スポンサーリンク
C++でpartitionするプログラムを書く
partitionは配列を[条件を満たす領域][満たさない領域]に分割する。C++の標準ライブラリにはstd::partitionという関数が用意されているので、用途によってはこれを使ってもよい。
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> // 偶数かどうかを判定する関数 bool is_even(int n) { return n % 2 == 0; } int main() { std::vector<int> numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }; // 偶数の要素を表示 std::cout << "全データ: "; for (int i = 0; i < numbers.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << numbers[i] << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; // std::partitionで偶数と奇数に分ける auto it = std::partition(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), is_even); size_t bound = std::distance(numbers.begin(), it); // 偶数の要素を表示 std::cout << "偶数: " << 0 << " ... " << bound-1 << std::endl; for(int i=0;i< bound;i++){ std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << numbers[i] << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; // 奇数の要素を表示 std::cout << "奇数: " << bound << " ... " << numbers.size() << std::endl; for (int i = bound; i < numbers.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << numbers[i] << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; return 0; }
自前で実装
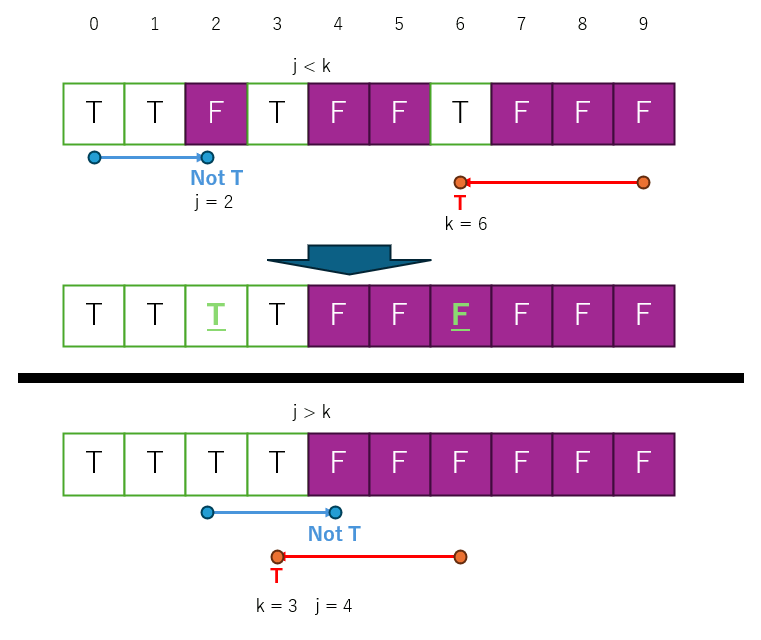
クイックソートと同じ原理で、配列の先頭と末尾から探索し、条件に合うものと合わないものを交換していけばできる。というかパーティションを再帰的に繰り返したのがクイックソートだといえる。
コード
#include <iostream> #include <vector>
// 配列の分割を行う関数 template<typename Container, class PCond> int64_t partition(Container& arr, int64_t low, int64_t high, PCond pivot) { int64_t i = low; int64_t j = high-1; int64_t bound; while (true) { // 条件に合致するものを探す while ( (pivot.IsTrue(i) == true) ) { i++; if (i >= high) break; } // 条件に合致しないものを探す while ( (pivot.IsFalse(j) == true) ) { j--; if (j == -1) break; } // 左右の走査が交差した場合に分割終了 if (i >= j) { bound = i; break; } // 条件に合致しない要素とする要素を交換 pivot.Swap(i, j); // 走査を進める i++; j--; } return bound; }
enum MyBOOL { True, False }; using PairType = std::pair<MyBOOL, std::string>;
// データを分割する時に必要な関数をまとめたもの struct PartitionFunc { std::vector<PairType>& _array; PartitionFunc(std::vector<PairType>& arr):_array(arr) {} // 要素の交換関数 void Swap(size_t i, size_t j) { std::swap(_array[i], _array[j]); } // 条件判定関数 bool IsTrue(size_t i) { return _array[i].first == True; } bool IsFalse(size_t i) { return !IsTrue(i); } };
int main() { std::vector<PairType> arr; arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "a")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "b")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "c")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "d")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "e")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "f")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "g")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "h")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(False, "i")); arr.push_back(std::make_pair(True , "j")); std::cout << "分割前の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } PartitionFunc cond(arr); size_t bound_idx = partition< std::vector<PairType>, PartitionFunc>(arr, (size_t)0, arr.size(), cond); std::cout << "分割後の配列: " << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < bound_idx; i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } std::cout << std::endl; for (size_t i = bound_idx; i < arr.size(); i++) { std::cout << "[" << i << "] " << arr[i].first << " " << arr[i].second << std::endl; } return 0; }
分割前の配列:
[0] 0 a
[1] 1 b
[2] 1 c
[3] 0 d
[4] 0 e
[5] 0 f
[6] 1 g
[7] 0 h
[8] 1 i
[9] 0 j
分割後の配列:
[0] 0 a
[1] 0 j
[2] 0 h
[3] 0 d
[4] 0 e
[5] 0 f
[6] 1 g
[7] 1 c
[8] 1 i
[9] 1 b
この記事のトラックバックURL: