スポンサーリンク
NBytesのデータを扱うクラス
PPMのような3byteのデータを扱うと画素のコピーとか素直にできない。あとループ時のメモリ計算が面倒くさい。sizeofでとれないので*3しなければならないが、PGM等に変えるとcharなので*3を外さなければいけない。
かといって専用構造体を作るとそれはそれで使いにくい。そんなときNByteのデータを扱うようなデータ型が欲しい。
NByteData.hpp
#include<array> #include<cstring> template<size_t SIZE> class NByteData { std::array<unsigned char, SIZE> m_data; public: using ThisT = NByteData<SIZE>; unsigned char* data() { return m_data.data(); }
ThisT& operator=(const ThisT& t) { for (size_t i = 0; i < m_data.size(); i++) { m_data[i] = t.m_data[i]; } return *this; }
bool operator==(const ThisT& t)const { for (size_t i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { if (m_data[i] != t.m_data[i]) return false; } return true; }
bool operator!=(const ThisT& t)const { return !this->operator==(t); }
NByteData() {}
NByteData(const ThisT& src) { this->operator=(src); }
NByteData(std::initializer_list<unsigned char> inits) { unsigned char* p = m_data.data(); for (auto uc : inits) { *p = uc; ++p; } }
};
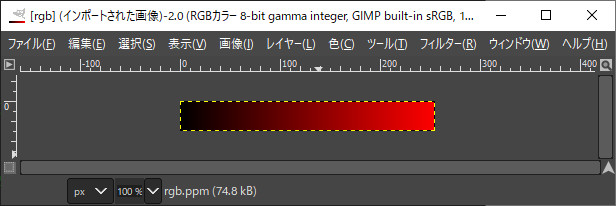
PPM出力の例
#include <iostream> #include<vector> #pragma warning(disable:4996) #include "NByteData.hpp"
// 3byte rgbの画素作成 NByteData<3> uc3rgb( unsigned char r, unsigned char g, unsigned char b) { return NByteData<3>({r,g,b}); }
void pnmP3_Write(const char* const fname, const int vmax, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p);
int main() { std::vector<NByteData<3> > rgb_ppm; int width = 255; int height = 30; rgb_ppm.resize(width*height); for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) { for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) { rgb_ppm[y*width+x] = uc3rgb(x, 0, 0); } } pnmP3_Write(R"(C:\data\rgb.ppm)", 255, width, height, rgb_ppm.begin()->data()); }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //! @brief PPM(RGB各1byte,カラー,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] vmax 全てのRGBの中の最大値 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details RGBRGBRGB....のメモリを渡すと、RGBテキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pnmP3_Write(const char* const fname, const int vmax, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p) { // PPM ASCII FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P3\n%d %d\n%d\n", width, height, vmax); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d ", p[k * 3 + 0], p[k * 3 + 1], p[k * 3 + 2]); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
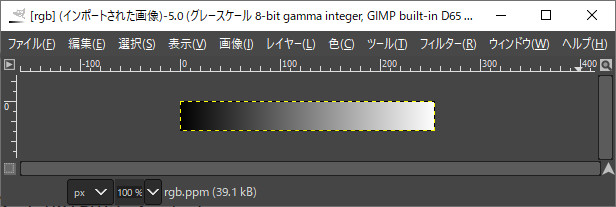
PGM出力の例
#include <iostream> #include<vector> #pragma warning(disable:4996) #include "NByteData.hpp"
// 1byte グレイスケールの画素作成 NByteData<1> uc1gray(unsigned char gray) { return NByteData<1>({gray}); }
void pnmP2_Write(const char* const fname, const int vmax, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p);
int main() { std::vector<NByteData<1> > gray_pgm; int width = 255; int height = 30; gray_pgm.resize(width*height); for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) { for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) { gray_pgm[y*width+x] = uc1gray(x); } } pnmP2_Write(R"(C:\data\gray.pgm)", 255, width, height, gray_pgm.begin()->data()); }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //! @brief PPM(RGB各1byte,カラー,テキスト)を書き込む //! @param [in] fname ファイル名 //! @param [in] vmax 全てのRGBの中の最大値 //! @param [in] width 画像の幅 //! @param [in] height 画像の高さ //! @param [in] p 画像のメモリへのアドレス //! @details RGBRGBRGB....のメモリを渡すと、RGBテキストでファイル名fnameで書き込む void pnmP2_Write(const char* const fname, const int vmax, const int width, const int height, const unsigned char* const p) { // PPM ASCII FILE* fp = fopen(fname, "wb"); fprintf(fp, "P2\n%d %d\n%d\n", width, height, vmax); size_t k = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t)height; i++) { for (size_t j = 0; j < (size_t)width; j++) { fprintf(fp, "%d ", p[k]); k++; } fprintf(fp, "\n"); } fclose(fp); }
この記事のトラックバックURL: