スポンサーリンク
Welzlの最小球を求めるアルゴリズムをC++で実装
点群の最小球を求めるのにWelzlのアルゴリズムというのがあるのを知った。
とりあえずコピペで動くことを確認したのでここに置く。何をやっているのかわからないのでこれから調べていく。
あと、そのままだと再帰が激しすぎてたった5000頂点でオーバーフローした。スタックサイズを変えればいけるのだろうがそういう問題ではない。
#include <iostream> #include <unordered_map> #include <set> #pragma warning(disable:4996) #include <vtkUnsignedCharArray.h> #include <vtkPointData.h> #include <vtkActor.h> #include <vtkRenderer.h> #include <vtkRenderWindow.h> #include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h> #include <vtkProperty.h> #include <vtkSphere.h> #include <vtkVertexGlyphFilter.h> //球とその表示に必要 #include <vtkSphereSource.h> #include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h> //VTK_MODULE_INITに必要 #include <vtkAutoInit.h> //必須 VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2); VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle); #pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "Psapi.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "Dbghelp.lib") #include <Eigen/Dense> #include <random> #pragma comment(lib,"opengl32.lib") // 点群型 struct MyCloud { std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> points; std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> colors; }; namespace welzl {
// 球を表す struct Sphere { Eigen::Vector3d center; double radius; Sphere() : center(Eigen::Vector3d::Zero()), radius(0.0) {} Sphere(const Eigen::Vector3d& c, double r) : center(c), radius(r) {} };
//------------------------------------- // R(最大4点)から決まる球を求める補助関数群 //-------------------------------------
// 1点からなる球(その点が中心、半径0) Sphere ball_from_one_point(const Eigen::Vector3d& a) { return Sphere(a, 0.0); }
// 2点からなる最小球(2点の中点が中心、半径は両点から中点までの距離) Sphere ball_from_two_points(const Eigen::Vector3d& a, const Eigen::Vector3d& b) { Eigen::Vector3d c = 0.5 * (a + b); double r = (a - c).norm(); return Sphere(c, r); }
// 3点から決まる球(3点が共通で外接する円=2次元平面での外接円を3D空間で表現) // 外接円の中心は3点からなる三角形の外心 Sphere ball_from_three_points(const Eigen::Vector3d& a, const Eigen::Vector3d& b, const Eigen::Vector3d& c) { // 2次元外心計算を3次元対応。3点は同一平面上にあるため、 // 外心は、(b - a), (c - a)に直交する2本の垂直二等分線の交点。 Eigen::Vector3d ab = b - a; Eigen::Vector3d ac = c - a; Eigen::Matrix3d M; M << ab.x(), ab.y(), ab.z(), ac.x(), ac.y(), ac.z(), ab.cross(ac).x(), ab.cross(ac).y(), ab.cross(ac).z(); // 上記はそのままでは重複があり、もう少し安定的な方法を取る必要がある。 // 簡易的には、外心は以下の方程式で求められる: // |x - a|^2 = |x - b|^2 = |x - c|^2 を解く。 // この方程式は線形代数で解ける。 // 以下では直接外心を求める一般的な手続きの1つを示す。 // 行列方程式で外心を求めるための設定 // (参考実装) 外心は幾何的には以下で求まる: // Let A, B, C be points. 外心Oは: // solve for O: // (O - A)・(B - A) = (|B-A|^2)/2 // (O - A)・(C - A) = (|C-A|^2)/2 // この2式からOが求まる。(O - A)を未知変数にした線形方程式となる Eigen::Matrix2d A_mat; A_mat << ab.dot(ab), ab.dot(ac), ab.dot(ac), ac.dot(ac); Eigen::Vector2d rhs; rhs << 0.5 * ab.dot(ab), 0.5 * ac.dot(ac); // 解く Eigen::Vector2d uv = A_mat.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(rhs); Eigen::Vector3d O = a + uv[0] * ab + uv[1] * ac; double r = (O - a).norm(); return Sphere(O, r); }
// 4点から決まる球(4点が共通球面上にある場合、その外接球を求める) // 4点外接球計算は3x3の線形方程式を解くことで可能。 Sphere ball_from_four_points(const Eigen::Vector3d& a, const Eigen::Vector3d& b, const Eigen::Vector3d& c, const Eigen::Vector3d& d) { // 方針: // (O - a)・(O - a) = (O - b)・(O - b) // (O - a)・(O - a) = (O - c)・(O - c) // (O - a)・(O - a) = (O - d)・(O - d) // という3つの方程式を立て、Oを求める。 Eigen::Vector3d A = a; Eigen::Vector3d B = b; Eigen::Vector3d C = c; Eigen::Vector3d D = d; // 方程式組み立て // (O - A)² = (O - B)² などは展開すると // O² - 2O·A + A² = O² - 2O·B + B² → 2O·(B - A) = B² - A² // 同様にC, Dについても同様の式を立てられる // よって: // 2(B - A)·O = B² - A² // 2(C - A)·O = C² - A² // 2(D - A)·O = D² - A² // ベクトルX = Oについて Eigen::Matrix3d M; M << 2 * (b.x() - a.x()), 2 * (b.y() - a.y()), 2 * (b.z() - a.z()), 2 * (c.x() - a.x()), 2 * (c.y() - a.y()), 2 * (c.z() - a.z()), 2 * (d.x() - a.x()), 2 * (d.y() - a.y()), 2 * (d.z() - a.z()); auto sq = [](const double& val) { return val * val; }; Eigen::Vector3d RHS; RHS << (b.squaredNorm() - a.squaredNorm()), (c.squaredNorm() - a.squaredNorm()), (d.squaredNorm() - a.squaredNorm()); Eigen::Vector3d O = M.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(RHS); double r = (O - a).norm(); return Sphere(O, r); }
// Rには最大4頂点が入っている。 // それに応じて最小包含球を求める Sphere ball_from_R(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& R) { switch (R.size()) { case 0: return Sphere(Eigen::Vector3d::Zero(), 0.0); case 1: return ball_from_one_point(R[0]); case 2: return ball_from_two_points(R[0], R[1]); case 3: return ball_from_three_points(R[0], R[1], R[2]); case 4: return ball_from_four_points(R[0], R[1], R[2], R[3]); default: // それ以上はありえない return Sphere(); } }
//------------------------------------- // 点 p が球 S の中に入っているか判定 //-------------------------------------
inline bool is_in_sphere(const Eigen::Vector3d& p, const Sphere& S) { return (p - S.center).squaredNorm() <= S.radius * S.radius + 1e-14; // 浮動小数対策 }
//------------------------------------- // Welzlの再帰関数 //------------------------------------- // 引数: // points: 対象の点集合(インデックス0〜endで使用) // R: 球を定義するための点集合 // end: 再帰処理内での有効点数境界
Sphere welzl(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& points, std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> R, int end) { // 再帰の末端、これ以上頂点がないか、Rが4点になったら球を求める if (end < 0 || R.size() == 4) { return ball_from_R(R); } // 頂点を一つ取り出して、それ以外の点で再帰処理 Eigen::Vector3d p = points[end]; Sphere D = welzl(points, R, end - 1); // 今取り出した点が、それ以外の点で求めた球に入っている場合 // 球を再計算する必要が無いので、そのまま返す if (is_in_sphere(p, D)) { return D; } // pがD内に収まらない場合 R.push_back(p); return welzl(points, R, end - 1); }
//------------------------------------- // 公開関数: 最小包含球を計算 //------------------------------------- Sphere minimum_enclosing_sphere(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d>& points) { // 頂点をシャッフルすると期待線形時間になるが // 頂点順を変えたくないため今回は使用しない // なお引数pointsがconst参照のため、ここを有効にしてもエラーになる。 // 有効化するときは引数のconstを外すか、コピーを作成すること。 #if 0 // ポイントシャッフル推奨(期待線形時間のため) std::random_device rd; std::mt19937 g(rd()); std::shuffle(points.begin(), points.end(), g); #endif std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> dumyR; return welzl(points, dumyR, (int)points.size() - 1); }
}
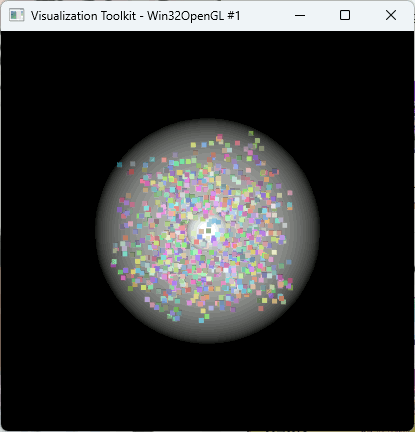
std::pair<Eigen::Vector3f,float> CalcBoundingSphere(MyCloud& cloud) { welzl::Sphere S = welzl::minimum_enclosing_sphere(cloud.points); return { S.center.cast<float>(), S.radius }; }
// 点群をVTK用のActorに変換 vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> ConvertCloudVTKActor(const MyCloud& cloud); // 座標と半径から球のActorを作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> CreateSphereActor(const std::pair<Eigen::Vector3f, float>& sphere_data); // ランダムな点群を作成 MyCloud CreateRandomCloud(int num_points); // 表示データを作成 bool PrepareData(vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer> renderer) { // ランダムな点群を作成 auto cloud = CreateRandomCloud(1000); // welzlでBounding Sphereを計算 auto sphere = CalcBoundingSphere(cloud); std::cout << "center : " << sphere.first.transpose() << std::endl; std::cout << "radius : " << sphere.second << std::endl; // VTK Actorを作成 auto cloudActor = ConvertCloudVTKActor(cloud); auto sphereActor = CreateSphereActor(sphere); // Create a vtkSphereSource vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource> sphereSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource>::New(); sphereSource->SetCenter(sphere.first.x(), sphere.first.y(), sphere.first.z()); sphereSource->SetRadius(0.3); sphereSource->SetThetaResolution(32); sphereSource->SetPhiResolution(32); // Create a vtkPolyDataMapper vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputConnection(sphereSource->GetOutputPort()); // Create a vtkActor and assign the mapper vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> CenterActor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); CenterActor->SetMapper(mapper); renderer->AddActor(cloudActor); renderer->AddActor(sphereActor); renderer->AddActor(CenterActor); return true; } // 座標と半径から球のActorを作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> CreateSphereActor(const std::pair<Eigen::Vector3f, float>& sphere_data) { // 球の中心と半径を取得 const Eigen::Vector3f& center = sphere_data.first; float radius = sphere_data.second; // vtkSphereSourceを設定 vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource> sphereSource = vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource>::New(); sphereSource->SetCenter(center.x(), center.y(), center.z()); sphereSource->SetRadius(radius); sphereSource->SetThetaResolution(32); // 解像度設定 sphereSource->SetPhiResolution(32); // 解像度設定 // Mapperを作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputConnection(sphereSource->GetOutputPort()); // Actorを作成 vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); // 半透明に設定 actor->GetProperty()->SetOpacity(0.5); // 透明度(0.0~1.0) actor->GetProperty()->SetColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); // 白 return actor; }
// ランダムな点群を作成 MyCloud CreateRandomCloud(int num_points) { MyCloud cloud; std::random_device seed_gen; std::mt19937 engine(seed_gen()); std::uniform_real_distribution<> dist(-1.0, 1.0); for (int i = 0; i < num_points; i++) { cloud.points.emplace_back(dist(engine), dist(engine), dist(engine)); cloud.colors.emplace_back(dist(engine), dist(engine), dist(engine)); } return cloud; }
// 点群をVTK用のActorに変換 vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> ConvertCloudVTKActor(const MyCloud& cloud) { // VTK用のポイントリストを作成 auto points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); for (const auto& point : cloud.points) { points->InsertNextPoint(point.x(), point.y(), point.z()); } // VTK用の頂点色リストを作成(Open3Dのcolors_を使用) auto colors = vtkSmartPointer<vtkUnsignedCharArray>::New(); colors->SetNumberOfComponents(3); // RGB if (!cloud.colors.empty()) { for (const auto& color : cloud.colors) { unsigned char r = static_cast<unsigned char>(color.x() * 255); unsigned char g = static_cast<unsigned char>(color.y() * 255); unsigned char b = static_cast<unsigned char>(color.z() * 255); colors->InsertNextTuple3(r, g, b); } } // ポリデータに点とオプションの属性(色、法線)を設定 auto polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(points); if (!cloud.colors.empty()) { polyData->GetPointData()->SetScalars(colors); } // 点を頂点として描画可能にするフィルター auto glyphFilter = vtkSmartPointer<vtkVertexGlyphFilter>::New(); glyphFilter->SetInputData(polyData); glyphFilter->Update(); // マッパーを作成 auto mapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New(); mapper->SetInputData(glyphFilter->GetOutput()); if (!cloud.colors.empty()) { mapper->ScalarVisibilityOn(); // 頂点色を使用する } else { mapper->ScalarVisibilityOff(); // 頂点色がない場合はオフ } // Actorを作成 auto actor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New(); actor->SetMapper(mapper); actor->GetProperty()->SetPointSize(5.0); actor->GetProperty()->SetInterpolationToFlat(); return actor; } int main() { vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer> renderer = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow> window = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New(); window->AddRenderer(renderer); vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor> interactor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New(); window->SetInteractor(interactor); PrepareData(renderer); window->SetSize(700, 400); interactor->Initialize(); window->Render(); interactor->Start(); }
この記事のトラックバックURL: