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 0.5433409214019775 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 0.853459358215332 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 0.920318603515625 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 1.2055344581604004 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 1.5156524181365967 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 1.8214571475982666 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 2.1207892894744873 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 2.4114935398101807 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); points.push_back({ 2.2826988697052 , 0.0 , 0.0 }); interpo = interporate(50,points); } int main(int argc,char*argv[]) { glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGBA); glutCreateWindow(argv[0]); glutDisplayFunc(display); init(); glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0); glutMainLoop(); return 0; }
この記事のトラックバックURL: