スポンサーリンク
塗りつぶし Flood fill(1)
Flood fillを実装する。データには前回作ったNByteDataのクラスを使う。
参考
WikipediaのFloodFillの項目に疑似コードがあるので、それをC++に書き直す。
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flood_fill
コード(FloodFill.hpp)
#pragma once #include "NByteData.hpp" using uc3T = NByteData<3>;
//! @brief 座標計算などを行う補助クラス class accessor { int width; int height; public: void set(int Width, int Height) { width = Width; height = Height; } bool is_in(const int x, const int y) { if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= width || y >= height) return false; return true; } size_t get_pos(const int x, const int y) { return (size_t)y * width + (size_t)x; } };
//! @brief floodfill本体 //! @param [in] x 対象の画素のX座標 //! @param [in] y 対象の画素のY座標 //! @param [in] targetcolor 塗りつぶし対象の色 //! @param [in] replacementcolor 塗りつぶし結果の色 //! @param [in,out] img 対象の画像データ //! @param [in] acc 画素の座標等を求めたりする補助クラスのインスタンス void ff_fill( int x, int y, uc3T targetcolor, uc3T replacementcolor, uc3T* img, accessor* acc) { if (acc->is_in(x, y) == false) return; uc3T* node = &img[acc->get_pos(x, y)]; //1. If target - color is equal to replacement - color, return. if (targetcolor == replacementcolor) { return; } //2. If the color of node is not equal to target - color, return. if (*node != targetcolor) { return; } // 3. Set the color of node to replacement - color. *node = replacementcolor; // 4. ff_fill(x, y + 1, targetcolor, replacementcolor, img, acc); // Perform Flood - fill(one step to the south of node, target-color, replacement-color). ff_fill(x, y - 1, targetcolor, replacementcolor, img, acc); // Perform Flood - fill(one step to the north of node, target-color, replacement-color). ff_fill(x - 1, y, targetcolor, replacementcolor, img, acc); // Perform Flood - fill(one step to the west of node, target-color, replacement-color). ff_fill(x + 1, y, targetcolor, replacementcolor, img, acc); // Perform Flood - fill(one step to the east of node, target-color, replacement-color). // 5. Return. return; }
//! @brief floodfillエントリポイント //! @param [in] seedx 塗りつぶし開始点 //! @param [in] seedy 塗りつぶし開始点 //! @param [in] replacementcolor 塗りつぶし結果の色 //! @param [in,out] img 対象の画像データ //! @param [in] Width 画像幅(画素数) //! @param [in] Height 画像高さ(画素数) void f_fill( int seedx, int seedy, uc3T replacementcolor, uc3T* img, int Width, int Height) { accessor acc; acc.set(Width, Height); if (acc.is_in(seedx, seedy) == false) return; uc3T targetcolor = img[acc.get_pos(seedx, seedy)]; ff_fill(seedx, seedy, targetcolor, replacementcolor, img, &acc); }
呼び出し側
#include <iostream> #include<vector> #pragma warning(disable:4996) #include "NByteData.hpp" #include "floodfill.hpp" void pnmP3_Write( const char* const fname, const int vmax, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p); bool pnmP6_Read( const char* fname, int* vmax, int *width, int *height, unsigned char** p); // PPM BINARY uc3T getrgb( unsigned char r, unsigned char g, unsigned char b ) { return uc3T({ r,g,b }); }
int main() { int width = 255; int height = 30; unsigned char* image; int vmax; pnmP6_Read(// 画像準備 R"(C:\data\p6ascii.ppm)", &vmax, &width, &height, &image ); uc3T* img = (uc3T*)image; f_fill(// 塗りつぶし 300, 200, getrgb(0, 0, 0), img, width, height );
// 結果をファイルに出力 pnmP3_Write(R"(C:\data\floodfill.ppm)", 255, width, height, image); }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //! @brief PPM(RGB各1byte,カラー,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] vmax 全てのRGBの中の最大値 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details RGBRGBRGB....のメモリを渡すと、RGBテキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pnmP3_Write( const char* const fname, const int vmax, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p) { // PPM ASCII FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P3\n%d %d\n%d\n", width, height, vmax); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d ", p[k * 3 + 0], p[k * 3 + 1], p[k * 3 + 2]); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
//! @brief PPM(RGB各1byte,カラー,バイナリ)を読み込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [out] vmax 全てのRGBの中の最大値 //! @param [out] width 画像の幅 //! @param [out] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] 画像を読み込んだメモリアドレスを返すためのポインタへのポインタ //! @retval true 成功 //! @retval false 失敗 //! @warning RGBが各1byteでないと動作しない //! @details ファイルを読み込み、width*height*3のメモリを確保したうえでRGBをそこへ格納する bool pnmP6_Read(const char* fname, int* vmax, int *width, int *height, unsigned char** p) { // PPM BINARY *width = -1; *height = -1; *vmax = -1; FILE* fp; fp = fopen(fname, "rb"); char tmp[2048]; char c; while (c = fgetc(fp)) { if (isspace(c)) continue; if (c == 'P') { //フォーマットを特定する c = fgetc(fp) - '0'; if (c != 6) { fclose(fp); return false; } continue; } if (c == '#') { //コメントを読み飛ばす while (c != '\r' && c != '\n') c = fgetc(fp); continue; } if (*width < 0) { int s = 0; while (1) { if (isdigit(c)) { tmp[s++] = c; c = fgetc(fp); } else { tmp[s] = '\0'; *width = atoi(tmp); break; } } continue; } if (*height < 0) { int s = 0; while (1) { if (isdigit(c)) { tmp[s++] = c; c = fgetc(fp); } else { tmp[s] = '\0'; *height = atoi(tmp); break; } } continue; } if (*vmax < 0) { int s = 0; while (1) { if (isdigit(c)) { tmp[s++] = c; c = fgetc(fp); } else { tmp[s] = '\0'; *vmax = atoi(tmp); break; } } break; } else { break; } } if (*width < 0 || *height < 0 || *vmax < 0) { return false; } const size_t maxsize = *width* *height; unsigned char r, g, b; *p = new unsigned char[maxsize * 3]; for (size_t i = 0; i < maxsize; i++) { fread(&r, 1, 1, fp); fread(&g, 1, 1, fp); fread(&b, 1, 1, fp); (*p)[i * 3 + 0] = r; (*p)[i * 3 + 1] = g; (*p)[i * 3 + 2] = b; } fclose(fp); return true; }
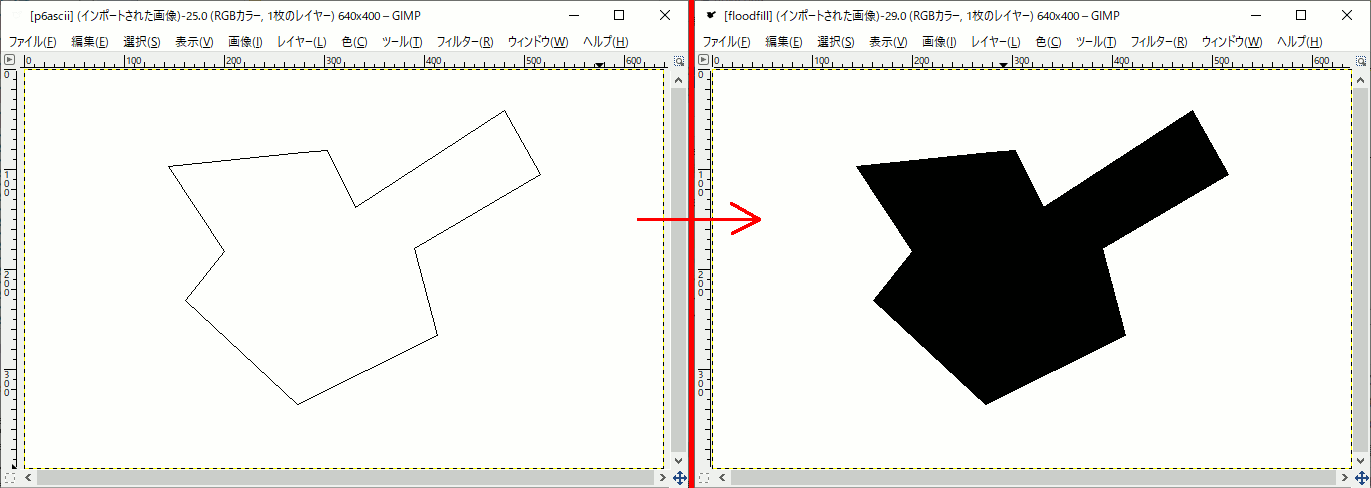
結果
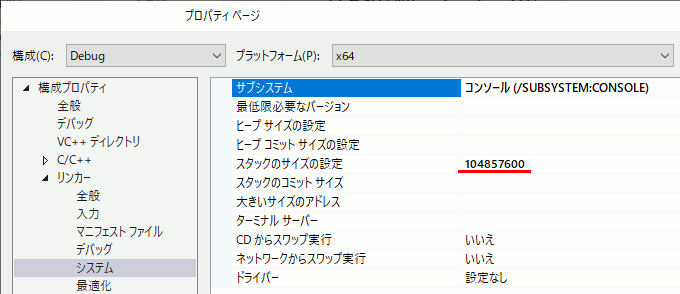
スタックサイズ
FloodFillは再帰を使うが、再帰はスタックを食いつぶすのでStack over flowが起こる。
VC++の初期設定は1MBらしいので、[プロジェクトのプロパティ]→[リンカー]→[システム]→[スタックのサイズ設定]からスタックを大きめに確保しておく。なおここはバイト単位なのでメガバイト単位で指定するには1024*1024しなければならない。
関連
この記事のトラックバックURL: